And potentially very embarrassing for all of crypto.
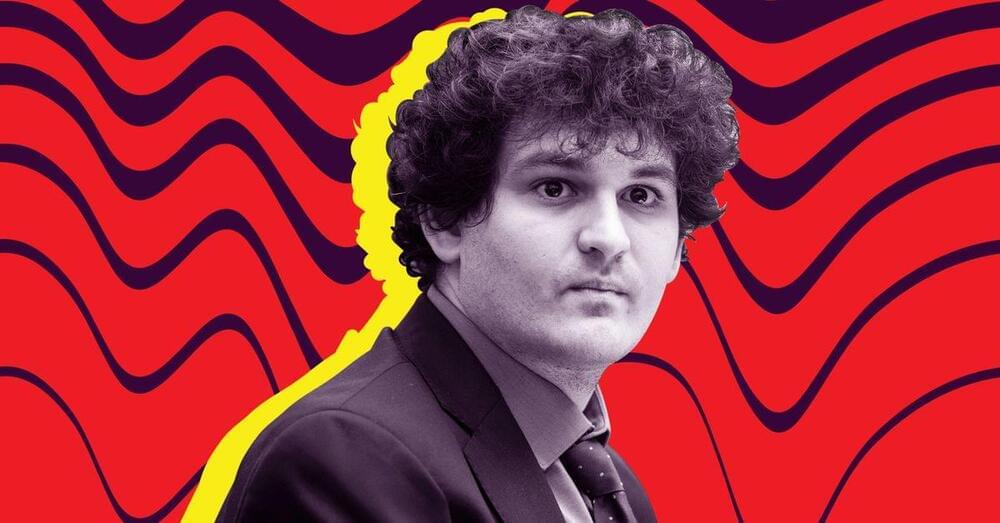
The trial of Sam Bankman-Fried is likely to be more consequential than just whether the man himself is found guilty. Depending on what evidence is introduced during the trial, it could be rough for the entire crypto industry.
“How much damage can this trial do to the already beaten-down reputation of the industry at this point?” asks Yesha Yadav, a law professor at Vanderbilt University. “This trial is going to be an excruciating moment for the industry because no one knows what kind of evidence might come out.”
“Is he going to throw the entire industry under the bus?”
Bankman-Fried’s behavior after the fall of FTX suggests he’s something of a wild card. He may suggest he was acting on the advice of his lawyers. But he may also introduce other evidence that could be troublesome — implying, for instance, that he was engaged in standard industry behavior or that everything that happened was Binance’s fault. That may be risky, but we already know that Bankman-Fried loves risk.
“Is he going to throw the entire industry under the bus?” Wong asks. “An idea like, ‘Everyone was doing this, it’s not fair I’m the only one who was charged?’” That may not fly in a court of law, but it could absolutely damage public perception of crypto at large.