A team of researchers at DeepMind, London, working with colleagues from the University of Exeter, University College London and the University of Oxford, has trained an AI system to find a policy for equitably distributing public funds in an online game. In their paper published in the journal Nature Human Behavior, the group describes the approach they took to training their system and discuss issues that were raised in their endeavor.
How a society distributes wealth is an issue that humans have had to face for thousands of years. Nonetheless, most economists would agree that no system has yet been established in which all of its members are happy with the status quo. There have always been inequitable levels of income, with those on top the most satisfied and those on the bottom the least satisfied. In this latest effort, the researchers in England took a new approach to solving the problem—asking a computer to take a more logical approach.
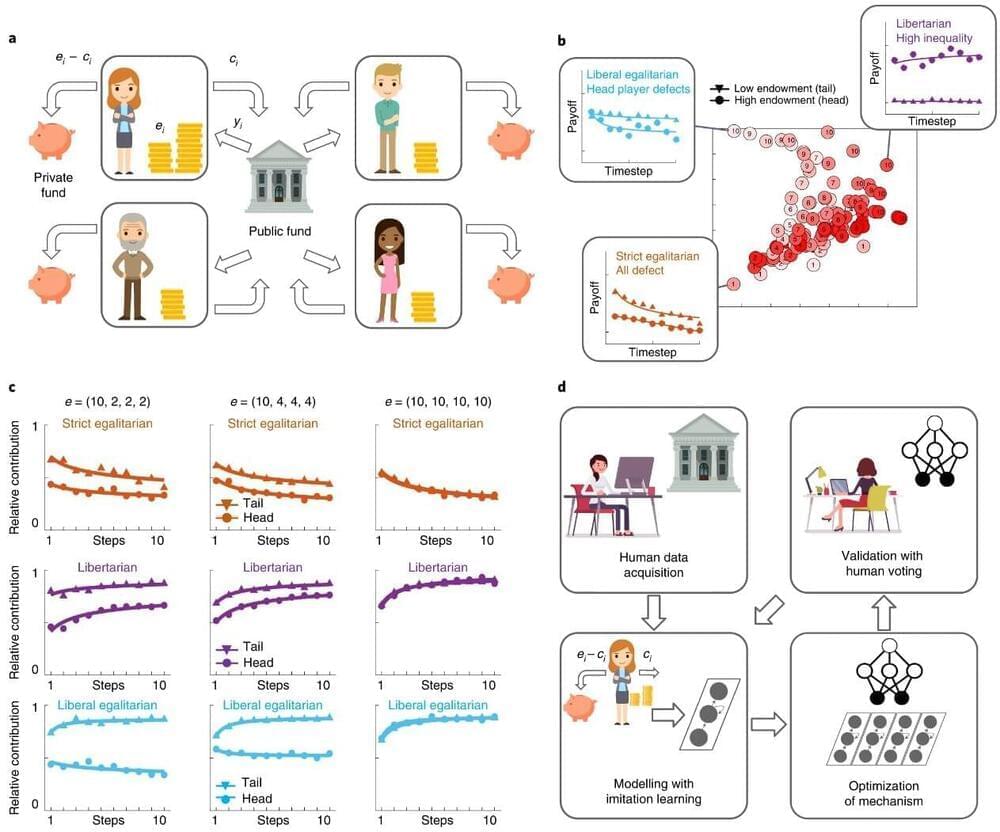
The researchers began with the assumption that democratic societies, despite their flaws, are thus far the most agreeable of those tried. They then enlisted the assistance of volunteers to play a simple resource allocation game —the players of the game decided together the best ways to share their mutual resources. To make it more realistic, the players received different amounts of resources at the outset and there were different distribution schemes to choose from. The researchers ran the game multiple times with different groups of volunteers. They then used the data from all of the games played to train several AI systems on the ways that humans work together to find a solution to such a problem. Next, they had the AI systems play a similar game against one another, allowing for tweaking and learning over multiple iterations.