Anthropic is an AI safety and research company that’s working to build reliable, interpretable, and steerable AI systems.




Whether the Universe will ‘end’ at all is not certain, but all evidence suggests it will continue being humanity’s cosmic home for a very, very long time.
The Universe – all of space and time, and all matter and energy – began about 14 billion years ago in a rapid expansion called the Big Bang, but since then it has been in a state of continuous change.
First, it was full of a diffuse gas of particles that now make up atoms: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Then, that gas collapsed into stars and galaxies.


Artificial intelligence is booming. Technology companies are pouring trillions of dollars into research and infrastructure, and millions of people now interact with AI in one form or another. But what is it all for?
To find out, Nature spoke to six people at the forefront of AI development — people who are driving the technology’s development and adoption, and those who are preparing society to adapt to its rapid rise.
In this video series, they describe their greatest ambitions for the technology, their expectations of where and how it will be adopted in the coming years, and their concerns for the future.
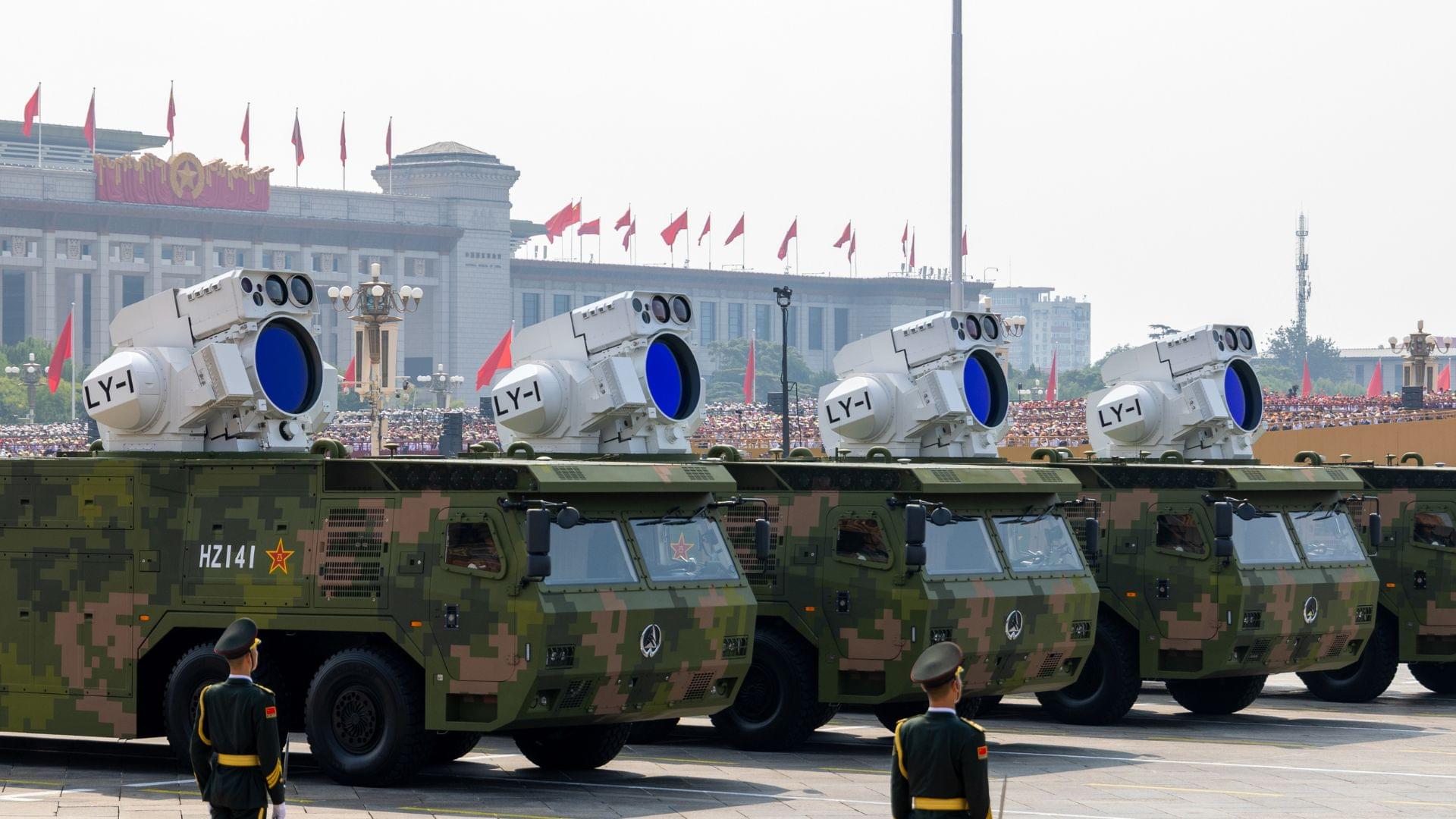
A new simulation by Chinese defense researchers suggests that jamming Starlink coverage over an area the size of Taiwan is technically possible.

Chinese scientists claim to have reported a major jump in capacitor manufacturing earlier this month. The group has cut the production time for dielectric energy storage parts to one second.
The announcement has drawn widespread attention because it points to fast, stable energy storage for advanced defense systems and electric vehicles.
The team used a flash annealing method that heats and cools material at a rate of about 1,832°F (1,000°C) per second. This speed allows crystal films to form on a silicon wafer in a single step. Other techniques require far more time and can take from 3 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the film quality.
Longshot, an aerospace technology start-up founded in 2021, is developing a launch system to shoot payloads, such as satellites, into Earth’s low orbit.
This ground-based kinetic launch system, or “space gun,” aims to reduce the high cost of launching payloads into Earth orbit.
Earlier, the US-based company announced it had leased a former U.S. Navy indoor cannon testing facility at Alameda Point from the City of Alameda.