In 1977, the Big Ear Radio Telescope at Ohio State University picked up a strong narrowband signal from space. The signal was a continuous radio wave that was very strong in intensity and frequency and had many expected characteristics of an extraterrestrial transmission. This event would come to be known as the Wow! Signal, and it remains the strongest candidate for a message sent by an extraterrestrial civilization. Unfortunately, all attempts to pinpoint the source of the signal (or detect it again) have failed.
This led many astronomers and theorists to speculate as to the origin of the signal and what type of civilization may have sent it. In a recent series of papers, amateur astronomer and science communicator Alberto Caballero offered some fresh insights into the Wow! Signal and extraterrestrial intelligence in our cosmic neighborhood. In the first paper, he surveyed nearby Sun-like stars to identify a possible source for the signal. In the second, he estimates the prevalence of hostile extraterrestrial civilizations in the Milky Way Galaxy and the likelihood that they’ll invade us.
Almost fifty years after it was detected, the Wow! Signal continues to tantalize and defy explanation. In recent years, attempts have been made to attribute it to comets at the edge of our Solar System, an explanation that the astronomical community has since rejected. In 2020, interest in this candidate ETI signal was revitalized when Cabellaro identified a Sun-like star in the vicinity of the sky where the Wow! Signal was detected. If the analysis is correct, this famous signal may have come from a Sun-like star located 1,800 light-years away.
Qubits are a basic building block for quantum computers, but they’re also notoriously fragile—tricky to observe without erasing their information in the process. Now, new research from the University of Colorado Boulder and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) could be a leap forward for handling qubits with a light touch.
In the study, a team of physicists demonstrated that it could read out the signals from a type of qubit called a superconducting qubit using laser light, and without destroying the qubit at the same time.
The group’s results could be a major step toward building a quantum internet, the researchers say. Such a network would link up dozens or even hundreds of quantum chips, allowing engineers to solve problems that are beyond the reach of even the fastest supercomputers around today. They could also, theoretically, use a similar set of tools to send unbreakable codes over long distances.
University of Copenhagen
Posted in biotech/medical
Researchers from the University of Copenhagen found an alternative route that certain cells take to make organs and used that knowledge to exploit a new type of stem cells as a potential source of organs in a dish.
Eric Topol speaks with DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis about harnessing the potential of AI in health and medicine.
Yasir Arafat is a MARVEL superhero. No, he’s not a Marvel Comics superhero. Rather, he’s a nuclear engineer leading development of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Microreactor Applications Research Validation and Evaluation (MARVEL) project at Idaho National Laboratory.
And from concept to construction, MARVEL is coming together at lightning speed.
By donna kemp spangler, INL communications & outreach.
No, he’s not a Marvel Comics superhero. Rather, he’s a nuclear engineer leading development of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Microreactor Applications Research Validation and Evaluation (MARVEL) project at Idaho National Laboratory.
All monkeys appeared clinically normal on Day 0 of the study. Monkeys began to show evidence of exanthema, enanthema, mild anorexia, fever, cough, and nasal discharge on Days 6 and 7 postexposure. Dyspnea, noted as early as Day 8 postexposure, was evident in all animals by Day 10. By Days 9 and 10, all animals had exanthema and enanthema, were depressed and severely anorectic, and showed signs of weakness. Clinical signs progressed until the animals died naturally or were killed 9 to 17 days postexposure (mean 11.7 days). There was no correlation of inhaled dose to survival time. Leukocytosis (absolute and relative monocytosis) developed with the onset of clinical signs on Day 6. There were no trends detected in clinical chemistry data. Virus was first isolated from buffy coat cells of one of eight animals tested on Day 6. Nine of 11 animals were positive on Day 9, and 2 of 7 remained positive on Days 12 or 13. There was no cell-free viremia detected at any time.
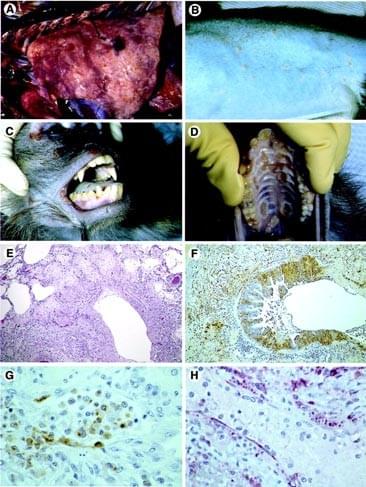
Principal gross necropsy findings are presented in Table 1. All deaths were attributed to bronchopneumonia, although secondary bacterial septicemia was considered to be a contributing factor in one animal. Lungs were heavy and congested and failed to collapse. A dark red, lobular, mottled pattern of edema, atelectasis, and necrosis was distributed throughout all lung lobes (Fig. 1A). Occasionally, there was fibrinous pleuritis with pleural adhesions and multifocal, white, plaque-like thickenings of the visceral pleura. We observed a clear pericardial effusion in two monkeys.
Dermatitis, present in all monkeys, varied from barely detectable, single, small papules to extensive involvement primarily affecting the inguinal, ventral abdominal, ventral thoracic, perineal, and facial regions (Fig. 1, B and C). Palmar surfaces of the hands and plantar surfaces of the feet were only occasionally involved. The extent of involvement and the stage of skin lesion development noted at necropsy exhibited a positive correlation with the number of days elapsed since initial onset of the lesions was noted clinically. In animals necropsied 1 to 2 days after onset of exanthema, lesions were generally minimal in extent and were in the papular stage, appearing as pale tan to white, slightly raised foci, 2 to 4 mm in diameter. At 3 to 5 days post onset, lesion distribution was characterized as mild. Papules were accompanied by 1 to 2 mm vesicles. Vesicle formation, however, was not prominent grossly.
A good read.
Everybody’s talking about the Google engineer who thinks a company chatbot is sentient. But what does sentience mean? property= description.
Until now, the ability to travel faster than the speed of light has only been seen in Sci-Fi movies. What if we can actually make that a reality!
If we ever hope to visit other parts of our galaxy, we’ll have to travel at speeds we’ve never imagined.
A possible solution to the problem of traveling at the speed of light or even faster is the “warp drive” popularized by Star Trek, the sci-fi franchise still ongoing.
Therefore, if we could find a way to bend or warp spacetime, we would be able to move around the cosmos in the blink of an eye. Although, warp drives have mostly remained the preserve of science fiction.
After years of scandals left NSO Group broke and on a U.S. blacklist, L3Harris Technologies expressed interest, and the White House expressed concern.