Officials released more details on bidding for work that will support the preservation and distribution of defense research and analysis.




A potential new way to protect sensitive electronics from the extreme heat generated by flying at high speed could give the United States an edge in the race to deploy hypersonic missiles and new spacecraft.
A July research paper in the American Chemical Society’s journal ACS Nano describes one potential solution that uses focused plasma, the photons and highly charged particles that make up the so-called fourth state of matter. If the method bears out in further research, it could usher in hypersonic weapons with much more advanced electronic guidance and could even enable on-the-ground weapons to evade heat sensors.
The breakthrough grew out of efforts to use a laser to measure the temperature of electronics in plasma-facing environments, work the Air Force is supporting through a grant at the University of Virginia, said professor Patrick Hopkins, one of the researchers on the paper.


Regrowing the cells of the human retina on a scaffold of synthetic, tissue-like material showed substantial improvements over previously used materials such as cellulose, and the scientists hope they can move on to testing their method in the already blind.
Macular degeneration is increasing in prevalence in the developed world. It’s the leading cause of blindness and is caused by the loss of cells in a key part of the eye called the retina.
Humans have no ability to regrow retinal pigment cells, but scientists have determined how to do it in vitro using pluripotent stem cells. However as the study authors describe, previous examples of this procedure saw scientists growing the cells on flat surfaces rather than one resembling the retinal membrane.

In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changer in various industries. With its ability to analyze vast amounts of data and derive meaningful insights, AI has now made its way into the realm of circuit design and hardware engineering. This article explores the transformative potential of AI in these domains, focusing on how it can accelerate component selection, enhance quality control, enable failure analysis, predict maintenance requirements, streamline supply chain management, optimize demand forecasting, and much more.
Circuit Design
Through the adoption of AI, hardware engineers are given unparalleled help in their pursuit of excellence. AI reveals secrets to sublime circuit performance through its industrious investigation of component databases and innovative simulations. Engineers can then go onto augment their own intelligence to design circuits that exceed expectations and reinvent what is possible in the realm of technology.

In the last ten years, AI systems have developed at rapid speed. From the breakthrough of besting a legendary player at the complex game Go in 2016, AI is now able to recognize images and speech better than humans, and pass tests including business school exams and Amazon coding interview questions.
Last week, during a U.S. Senate Judiciary Committee hearing about regulating AI, Senator Richard Blumenthal of Connecticut described the reaction of his constituents to recent advances in AI. “The word that has been used repeatedly is scary.”
The Subcommittee on Privacy, Technology, and the Law overseeing the meeting heard testimonies from three expert witnesses, who stressed the pace of progress in AI. One of those witnesses, Dario Amodei, CEO of prominent AI company Anthropic, said that “the single most important thing to understand about AI is how fast it is moving.”
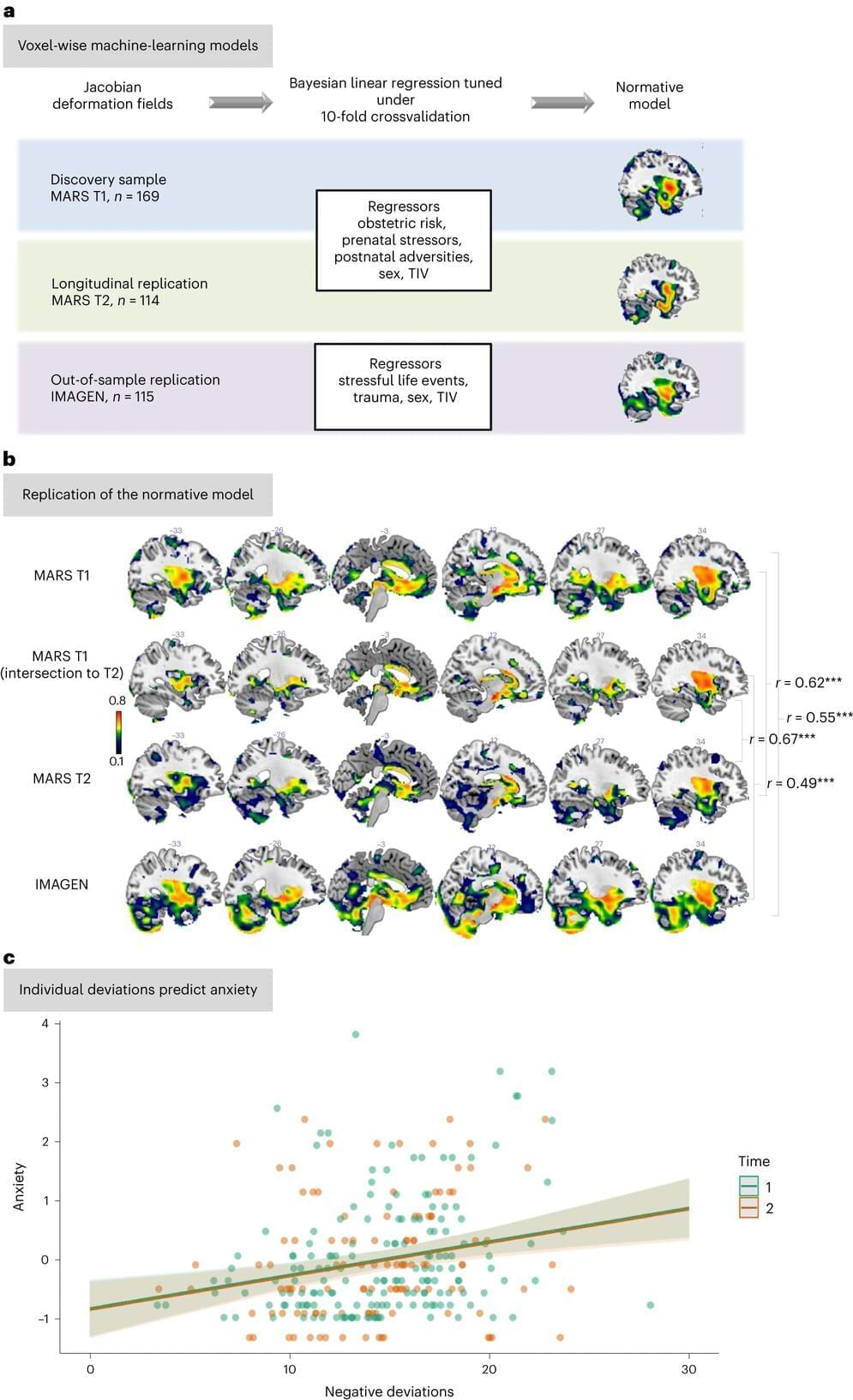
Neuroscientists at Radboud University show that adversities permanently change the functioning of the brain. Furthermore, an aberrant reaction of the brain to adversities is related to anxiety symptoms. This may have predictive value for the development of psychiatric disorders.
Your brain is shaped by the things you experience. That sounds logical, but can you really measure that? And what can you do with it? Neuroscientists at Radboud University medical center investigated the influence of adversities in life on patterns in the brain. They found remarkable associations that may have predictive value for the development of psychiatric disorders.
The researchers conducted their study on approximately 170 people—a special group, because all kinds of data have been collected from them during their lifetime. For this study, the scientists specifically focused on adversities: factors or events that are known to have a negative effect on development. Consider, for example, the mother’s smoking during pregnancy, complications during childbirth, abuse, or a major accident.

Diamond has long been the preferred material for quantum sensing, but its size limits its applications. Recent research highlights hBN’s potential as a replacement, especially after TMOS researchers developed methods to stabilize its atomic defects and study its charge states, opening doors for its integration into devices where diamond can’t fit.
Diamond has long held the crown in the realm of quantum sensing, thanks to its coherent nitrogen-vacancy centers, adjustable spin, magnetic field sensitivity, and capability to operate at room temperature. With such a suitable material so easy to fabricate and scale, there’s been little interest in exploring diamond alternatives.
However, this titan of the quantum domain has a vulnerability. It’s simply too large. Much like how an NFL linebacker isn’t the top pick for a jockey in the Kentucky Derby, diamond falls short when delving into quantum sensors and data processing. When diamonds get too small, the super-stable defect it’s renowned for begins to crumble. There is a limit at which a diamond becomes useless.