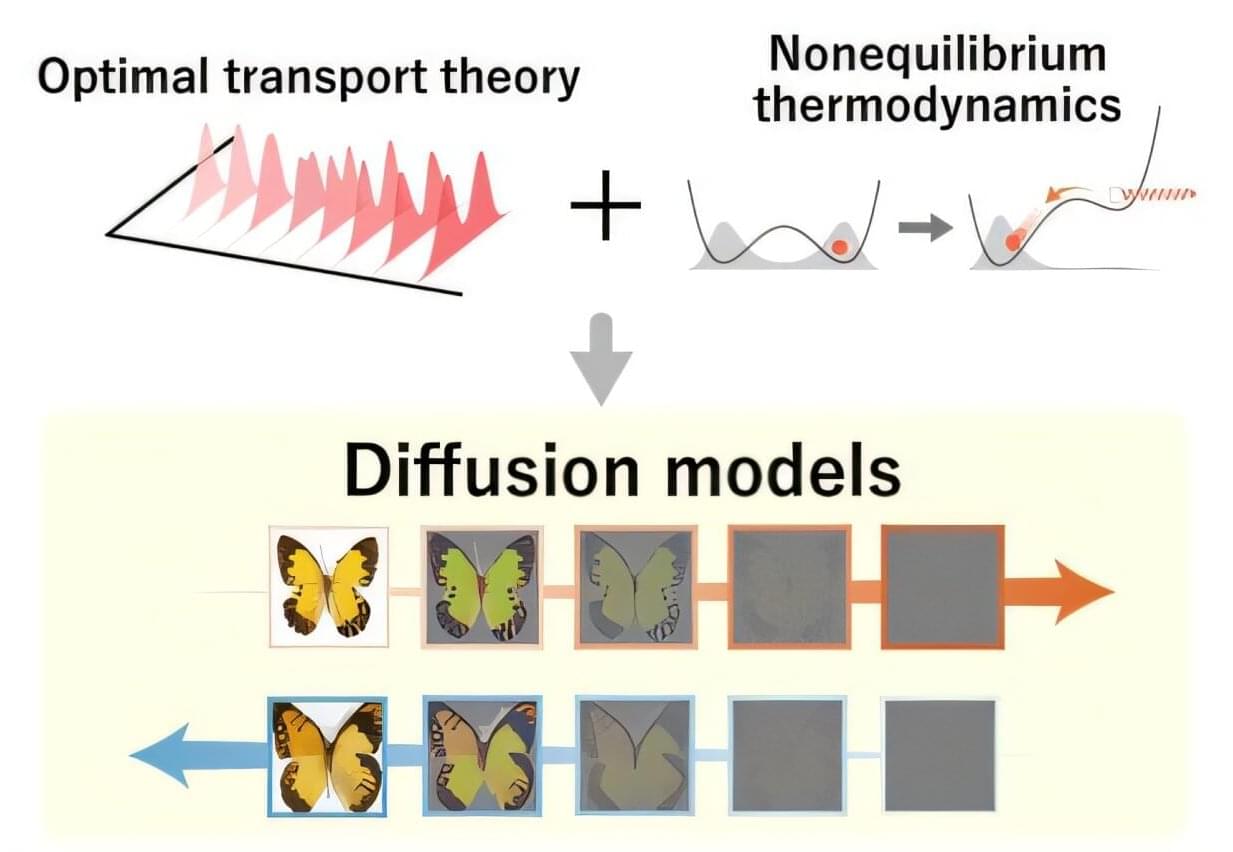
Joint research led by Sosuke Ito of the University of Tokyo has shown that nonequilibrium thermodynamics, a branch of physics that deals with constantly changing systems, explains why optimal transport theory, a mathematical framework for the optimal change of distribution to reduce cost, makes generative models optimal. As nonequilibrium thermodynamics has yet to be fully leveraged in designing generative models, the discovery offers a novel thermodynamic approach to machine learning research. The findings were published in the journal Physical Review X.
Image generation has been improving in leaps and bounds over recent years: a video of a celebrity eating a bowl of spaghetti that represented the state of the art a couple of years ago would not even qualify as good today. The algorithms that power image generation are called diffusion models, and they contain randomness called “noise.”
During the training process, noise is introduced to the original data through diffusion dynamics. During the generation process, the model must eliminate the noise to generate new content from the noisy data. This is achieved by considering the time-reversed dynamics, as if playing the video in reverse. One piece of the art and science of building a model that produces high-quality content is specifying when and how much noise is added to the data.