Today’s batteries lose efficiency – or “age” – through use, but theoretical quantum batteries might be immune to the problem if they are charged wirelessly.


Today’s batteries lose efficiency – or “age” – through use, but theoretical quantum batteries might be immune to the problem if they are charged wirelessly.

For about a year and a half, Coca-Cola has experimented with limited-edition beverages that have mystery tastes — most of them with vague, futuristic concepts and undisclosed flavors.
The latest one, Coca-Cola Y3000, fits the bill. The one distinction: It’s supposed to taste like the future. Fittingly, the soft-drink giant used artificial intelligence to help determine the flavor and packaging.
It’s important for Coca-Cola to keep customers — particularly younger ones — excited about Coke, its more-than-a-century-old signature product. In recent years, health-conscious consumers have shied away from sugary beverages, making it trickier for soda sellers to market their legacy brands. Coca-Cola has used its Creations platform, responsible for limited-edition flavors like Y3000, to try to make the brand resonate with younger consumers.

Companies are struggling with where to start with generative AI. The authors’ case studies, based on their growing global community of over 3,000 GenAI practitioners, point to a new category of work, more precise and actionable than “knowledge work.” They call it WINS Work — the places where tasks, functions, possibly your entire company or industry — are dependent on the manipulation and interpretation of Words, Images, Numbers, and Sounds (WINS). This framework can help leaders identify how vulnerable their business is to changes from this new technology and plan their response.
Page-utils class= article-utils—vertical hide-for-print data-js-target= page-utils data-id= tag: blogs.harvardbusiness.org, 2007/03/31:999.362921 data-title= Where Should Your Company Start with GenAI? data-url=/2023/09/where-should-your-company-start-with-genai data-topic= AI and machine learning data-authors= Paul Baier; Jimmy Hexter; John J. Sviokla data-content-type= Digital Article data-content-image=/resources/images/article_assets/2023/09/Sep23_09_AlexWilliam-383x215.jpg data-summary=
Understand where your company stands — and what it needs to do.
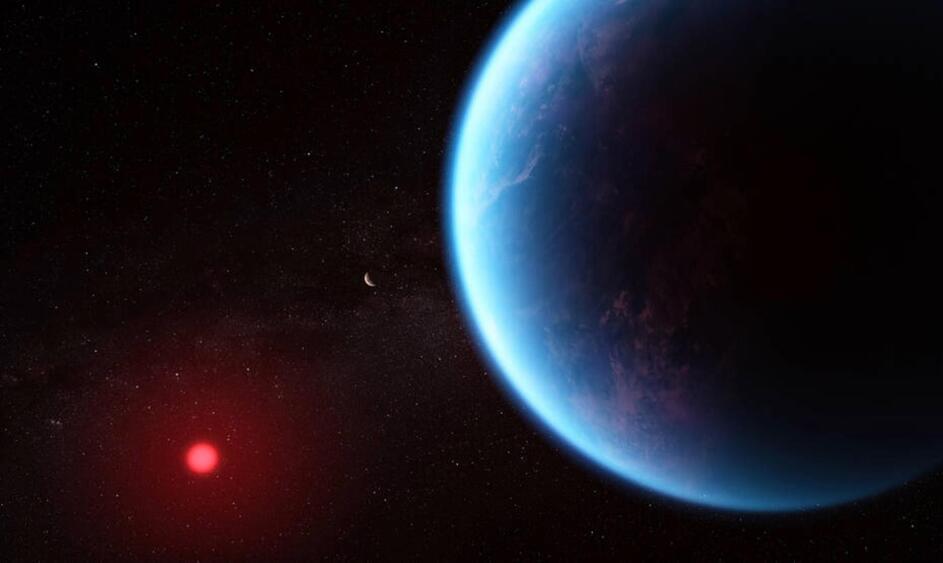

Carbon-based molecules, such as methane and carbon dioxide, have been detected in the atmosphere of a possibly ocean-bearing exoplanet.
Carbon-based molecules have been discovered in the atmosphere of a possibly ocean-bearing exoplanet by the cutting-edge James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
The exoplanet K2-18b is found in the habitable zone of the red dwarf star K2-18, around 120 light-years distant from Earth in the constellation Leo.

A Meta team, hand-picked by Zuckerberg, is working on the new AI tool.
Meta will unveil a superior artificial intelligence model in 2024, which is touted to be on par with the most powerful model created by OpenAI, the company that birthed ChatGPT and is backed by Microsoft, reported The Wall Street Journal.
WSJ spoke to people familiar with the matter, most likely Meta insiders, who said that the new model would be two times more advanced than Llama 2, the open-source large language model launched by Meta in July and distributed by Microsoft’s cloud Azure services.
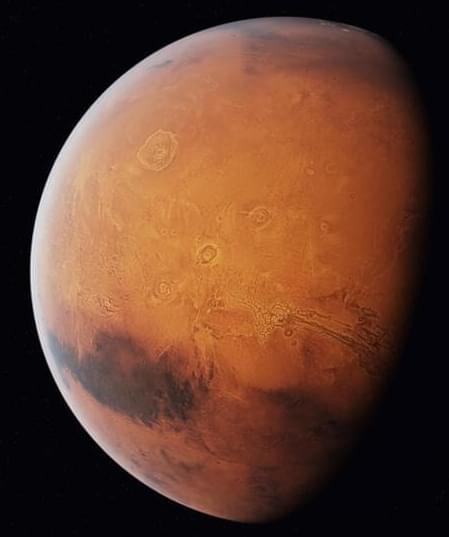

Astronomers have been observing and studying Mars for centuries, but the systematic mapping of Mars began in the 19th century.
Maps have played an essential role in helping us better comprehend our home planet. These tools visually represent the Earth’s surface features, allowing us to navigate, study geography, monitor changes, and conduct scientific studies.
As space organizations prepare to make humanity an interplanetary species, it is critical to sketch and construct a Mars map for better exploration and possible habitation.
German scientists present a method by which AI could be trained much more efficiently.
In the last couple of years, research institutions have been working on finding new concepts of how computers can process data in the future. One of these concepts is known as neuromorphic computing. Neuromorphic computing models may sound similar to artificial neural networks but have little to do with them.
Compared to traditional artificial intelligence algorithms, which require significant amounts of data to be trained on before they can be effective, neuromorphic computing systems can learn and adapt on the fly.
Rubio has spent more than 355 days aboard the ISS and will spend more than a year aboard the space station before returning to Earth.
NASA astronaut Frank Rubio now holds the record for the American who has flown the longest space mission in US history.
Rubio broke the record yesterday, September 11, at 1:39 p.m. EDT (1739 GMT) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). He surpassed the 355 days, 3 hours and 45 minutes logged by NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei in 2022.
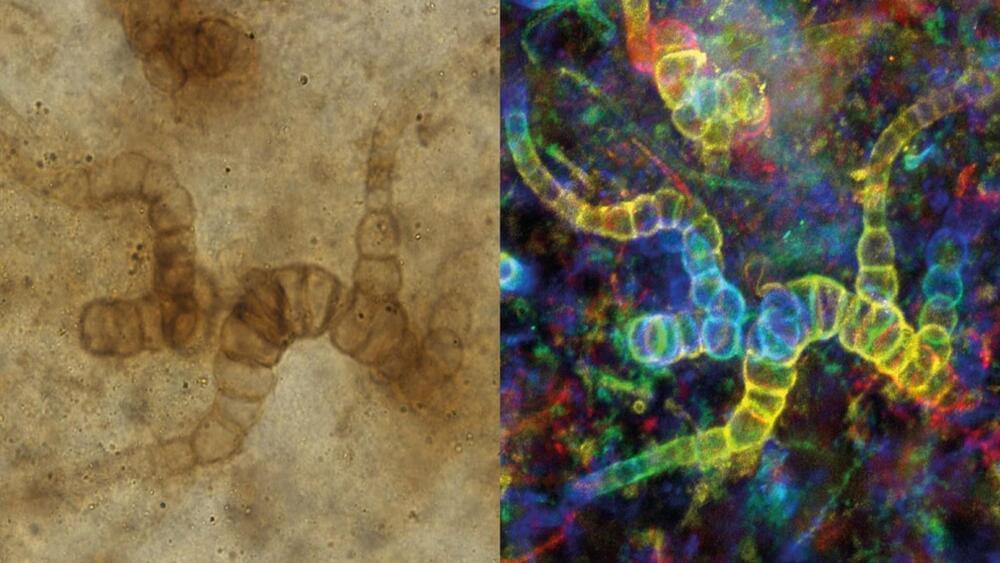
Scientists performed detailed 3D reconstructions of fossils discovered in Scotland.
Cyanobacteria, commonly known as blue-green algae, are the earliest known life forms on Earth. They are responsible for the Earth’s transition from a carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere to the present relatively oxygen-rich atmosphere due to oxygenic photosynthesis.
Ubiquitously found in ponds, lakes, water streams, rivers, and wetlands, they have played a significant role in shaping life.