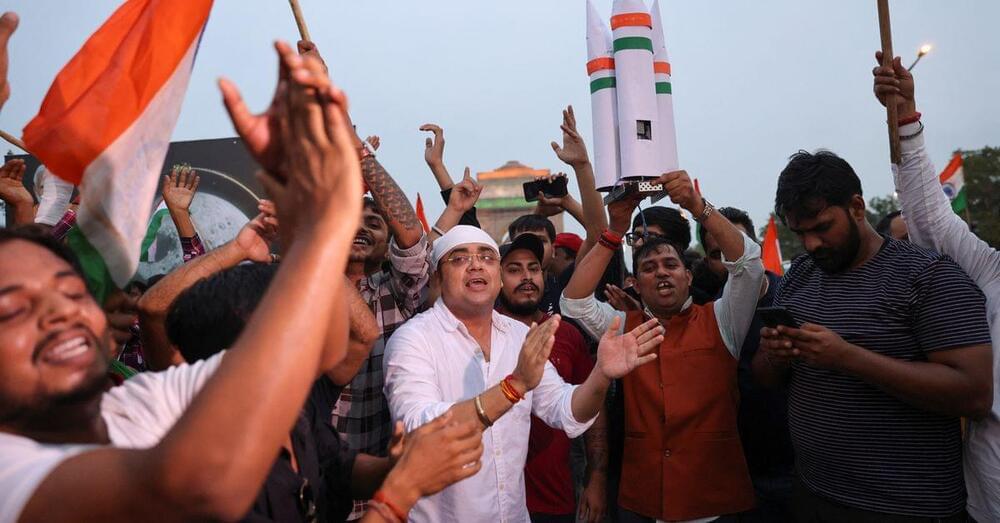
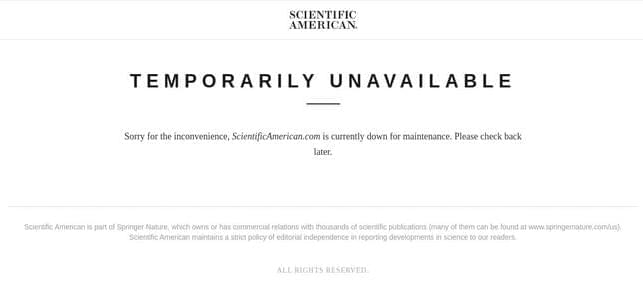
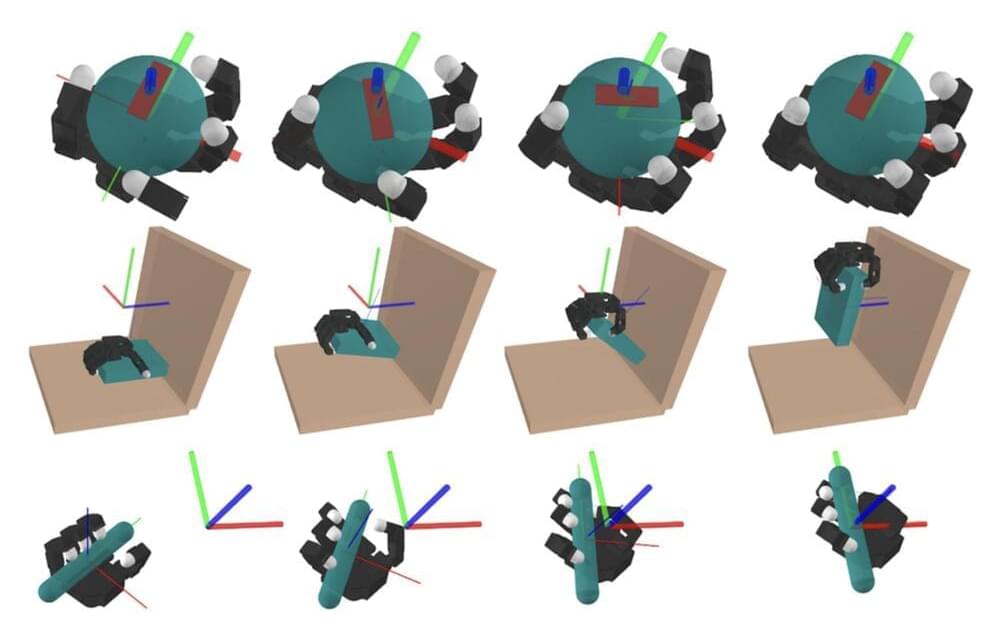
Whole-body manipulation is a strength of humans but a weakness of robots. The robot interprets each possible contact point between the box and the carrier’s fingers, arms, or torso as a separate contact event. This task becomes difficult to prepare for as soon as one considers the billions of possible contact events. Now, MIT researchers can streamline this technique, called contact-rich manipulation planning. An artificial intelligence approach called smoothing is used to reduce the number of judgments needed to find a good manipulation plan for the robot from the vast number of contact occurrences.
New developments in RL have demonstrated amazing results in manipulating through contact-rich dynamics, something that was previously challenging to achieve using model-based techniques. While these techniques were effective, it has yet to be known why they succeeded while model-based approaches failed. The overarching objective is to grasp and make sense of these factors from a model-based vantage point. Based on these understandings, scientists work to merge RL’s empirical success with the models’ generalizability and efficacy.
The hybrid nature of contact dynamics presents the greatest challenge to planning through touch from a model-based perspective. Since the ensuing dynamics are non-smooth, the Taylor approximation is no longer valid locally, and the linear model built using the gradient quickly breaks down. Since both iterative gradient-based optimization and sampling-based planning use local distance metrics, the local model’s invalidity poses serious difficulties for both. In response to these problems, numerous publications have attempted to take contact modes into account by either listing them or providing examples of them. These planners, who have a model-based understanding of the dynamic modes, often switch between continuous-state planning in the current contact mode and a discrete search for the next mode, leading to trajectories with a few-mode shifts here and there.