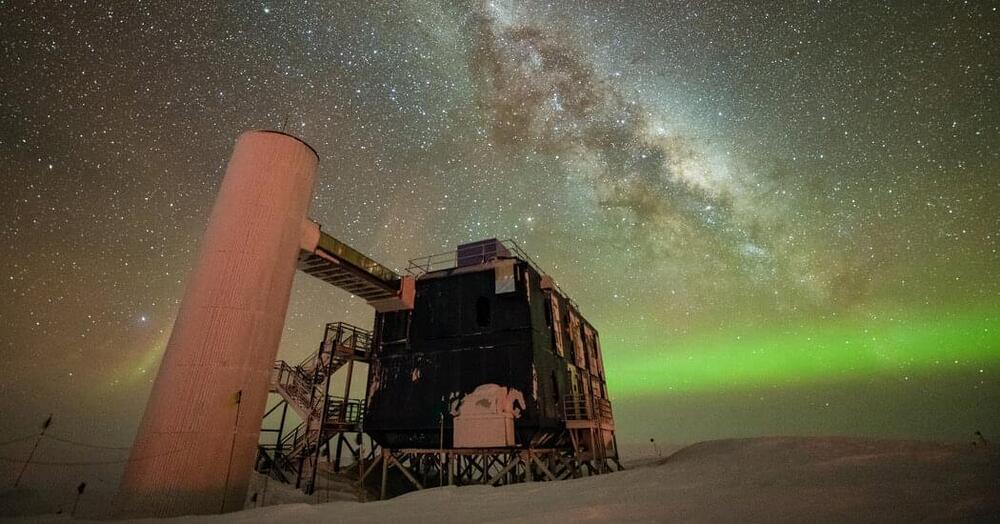
Astronomers for the first time detected neutrinos that originated within our local galaxy using a new technique.


Europe’s Euclid space telescope is scheduled to blast off Saturday on the first-ever mission aiming to shed light on two of the Universe’s greatest mysteries: dark energy and dark matter.
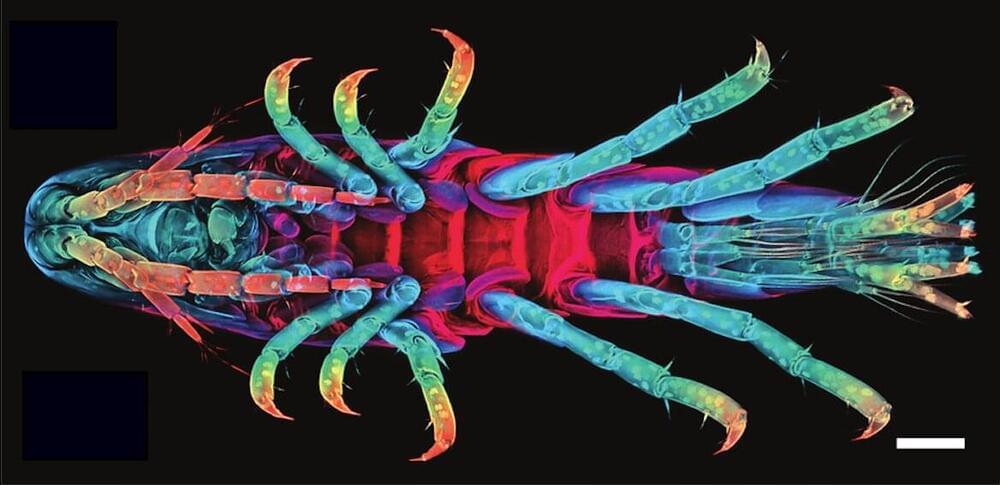
Consider the crustacean Parhyale hawaiensis, a tiny crustacean with some interesting attributes.
“It’s been called a ‘living Swiss army knife,’” said Dillon Cislo, the lead author of a study that appears in Nature Physics. “It has numerous different appendages and each one is uniquely specifiable by its size and shape. Furthermore, each one of these limbs has a very specific function.”
Their fascinating bodies and accessible growth conditions make these creatures a well-chosen model organism for developmental studies. But more than that, according to Cislo and UC Santa Barbara researchers Mark Bowick and Sebastian Streichan, their embryos are a window into the world of tissue morphogenesis, a field that seeks to understand how a mass of embryonic cells becomes the complex body parts of an adult organism.
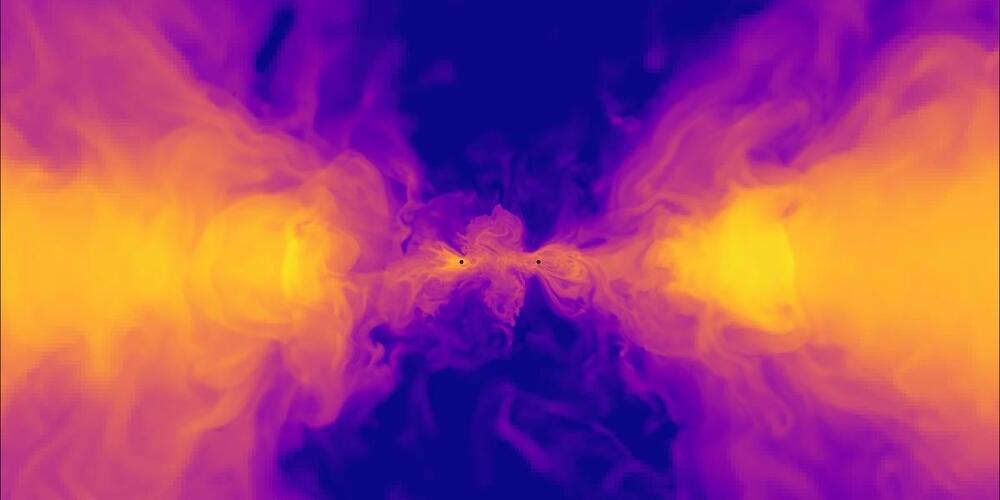

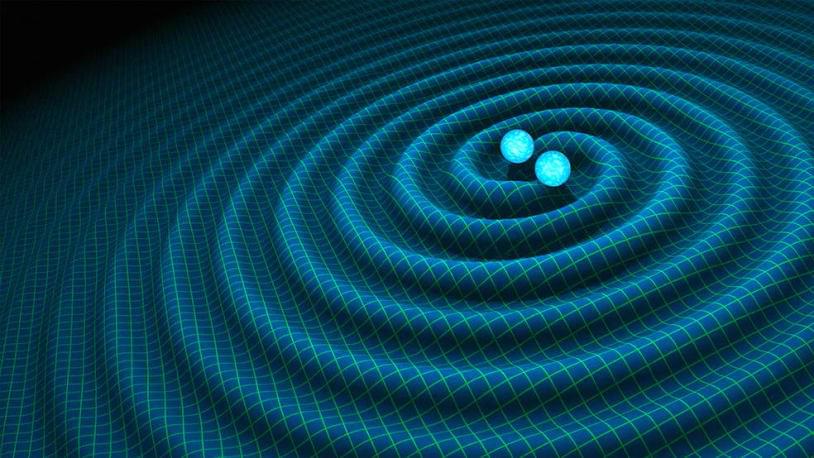
Albert Einstein proposed in 1916 that the universe was constantly being pushed and stretched by space-time waves undulating throughout the universe. A group of scientists won the Nobel Prize for finding proof of these waves in 2016, using a laser interferometer to detect a high-frequency gravitational wave emanating from the collision of two black holes or neutron stars less than 100 times the mass of the sun.
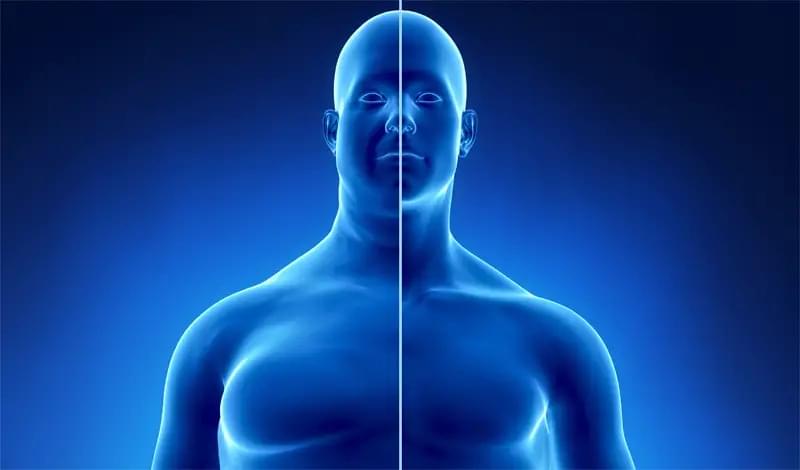
In a significant advance for the treatment of obesity, biotech giant Eli Lilly has announced the results from a trial of retatrutide, which produced a staggering 24.2% weight loss in patients.
Obesity, defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher, is a major health issue that has increased significantly over the years. As of today, it affects over 42% of adults in the United States, with 20% of children and adolescents also affected. Worldwide, more than 1 billion people are dealing with the condition, including 650 million adults, 340 million adolescents, and 39 million children.

The discovery of quantum Hall effects during the 1980s unveiled new forms of matter termed “Laughlin states”, named after the American Nobel laureate who successfully characterized them theoretically.
These exotic states uniquely appear in two-dimensional materials, under extremely cold conditions, and when subjected to a profoundly strong magnetic field. In a Laughlin state, electrons constitute an unusual liquid, where each electron dances around its congeners while avoiding them as much as possible.
Exciting such a quantum liquid generates collective states that physicists associate with fictitious particles, whose properties drastically differ from electrons: these “anyons” carry a fractional charge (a fraction of the elementary charge) and they surprisingly defy the standard classification of particles in terms of bosons or fermions.

At 19:46 Aubrey has a chart for 150 year olds and 1,000 year olds.
6th Edition: AGING & GERONTOLOGY — Sciinov Group.
www.agingcongress.com.
Aubrey De Grey.
President & CSO, LEV Foundation, USA
Title: Taking Rejuvenation to Longevity escape velocity.
Sciinov Group is a specialized international events organizer, and provider of customized data intelligence databases, trends and insights that solve information challenges and caters organizations needs.
Sciinov Conferences mission is to benefit attendees by networking their peers, often potential clients and learn from the high quality of information delivered by the expert speakers.