Meet XRISM, the telescope collaboration between JAXA and NASA that could reveal the universe’s secrets.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
STAR MAKER — Olaf Stapledon — ALL CHAPTERS
A distant far post human Eon.
Share your videos with friends, family, and the world.

Launch Roundup: SpaceX to launch four missions, Progress MS-24 to resupply ISS
Following several launch delays last week, the week of Aug. 21 through Aug. 27 is set to see seven launches marking the 129th through 135th orbital launch attempts of 2023.
Starting the week off, SpaceX will launch two back-to-back Starlink missions from Space Launch Complex (SLC) 4 East at the Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) and from SLC-40 at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS). Next, Russia will launch its Progress resupply mission, followed by Rocket Lab’s launch of “We Love the Nightlife.” SpaceX will then launch the Crew-7 mission from Launch Complex 39A (LC-39A); JAXA will launch the SLIM and XRISM mission; SpaceX is expected to end the week off with another Starlink mission from SLC-40.
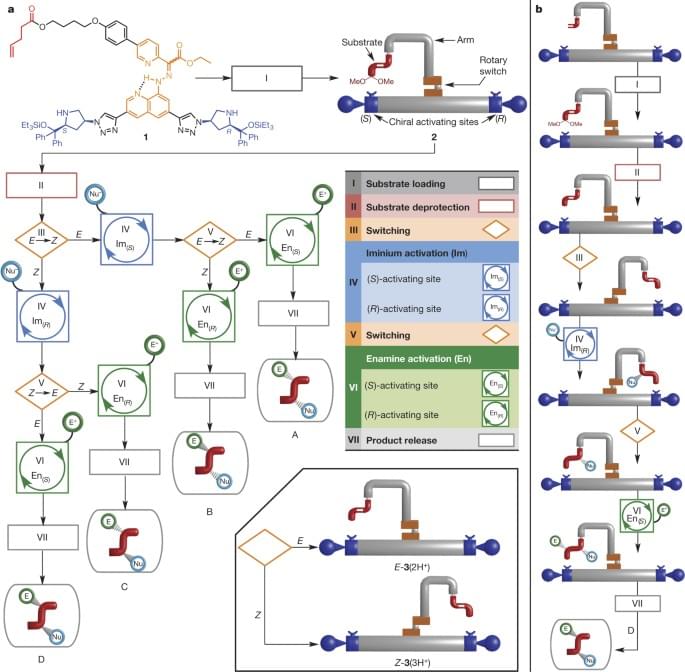
Stereodivergent synthesis with a programmable molecular machine
This could lead to cures of all diseases and disorders of the human biological systems because one could edit them out 😗😁.
A molecular machine that can be programmed to position a substrate at one of two directing sites on a molecule, which control the stereochemistry of addition to the substrate, demonstrates complexity, precision and function previously only observed in nature.
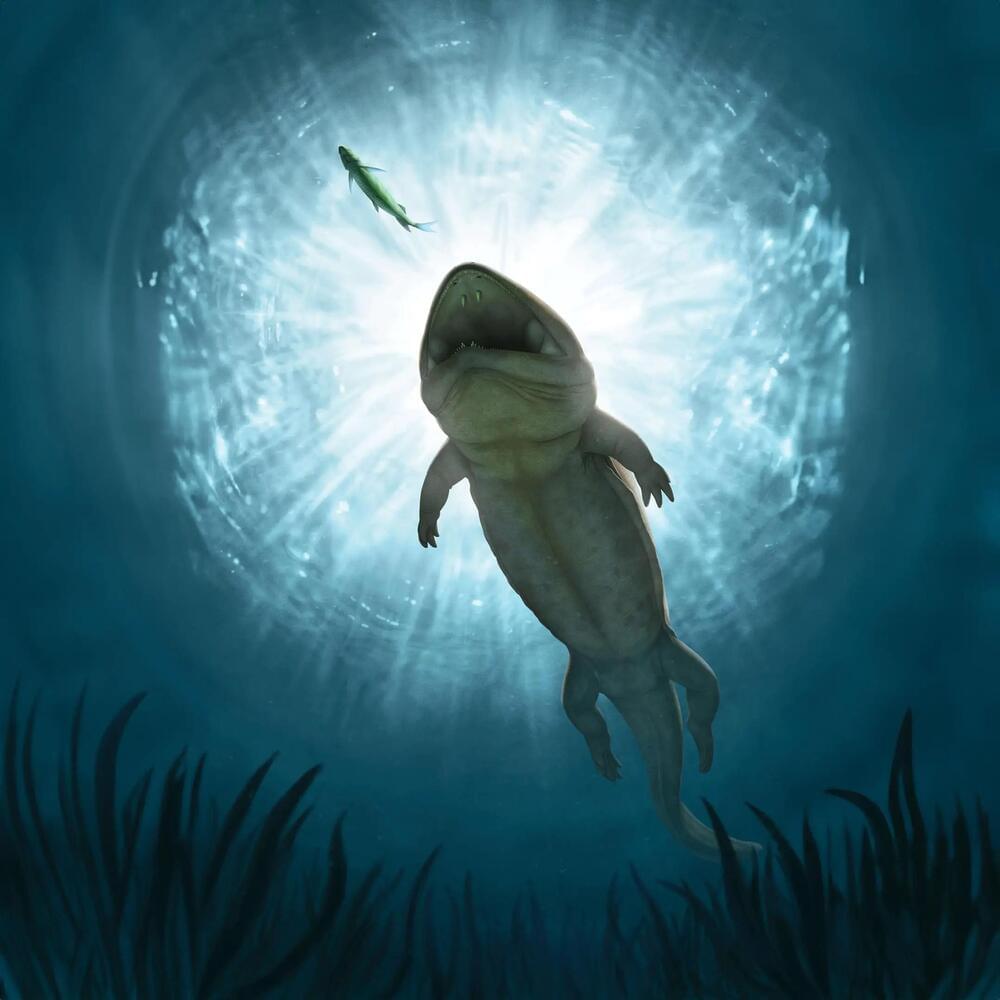

240-Million-Year-Old Giant Amphibian Discovered in Retaining Wall
O.o!!! The longevity of this complex organism could reveal new avenues for immortality.
Arenaerpeton supinatus was discovered in rocks cut from a nearby quarry that were intended for the building of a garden wall.
A 240-million-year-old fossil of an amphibian was found in a retaining wall in the 1990s. This significant find has now been formally named and described by scientists at the University of New South Wales (UNSW Sydney) and the Australian Museum.
The fossil was originally discovered by a retired chicken farmer in rocks from a local quarry. These rocks were intended for use in constructing a garden retaining wall, and the fossil was subsequently donated to the Australian Museum in Sydney.

The Kardashev Scale — Can We Advance Beyond a Type 3 Civilization?
A type 5 civilization often seen as unattainable is actually quite possible. We could have computers to use a developer mode to solve all sorts of problems like the entropy of the universe and even stop the entropy of the earth or stop meteorites from hitting earth with a computer click. This could easily be attainable with technological singularities leading to a new understanding of our universe but should be considered to essentially stop almost any problem to earth and beyond.
Type 1 civilization designation on the Kardashev scale may be possible in the next 100 years, which could influence the survival of mankind.
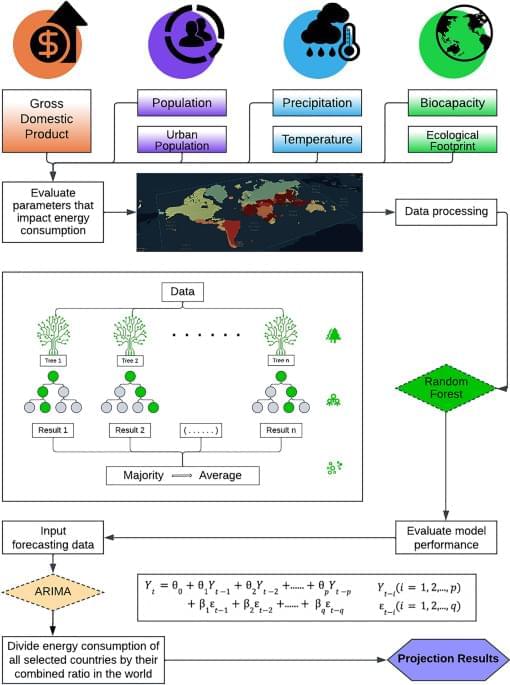
Forecasting the progression of human civilization on the Kardashev Scale through 2060 with a machine learning approach
Throughout the history of human civilization, energy has been holding an imperative role in humanity’s progress1. Especially in the past few centuries, innovations in the harnessing of power have catalyzed humanity’s rapid growth2. Energy remains a key driver of human development3, with each revolution in industry and agriculture highlighting human’s reliance on it. Revolution in the eighteenth century was a turning point. The development of steam engines powered by fossil fuels led to significant technological progress4. Electricity has then opened new possibilities for the future5. Humanity has grown at a compound annual rate of 2.43% from 1965 to 2020, demonstrating our continued increasing demand for and consumption of energy6,7. However, the pace at which human being can progress as a civilization in the future remains uncertain.
While mankind was establishing its identity in the universe, insatiable human curiosity over the realm of civilization peaked in the 1960s8, which led to deeper cogitation of the concept of civilization. Providing that some of the extraterrestrial civilizations are highly likely million years more advanced than mankind, Soviet astrophysicist Nikolai Kardashev proposed a scale to classifies a civilization’s technological development based on its energy consumption9, which was later known as the Kardashev Scale. The scale initially categorized civilizations into three types. Type 1 is known as the planetary civilization, which features the capability of harnessing and utilizing all forms of energies that can be reached on the host planet, such as wind, solar, and geothermal power; Type 2 and 3, known as the stellar and galactic civilizations, respectively, are capable of extracting and utilizing all energy created by their respective systems9. Yet, such a scale proved lackluster in the quantitative presentation of the civilization types. Subsequently, Carl Sagan furthered the Kardashev Scale with data extrapolation, and proposed a continuous function quantifying the Kardashev Scale in index K10
$$K=\frac{.
