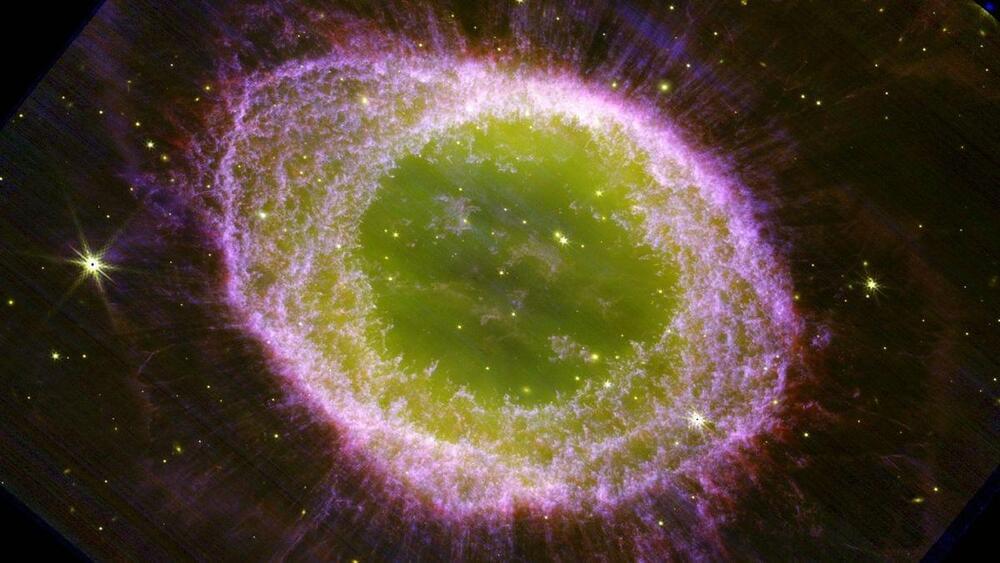
Astronomers reveal ‘the final chapters of a star’s life’ in a stunning James Webb Space Telescope’s image of the exploding Ring Nebula.



Just like pretty much every other major tech company, is placing a heavy focus on generative artificial intelligence. CEO Andy Jassy noted on Amazon’s latest earnings call that every division has multiple generative AI projects in the works.
“Inside Amazon, every one of our teams is working on building generative AI applications that reinvent and enhance their customers’ experience,”. “But while we will build a number of these applications ourselves, most will be built by other companies, and we’re optimistic that the largest number of these will be built on. Remember, the core of AI is data. People want to bring generative AI models to the data, not the other way around.”
To that end, Jassy said that AWS provides services and infrastructure that can help its customers, as notes. The AWS CodeWhisperer system, for instance, aims to by suggesting snippets of code they can use directly in the code editor.


Thinking of X-rays might trigger memories of broken bones or dental check-ups. But this extremely energetic light can show us more than just our bones: it is also used to study the molecular world, even biochemical reactions in real-time. One issue, though, is that researchers have never been able to study a single atom with X-rays. Until now.
Scientists have been able to characterize a single atom using X-rays. Not only were they able to distinguish the type of atoms they were seeing (there were two different ones), but they also managed to study the chemical behavior these atoms were showing.
“Atoms can be routinely imaged with scanning probe microscopes, but without X-rays, one cannot tell what they are made of. We can now detect exactly the type of a particular atom, one atom-at-a-time, and can simultaneously measure its chemical state,” senior author Professor Saw Wai Hla, from the University of Ohio and the Argonne National Laboratory, said in a statement.

An interdisciplinary team of mathematicians, engineers, physicists, and medical scientists has discovered a surprising connection between pure mathematics and genetics. This connection sheds light on the structure of neutral mutations and the evolution of organisms.
Number theory, the study of the properties of positive integers, is perhaps the purest form of mathematics. At first sight, it may seem far too abstract to apply to the natural world. In fact, the influential American number theorist Leonard Dickson wrote “Thank God that number theory is unsullied by any application.”
And yet, again and again, number theory finds unexpected applications in science and engineering, from leaf angles that (almost) universally follow the Fibonacci sequence, to modern encryption techniques based on factoring prime numbers. Now, researchers have demonstrated an unexpected link between number theory and evolutionary genetics.


Scientists engineered a synthetic metamaterial to direct mechanical waves along a specific path, which adds an innovative layer of control to 4D reality, otherwise known as the synthetic dimension.
Everyday life involves the three dimensions or 3D — along an X, Y, and Z axis, or up and down, left and right, and forward and back. But, in recent years scientists like Guoliang Huang, the Huber and Helen Croft Chair in Engineering at the University of Missouri, have explored a “fourth dimension” (4D), or synthetic dimension, as an extension of our current physical reality.
Creation of a new synthetic metamaterial.

In a recent article published in Scientific Reports, researchers describe the symptom profiles of respiratory viral infections from the Flu Watch Community and the Virus Watch cohort studies to compare the frequency of the range of symptoms experienced during influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), rhinovirus, seasonal coronaviruses (CoVs) infections, and infections from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) wild-type (wt) strain and variants of concerns (VOCs), including Alpha, Delta, Omicron BA1/BA2/BA5.
Study: Symptom profiles of community cases infected by influenza, RSV, rhinovirus, seasonal coronavirus, and SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Image Credit: KitjaKitja/Shutterstock.com.
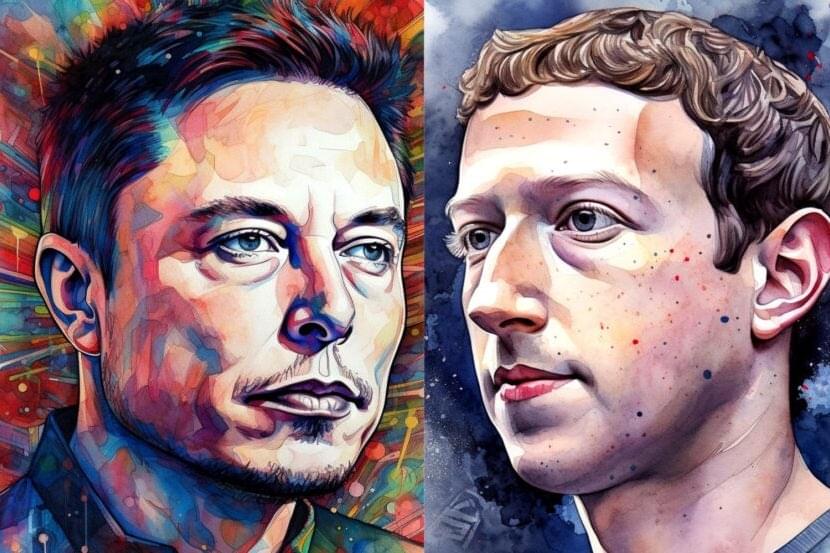

As Meta Platforms Inc.’s META latest social media platform, Threads’ daily active user count continues to drop, Elon Musk has accused Mark Zuckerberg’s forum of committing a “cardinal sin.”
What Happened: Meta’s Threads entered the social media arena with much fanfare, quickly attracting over 100 million sign-ups in just five days.
However, the initial hype didn’t translate into long-term user retention, as the daily active user count witnessed a staggering 82% decline since its peak at 44 million users on launch day, reported CNN, citing data from Sensor Tower.