Many believe AI will bring the end of the world, but Emad Mostaque (CEO of Stability AI) believes AI (and humans) can.



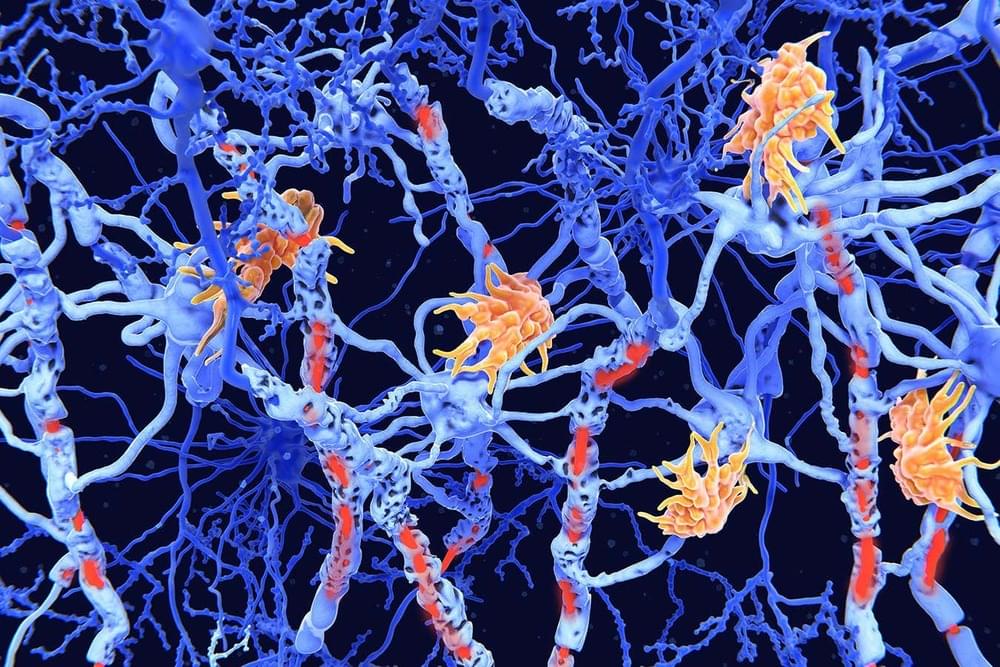
Analysis of data from more than 22,000 people with multiple sclerosis helped researchers identify a genetic variant that is associated with the severity of the disease.
By Grace Wade

Have you ever been compelled to enter sensitive payment data on the website of an unknown merchant? Would you be willing to consign your credit card data or passwords to untrustworthy hands? Scientists from the University of Vienna have now designed an unconditionally secure system for shopping in such settings, combining modern cryptographic techniques with the fundamental properties of quantum light. The demonstration of such “quantum-digital payments” in a realistic environment has been published in Nature Communications.
Digital payments have replaced physical banknotes in many aspects of our daily lives. Similar to banknotes, they should be easy to use, unique, tamper-resistant and untraceable, but additionally withstand digital attackers and data breaches.
In today’s payment ecosystem, customers’ sensitive data is substituted by sequences of random numbers, and the uniqueness of each transaction is secured by a classical cryptographic method or code. However, adversaries and merchants with powerful computational resources can crack these codes and recover the customers’ private data, and for example, make payments in their name.
Cancer spreads throughout the human body in cunning, almost militaristic, ways. For example, it can manipulate our genetic make-up, take over specific cell-to-cell signaling processes, and mutate key enzymes to promote tumor growth, resist therapies, and hasten its spread from the original site to the bloodstream or other organs.
Enzyme mutations have been of great interest to scientists who study cancer. Scientists in the Liu and Tan labs at UNC’s Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center have been studying mutations of enzyme recognition motifs in substrates, which may more faithfully reflect enzyme function with the potential to find new targets or directions for cancer treatment.
“We think understanding the roles of mutations on enzyme substrates, instead of the enzyme as a whole, may help to improve efficacy of targeted therapies, especially for enzymes that have both oncogenic and tumor suppressive function through controlling distinct subsets of substrates,” said Jianfeng Chen, Ph.D., who is first author and a postdoctoral fellow in the Liu lab in the UNC Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics.
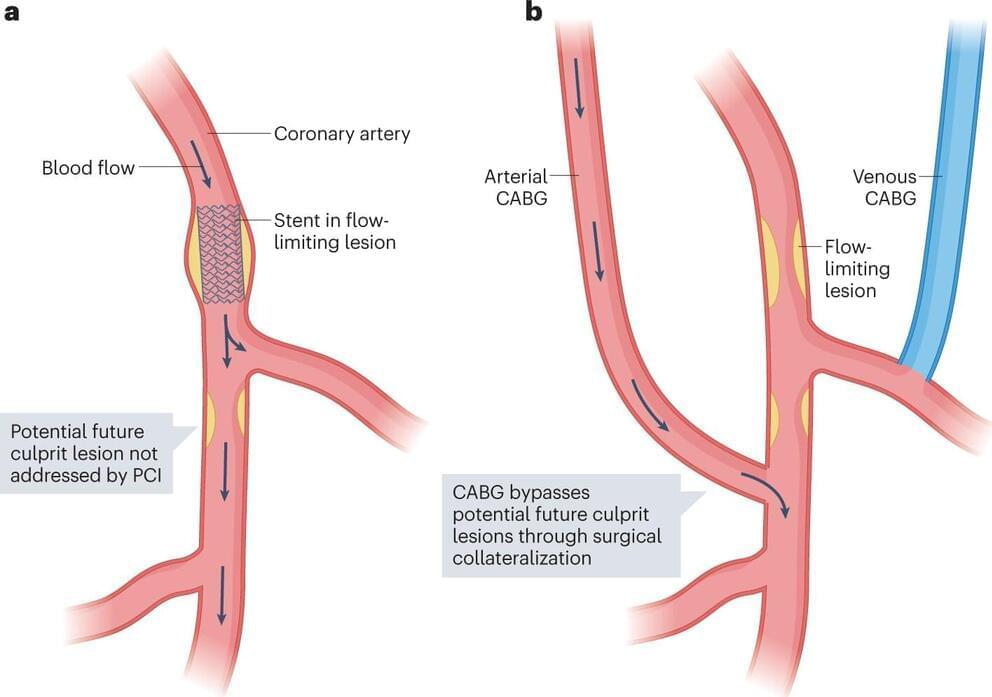
An interdisciplinary team of clinicians and scientists has published a consensus paper recommending appropriate quantitative imaging techniques for coronary artery stenosis and atherosclerosis related treatment and procedural planning. The paper has been published in Nature Reviews Cardiology.
Quantitative imaging has become increasingly important for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD) over the past five years. This is because new quantitative techniques can detect narrowed coronary arteries (coronary artery stenoses) and atherosclerosis, which play a major role in CHD patients.
It is important to correctly diagnose and accurately assess the severity of coronary artery stenosis or the extent of atherosclerotic burden for the selection of appropriate measures of therapy and the related further course of the disease. However, the complexity and variety of different quantitative imaging modalities, such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), invasive coronary angiography (ICA), intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), and optical coherence tomography (OCT), necessitated a comprehensive clinical consensus.
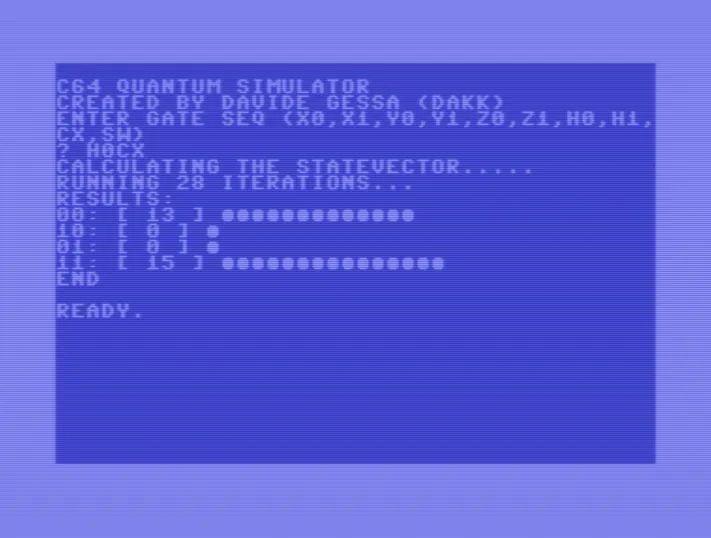
The term ‘quantum computer’ gets usually tossed around in the context of hyper-advanced, state-of-the-art computing devices, but much as how a 19th century mechanical computer, a discrete computer created from individual transistors, and a human being are all computers, the important quantifier is how fast and accurate the system is at the task, whether classical or quantum computing. This is demonstrated succinctly by [Davide ‘dakk’ Gessa] with 200 lines of BASIC code on a Commodore 64 (GitHub), implementing a range of quantum gates.
Much like a transistor in classical computing, the qubit forms the core of quantum computing, and we have known for a long time that a qubit can be simulated, even on something as mundane as an 8-bit MPU. Ergo [Davide]’s simulations of various quantum gates on a C64, ranging from Pauli-X, Pauli-Y, Pauli-Z, Hadamard, CNOT and SWAP, all using a two-qubit system running on a system that first saw the light of day in the early 1980s.
Naturally, the practical use of simulating a two-qubit system on a general-purpose MPU running at a blistering ~1 MHz is quite limited, but as a teaching tool it’s incredibly accessible and a fun way to introduce people to the world of quantum computing.
Quantum computing has long been heralded as the next frontier in computing. However, despite their immense potential, quantum computers today still make too many errors to be useful.
While it may become possible to correct these errors in the future, there is still a long way to go to reach fault tolerance. For now, the best strategy is to minimize errors and mitigate their impact on quantum computations by devising methods that can work with the existing quantum hardware.
QEDMA Quantum Computing was founded in 2020 by Asif Sinay, Netanel Lindner, and Dorit Aharonov to develop the quantum operating system of the future. QEDMA’s vision encompasses not only methods to characterize quantum hardware but also robust error mitigation strategies to get optimal results from the current generation of quantum computers.
In this informative and engaging video, we explore the fascinating world of quantum computing and its untapped potential. We delve into the challenges of building quantum computers and how artificial intelligence can help us overcome these challenges.
Whether you’re an AI or quantum computing enthusiast, or simply curious about the future of technology, this video is a must-watch. Join us as we unlock the potentials of quantum computing with AI and discover the limitless possibilities that lie ahead.
Don’t forget to subscribe to our channel if you find this video informative and helpful.
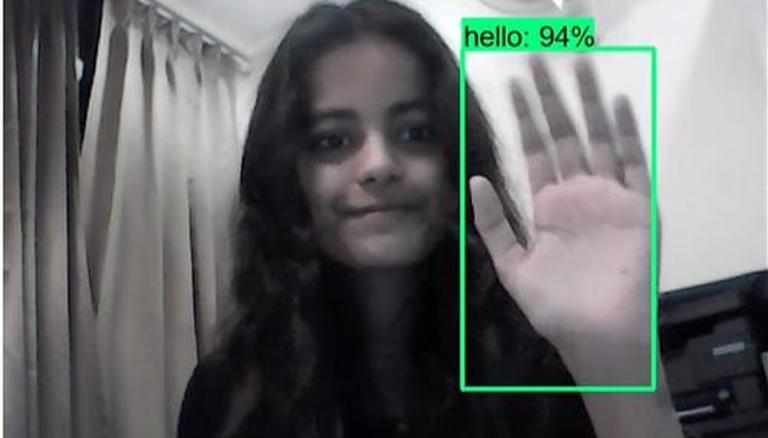
Priyanjali Gupta, an engineering student from Tamil Nadu’s Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT), has created an AI model which can translate American sign language to English in real-time. A third-year computer science student, Priyanjali Gupta is specialising in Data Science and developed the new model using Tensorflow object detection API and it is able to translate the signs using transfer learning from a pre-trained model named ssd_mobilenet.
Gupta has shared her creation on LinkedIn wherein she demonstrated the capabilities of her AI model in a demo video. According to her Github post, “The dataset is made manually by running the Image Collection Python file that collects images from your webcam for or all the mentioned below signs in the American Sign Language: Hello, I Love You, Thank you, Please, Yes and No”, She also displayed the same in her demo clip.