These 7 science-backed food habits support longevity without raising your grocery bill. Simple, affordable changes with real payoff.


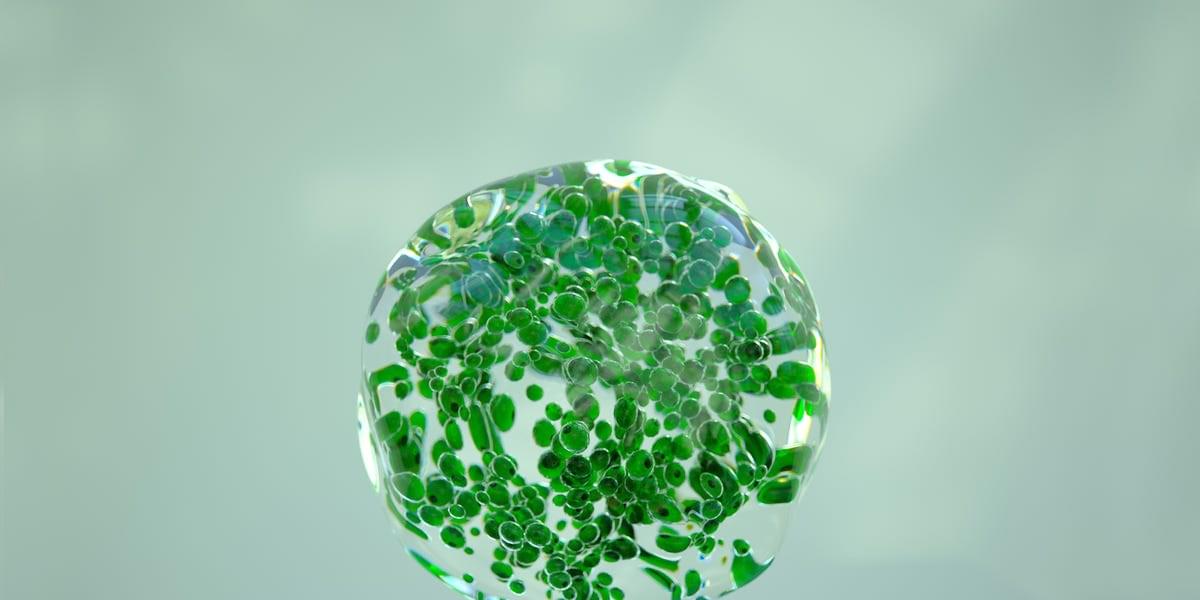
Wang et al. integrated ST-seq, scRNA-seq, and scATAC-seq data to profile transcriptional and chromatin dynamics in D. japonica head blastema at 5 dpa. They pinpointed the DjTcf4 gene network acting as a master transcription regulator to ensure cells rebuild complex structures like eyes in the right place and time.
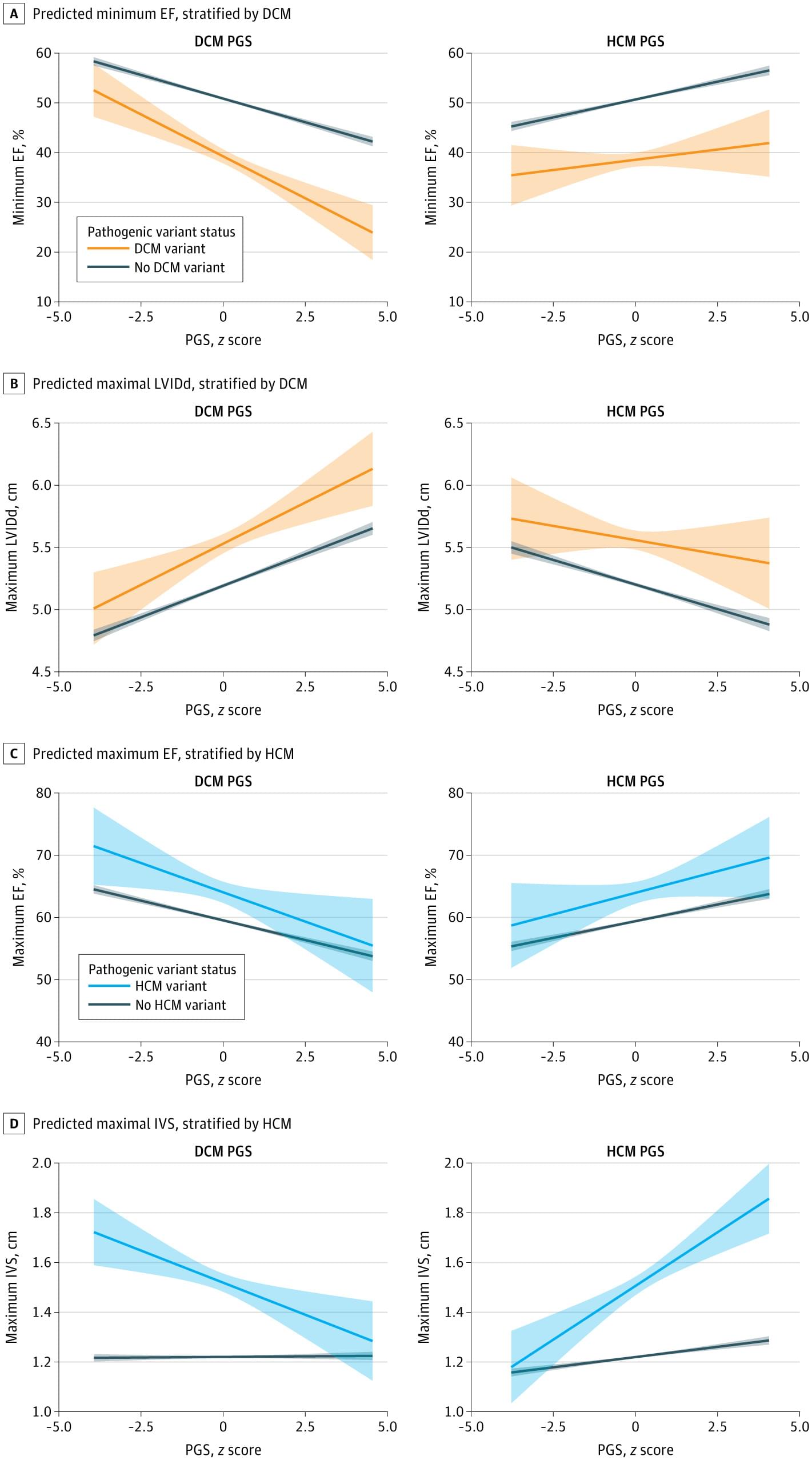
Polygenic scores for hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathies independently and oppositely modified disease risk and penetrance of pathogenic variants, supporting bidirectional genetic influences on Cardiomyopathy.
Question How is risk of hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy modified by polygenic background?
Findings In this cross-sectional study including 49 434 individuals in the Penn Medicine BioBank, polygenic scores for hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathies were associated with clinical and echocardiographic measures relevant to both diseases and inversely modified the penetrance of pathogenic variants.
Meaning The findings indicate that polygenic background exists on an overlapping, opposing spectrum and may contribute to hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy susceptibility.

Recent studies have examined the connection between endometriosis and cancer, revealing that the condition may exhibit several traits commonly associated with malignant tumors. Researchers have identified specific characteristics of endometriosis that align with established hallmarks of cancer, prompting a reevaluation of how this chronic gynecological disorder is understood and approached in medical research.
The investigation highlights parallels between endometriosis and cancer, including features such as abnormal cell growth, resistance to cell death, and the ability to invade surrounding tissues. These findings suggest that while endometriosis is not classified as a form of cancer, it shares biological behaviors typically observed in malignancies. The study underscores the complexity of endometriosis and its potential implications for treatment strategies and further research into its underlying mechanisms.
Newsflash | powered by geneonline AI.
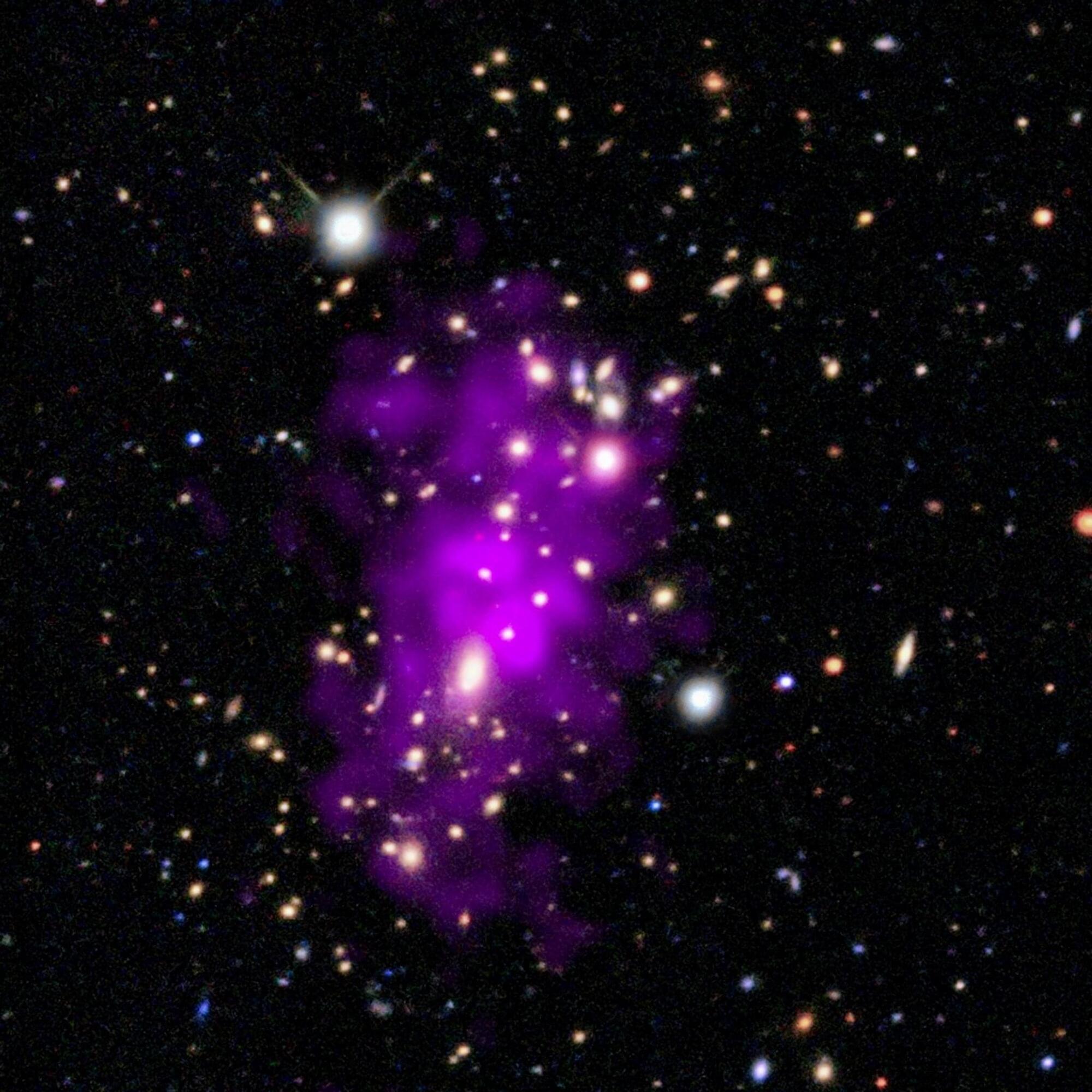


Celebrate the New Year with the “Champagne Cluster,” a galaxy cluster seen in this new image from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and optical telescopes.
Astronomers discovered this galaxy cluster on Dec. 31, 2020. The date, combined with the bubble-like appearance of the galaxies and the superheated gas seen with Chandra observations (represented in purple), inspired the scientists to nickname the galaxy cluster the Champagne Cluster, a much easier-to-remember name than its official designation of RM J130558.9+263048.4.
The new composite image shows that the Champagne Cluster is actually two galaxy clusters in the process of merging to form an even larger cluster.
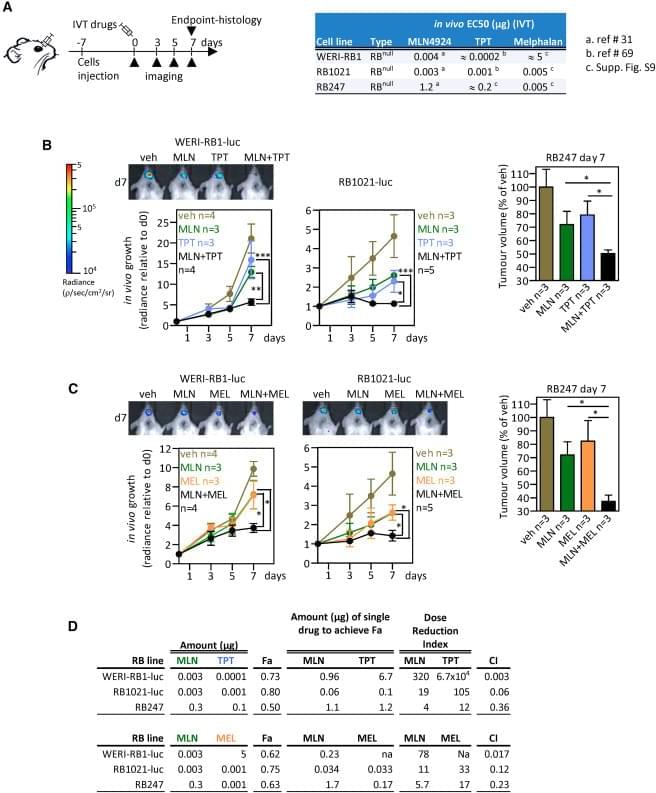
(Cell Reports 42, 112925; August 29, 2023)
The authors were made aware of an image duplication in their published paper. The representative photo in Figure 5B is the same as the image in Fig. 4g of Aubry et al., 2020, Oncogene 39, p. 5338–5357. The assays involved treating xenografts of the RB1021-luc retinoblastoma line, using either MLN4924 (MLN) and topotecan (TPT; Cell Reports) or the RAD51 inhibitor B02 and TPT (Oncogene). These assays were run and analyzed concurrently in 2018. For the Xenogen measurements of tumor growth, we first quantified the signal and recorded the values in tables. After all the mice were assessed, appropriate mice were placed together for representative images. Thus, the quantification, which was performed correctly, and acquisition/storage of the representative image, which was not, were performed separately. Our review of image files revealed that the representative image of the B02 + TPT series of mice was accidentally duplicated using the file name for the MLN + TPT series of mice.

