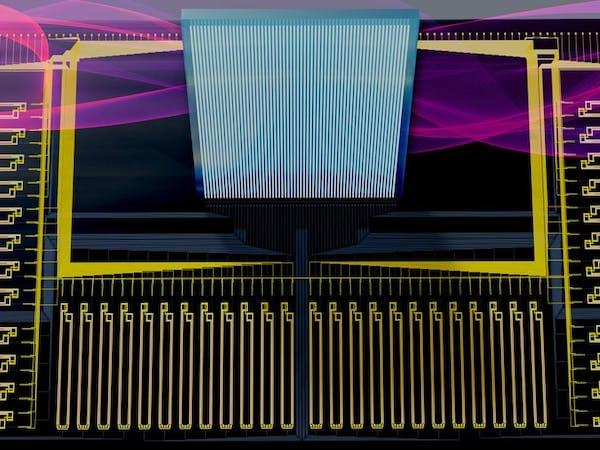
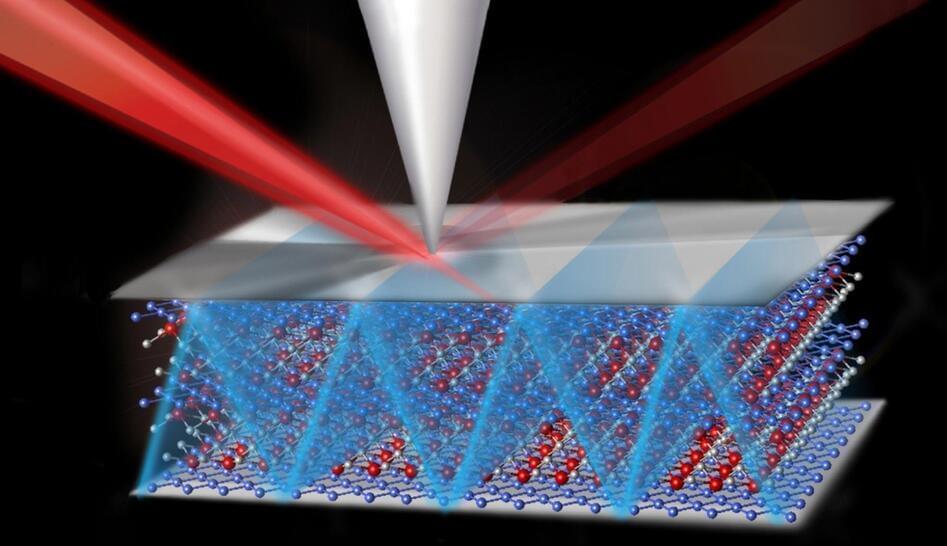
Of course running a state of the art machine learning model, with billions of parameters, is not exactly easy when memory is measured in kilobytes. But with some creative thinking and a hybrid approach that leverages the power of the cloud and blends it with the advantages of tinyML, it may just be possible. A team of researchers at MIT has shown how this may be possible with their method called Netcast that relies on heavily-resourced cloud computers to rapidly retrieve model weights from memory, then transmit them nearly instantaneously to the tinyML hardware via a fiber optic network. Once those weights are transferred, an optical device called a broadband “Mach-Zehnder” modulator combines them with sensor data to perform lightning-fast calculations locally.
The team’s solution makes use of a cloud computer with a large amount of memory to retain the weights of a full neural network in RAM. Those weights are streamed to the connected device as they are needed through an optical pipe with enough bandwidth to transfer an entire full feature-length movie in a single millisecond. This is one of the biggest limiting factors that prevents tinyML devices from executing large models, but it is not the only factor. Processing power is also at a premium on these devices, so the researchers also proposed a solution to this problem in the form of a shoe box-sized receiver that performs super-fast analog computations by encoding input data onto the transmitted weights.
This scheme makes it possible to perform trillions of multiplications per second on a device that is resourced like a desktop computer from the early 1990s. In the process, on-device machine learning that ensures privacy, minimizes latency, and that is highly energy efficient is made possible. Netcast was test out on image classification and digit recognition tasks with over 50 miles separating the tinyML device and cloud resources. After only a small amount of calibration work, average accuracy rates exceeding 98% were observed. Results of this quality are sufficiently good for use in commercial products.