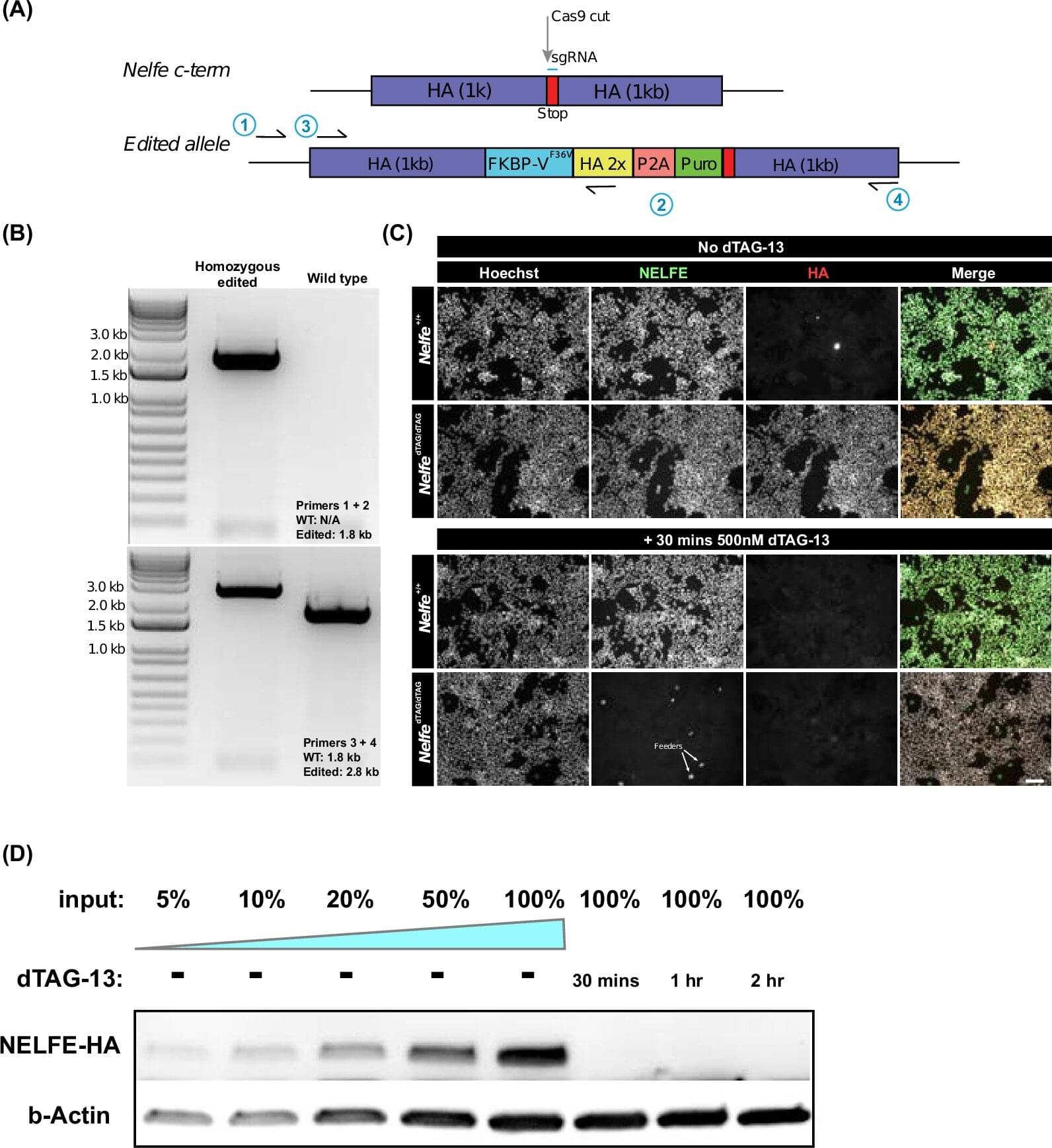
Humans have it. So does Drosophila. But not yeast. That “it” is a small pause at the start of gene activity—a brief molecular halt that may have helped life evolve from simple cells to complex animals.
A new study by Charles Danko, associate professor in life science and technology at Cornell’s Baker Institute for Animal Health and in the Department of Biomedical Sciences in the College of Veterinary Medicine, and colleagues explores how this key step in gene regulation—promoter-proximal pausing—evolved across species.
Promoter-proximal pausing occurs just after a cell’s molecular “copy machine”– RNA polymerase II—is activated. The polymerase temporarily stops, usually after about 20 to 60 nucleotides or “letters” of the gene, waiting for further signals.