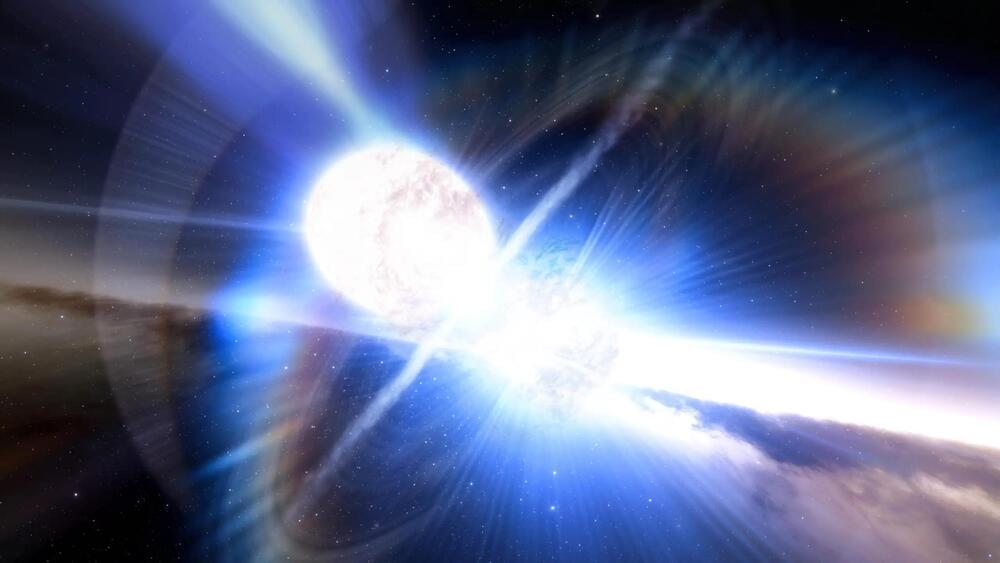
The gold that makes up your most precious jewelry may have been forged in a violent cosmic collision millions or billions of light years away between two neutron stars. New research seeks to better understand this process.
There is only a single confirmed site in the Universe capable of generating conditions extreme enough to initiate the production process for many of the heaviest elements in the Universe, including gold, platinum, uranium – neutron star.
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a large (between 10 and 29 solar masses) star. Neutron stars are the smallest and densest stars known to exist. Though neutron stars typically have a radius on the order of just 10 — 20 kilometers (6 — 12 miles), they can have masses of about 1.3 — 2.5 that of the Sun.