Differential equations are fundamental tools in physics: they are used to describe phenomena ranging from fluid dynamics to general relativity. But when these equations become stiff (i.e. they involve very different scales or highly sensitive parameters), they become extremely difficult to solve. This is especially relevant in inverse problems, where scientists try to deduce unknown physical laws from observed data.
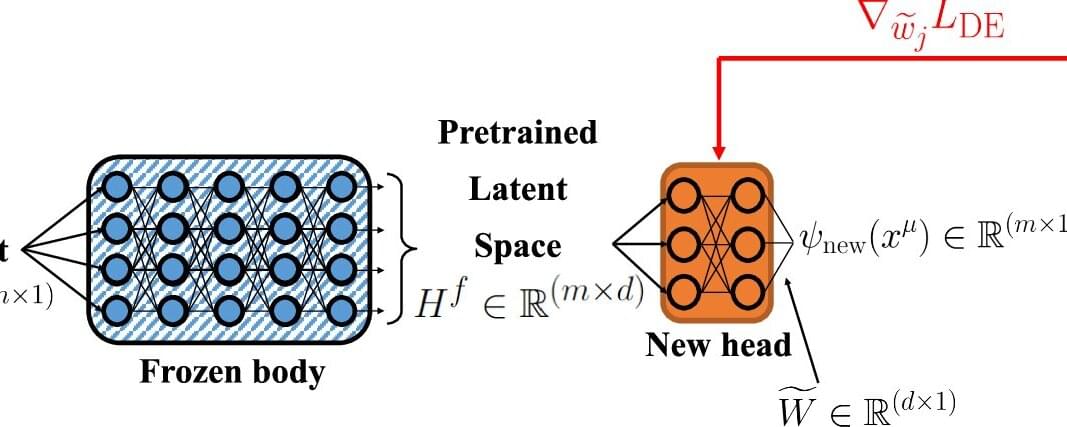
To tackle this challenge, the researchers have enhanced the capabilities of Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs), a type of artificial intelligence that incorporates physical laws into its learning process.
Their approach, reported in Communications Physics, combines two innovative techniques: Multi-Head (MH) training, which allows the neural network to learn a general space of solutions for a family of equations—rather than just one specific case—and Unimodular Regularization (UR), inspired by concepts from differential geometry and general relativity, which stabilizes the learning process and improves the network’s ability to generalize to new, more difficult problems.