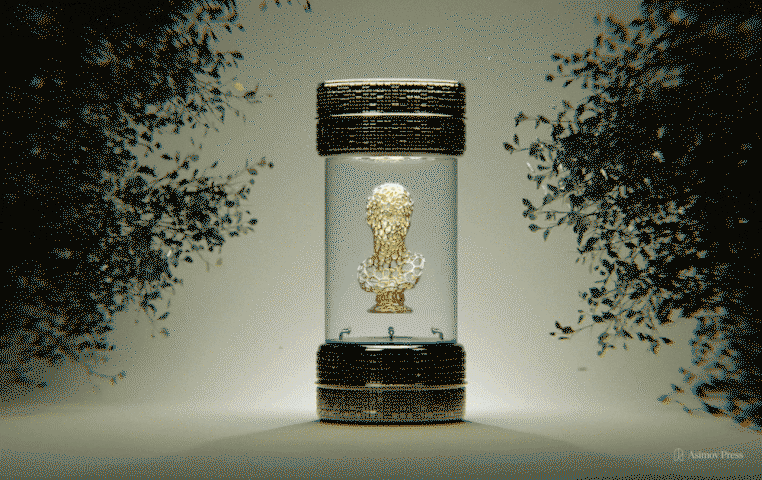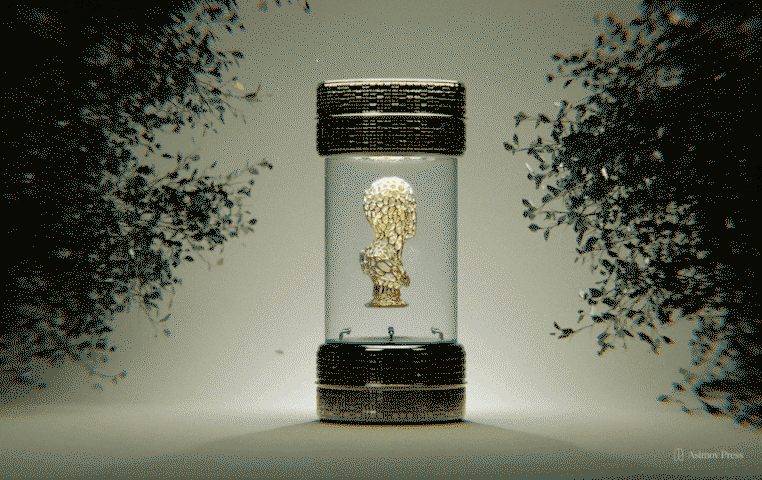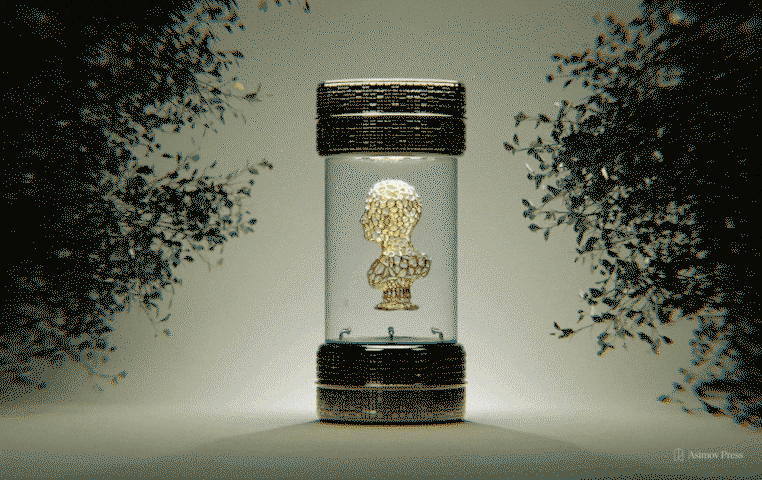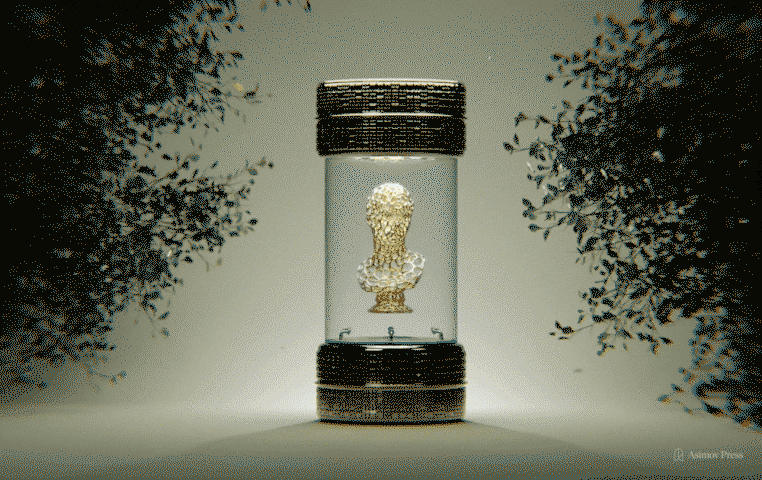Aging isn’t just about living longer. It’s about staying healthy while doing it. And a new study just brought us one step closer.
Promising breakthroughs in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis treatment through nanotechnology’s unexplored frontier
Posted in bioengineering, biotech/medical, nanotechnology, neuroscience | Leave a Comment on Promising breakthroughs in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis treatment through nanotechnology’s unexplored frontier
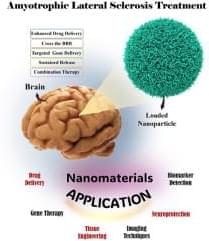
This review explores the transformative potential of nanotechnology in the treatment and diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor neuron degeneration, muscle weakness, and eventual paralysis. Nanotechnology offers innovative solutions across various domains, including targeted drug delivery, neuroprotection, gene therapy and editing, biomarker detection, advanced imaging techniques, and tissue engineering. By enhancing the precision and efficacy of therapeutic interventions, nanotechnology facilitates key advancements such as crossing the blood-brain barrier, targeting specific cell types, achieving sustained therapeutic release, and enabling combination therapies tailored to the complex pathophysiology of ALS.
The application of nanotechnology to the field of medicine and healthcare offers the possibility to produce innovative nanoengineering techniques in the repair and regeneration of tissues and organs.
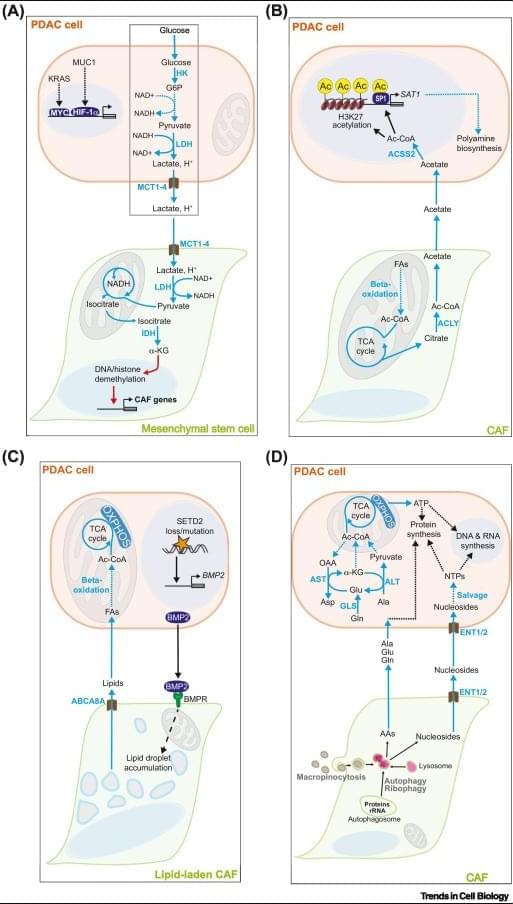
Metabolic crosstalk – the exchange of metabolites between cancer cells and non-malignant cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME) – contributes to the aggressiveness of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) through a diverse array of mechanisms.
Under the selection pressure imposed by chemical stressors (acidosis, hypoxia) and scarcity of essential nutrients in the TME, PDAC cells establish mutually fitness-enhancing metabolic crosstalk pathways with cancer-associated fibroblasts, tumor-associated macrophages, and other stromal cells.
PDAC cell metabolism inhibits the activity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells by outcompeting them for essential nutrients (glucose, amino acids, nucleosides, vitamins) and by flooding the TME with immunosuppressive metabolites (lactate, kynurenine, adenosine, and others).
Critical nodes of tumorigenic metabolic crosstalk pathways (enzymes and cell membrane transporters) are readily druggable and likely non-essential for healthy tissues. https://sciencemission.com/Tumor%E2%80%93stromal-metabolic-crosstalk-in-PC
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is an aggressive malignancy with a dire prognosis. Standard-of-care chemotherapy regimens offer marginal survival benefit and carry risk of severe toxicity, while immunotherapy approaches have uniformly failed in clinical trials. Extensive desmoplasia in the PDAC tumor microenvironment (TME) disrupts blood flow to and from the tumor, thereby creating a nutrient-depleted, hypoxic, and acidic milieu that suppresses the function of antitumor immune cells and imparts chemotherapy resistance. Additionally, recent seminal studies have demonstrated crucial roles for metabolic crosstalk – the exchange of metabolites between PDAC cells and stromal cell populations in the TME – in establishing and maintaining core malignant behaviors of PDAC: tumor growth, metastasis, immune evasion, and therapy resistance.
A new study explores how the brain quickly learns and remembers important locations by focusing not on excitatory neurons, but on inhibitory ones called parvalbumin interneurons (PVs).
Bioart emerges where biological science, technology, and aesthetics collide. For one terminally ill artist, it offered a chance at immortality.
Terraforming Mars moves from science fiction to scientific possibility — but what obstacles must we overcome first?
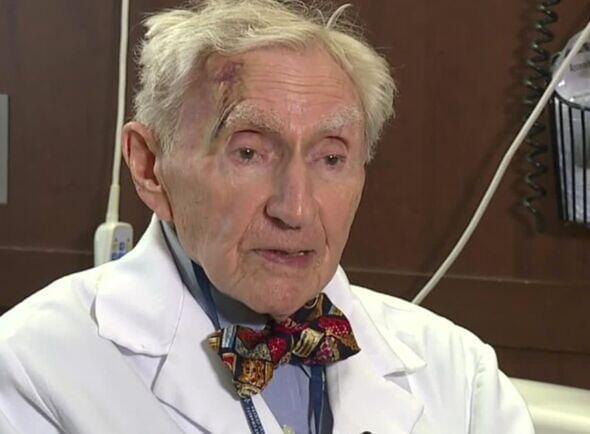
The world’s oldest practicing doctor, Dr Howard Tucker, has revealed his lust for life — and you won’t believe what he has to say.
A new European study out Monday throws into question conventional wisdom that the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies are on a collision course that will take
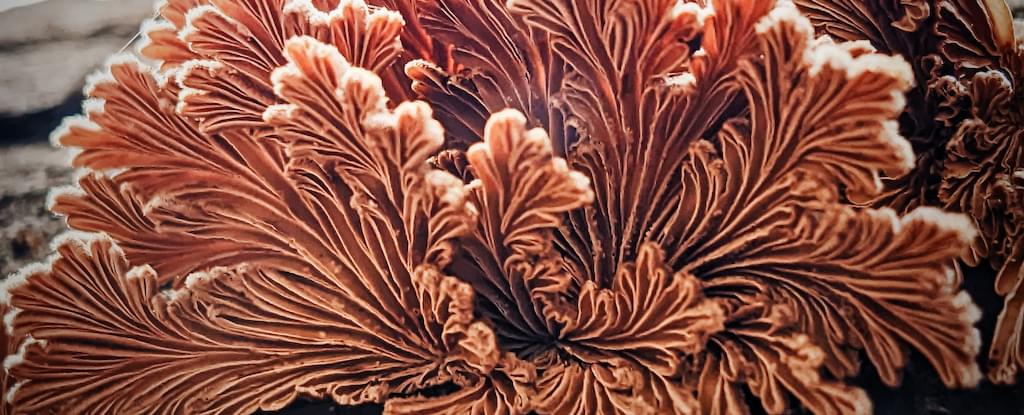
Swiss scientists have created a new plastic-like material that’s flexible, biodegradable, and even edible. The secret? It’s still alive.
The material, which was created by a team from Empa in Switzerland, manages to balance biodegradability with toughness and versatility – a feat that is far from easy in materials science.
The researchers processed fibers from the mycelium (the root-like part) of the split-gill mushroom (Schizophyllum commune) into a liquid mixture, without actually killing them off or destroying their natural biological functions.