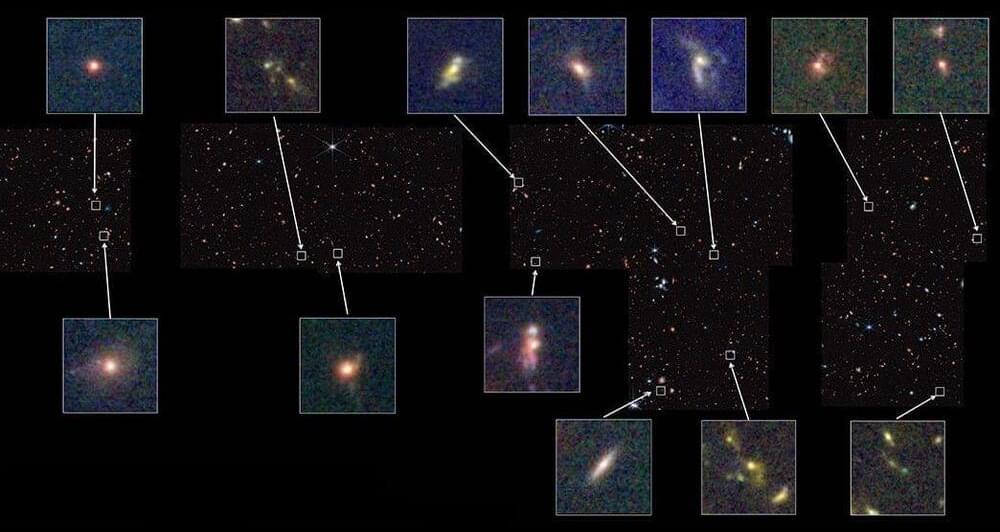
New results from the James Webb Space Telescope challenge prevailing models of the early universe.



Samsung has been on a hiring spree of top executives from reputed companies in the last few months. About a week ago, we reported that Samsung had hired two former Ericsson executives to its Samsung Networks team. Last December, Samsung roped in an ex-Mercedes designer, Hubert H. Lee, to lead its smartphone design team. Now, Samsung has now hired former Qualcomm Vice President Benny Katibian.
Benny previously worked for Qualcomm as the Vice President of the company’s engineering division. After joining Samsung, Benny will serve as the head of the Samsung Austin Research Center (SARC) and the Advanced Computing Lab (ACL), which are the core R&D centers of Samsung Electronics USA, as per Business Korea.
According to reports, Benny Katibian is an expert in semiconductors and was in charge of self-driving systems, including ADAS (Advanced Driving Assistance Systems) at Qualcomm. Later, he also served as the COO of the North American Cooperation in Xiaopeng, a Chinese electric car company. He also worked as the head of the development of self-driving chips.
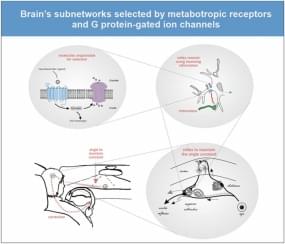
I am proud to announce that today came out probably my most important scientific paper. I propose a whole new paradigm in neuroscience. To understand the mind, synapses are not so important any more. Instead, critical are some other type of proteins on the neural membrane. These proteins have the capability to transiently select subnetworks that will be functional in the next few seconds or minutes. The paradigm proposes that cognition emerges from those transient subnetwork selections (and not from network computations of the classical, so-called connectionist paradigm). The proteins in question are metabotropic receptor and G protein-gated ion channels. Simply put, we think with those proteins. A result of a thought is a new state of network pathways, not the activity of neurons.
One can download the paper here:
Perhaps the most important question posed by brain research is: How the brain gives rise to the mind. To answer this question, we have primarily relied on the connectionist paradigm: The brain’s entire knowledge and thinking skills are thought to be stored in the connections; and the mental operations are executed by network computations. I propose here an alternative paradigm: Our knowledge and skills are stored in metabotropic receptors (MRs) and the G protein-gated ion channels (GPGICs). Here, mental operations are assumed to be executed by the functions of MRs and GPGICs. As GPGICs have the capacity to close or open branches of dendritic trees and axon terminals, their states transiently re-route neural activity throughout the nervous system. First, MRs detect ligands that signal the need to activate GPGICs. Next, GPGICs transiently select a subnetwork within the brain. The process of selecting this new subnetwork is what constitutes a mental operation – be it in a form of directed attention, perception or making a decision. Synaptic connections and network computations play only a secondary role, supporting MRs and GPGICs. According to this new paradigm, the mind emerges within the brain as the function of MRs and GPGICs whose primary function is to continually select the pathways over which neural activity will be allowed to pass. It is argued that MRs and GPGICs solve the scaling problem of intelligence from which the connectionism paradigm suffers.

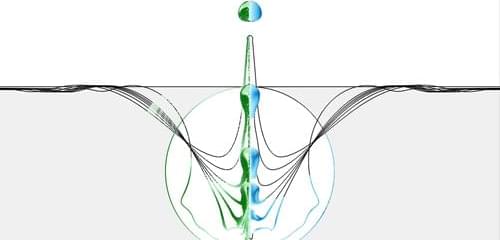
Claudiu Stan of Rutgers University—Newark, New Jersey, and his colleagues were watching moving drops of supercooled water spontaneously freeze when they noticed something unexpected: drops kept suddenly disappearing. Initially they thought that the lost drops had shattered as they froze. But, on closer inspection, they found that the icy drops were still there, they had just moved out of view. The team has now developed a quantitative model for this behavior, attributing it to a rocket-like propulsion mechanism induced by the freezing process [1]. Stan says that the finding could inspire scientists to design self-propelled systems powered by such phase transitions.
The team’s results add to a growing body of work on self-propelled drops. The mechanisms behind such motion vary wildly, but Stan notes that they all involve symmetry breaking. For the freezing drops, this symmetry breaking arises when the ice nucleation starts off-center. When ice nucleates, the change in structure releases latent heat, causing the local evaporation rate to suddenly increase, and if the nucleation is off-center, this enhanced evaporation occurs unevenly over the drop’s surface. Like a rocket ejecting a propellant heated by a chemical reaction, this asymmetrical evaporation increases the drop’s momentum, with the team’s model predicting peak velocities of nearly 1 m/s.
Stan says that this propulsion mechanism has a unique feature that could make it attractive for applications: unlike most self-propelled particles, it requires no surfaces and no surrounding fluid (the experiments were done under vacuum). But, for him, the findings have another bonus: “I am a fan of space exploration, so it was exciting to realize that [we could] draw an analogy between these tiny droplets and rockets,” he says.
Experiments reveal new details of the process by which contaminants in the ocean could reach the atmosphere through the bursting of bubbles in foam.
The bursting bubbles in ocean foam produce a mist of droplets that can contain enhanced concentrations of ocean pollutant particles. In single-bubble lab experiments, researchers have now shown that the inclusion of a particular particle in an airborne droplet depends on some details of the fluid motion that occurs when the droplet forms [1]. The researchers measured the efficiency with which particles are transferred to droplets and also ran simulations of the fluid motion. Their model predicts that the airborne droplets should contain more large particles, such as microplastics, and fewer smaller particles, such as viruses, than expected based on previous theories.
The droplets produced by bursting air bubbles in ocean foam provide the atmosphere’s main source of ocean-originated particles, including pollutants and bacteria, and environmental scientists want to understand this ocean-to-atmosphere transfer process in detail. Experiments in the 1970s showed that bursting bubbles transport pathogens into the environment and also that the droplets produced contain these particles at high concentrations.
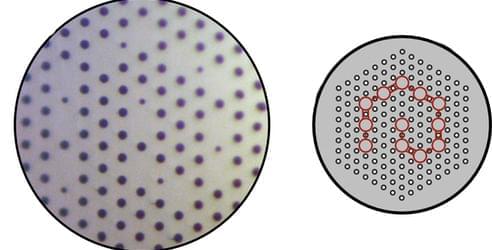
A new design for an optical fiber borrows concepts from topology to protect light from imperfections in the fiber’s light-guiding materials or from distortions in its cross section.
Using concepts from the mathematical field of topology, researchers at the University of Bath, UK, have designed an optical fiber that can robustly propagate light, even if there are variations in the properties of its light-guiding materials or in its overall geometry [1]. The team thinks that this newfound topological protection could enable advances in optical communication and photonic quantum computing.
The concept of topology is often explained using a joke about a donut and a coffee cup. A coffee cup made of rubber can be continuously twisted and stretched—no cuts need to be made—so that it takes on the shape of a donut. Even though the object’s outline changes under this transformation, its essence remains the same—it contains one hole. Thus, the quip goes, a topologist cannot tell the difference between the two things.
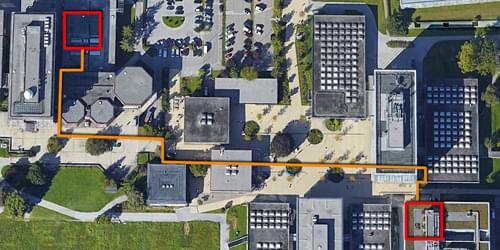
Researchers have achieved long-distance entanglement between two calcium ions, each of which lies in a different building, showing that trapped ions could be used to create quantum networks.
Among the many candidate platforms for quantum-information applications, trapped-ion qubits are promising because of their long coherence times and their potential for multiqubit operations (see Viewpoint: Trapped Ions Make Impeccable Qubits). Alone, those properties are insufficient for some quantum applications, however: to build quantum communication networks, for example, requires the qubits’ delicate quantum states be shared over long distances. Demonstrations of this ability have been lacking for trapped-ion systems. Now a team led by Benjamin Lanyon at the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information, Austria, and Tracy Northup at the University of Innsbruck, Austria, have addressed this shortfall by entangling two trapped-ion qubits residing in different buildings [1].
Lanyon, Northup, and colleagues used trapped-ion qubits inside optical cavities. For each qubit, they excited the ion using a dual-wavelength laser, prompting the ion to emit a single photon. The photon’s polarization depended on which of the two laser wavelengths the ion absorbed, entangling the photon with the ion’s final state. To entangle the two ions, the team then transmitted the photon from one ion through 510 m of optical fiber to a beam splitter near the other ion, where the two photons interacted. The researchers claimed successful entanglement when they subsequently detected a pair of photons with specific individual polarizations.


Artificial intelligence (AI) tools have achieved promising results on numerous tasks and could soon assist professionals in various settings. In recent years, computer scientists have been exploring the potential of these tools for detecting signs of different physical and psychiatric conditions.
Depression is one of the most widespread psychiatric disorders, affecting approximately 9.5% of American adults every year. Tools that can automatically detect signs of depression might help to reduce suicide rates, as they would allow doctors to promptly identify people in need of psychological support.
Researchers at Jinhua Advanced Research Institute and Harbin University of Science and Technology have recently developed a deep learning algorithm that could detect depression from a person’s speech. This model, introduced in a paper published in Mobile Networks and Applications, was trained to recognize emotions in human speech by analyzing different relevant features.
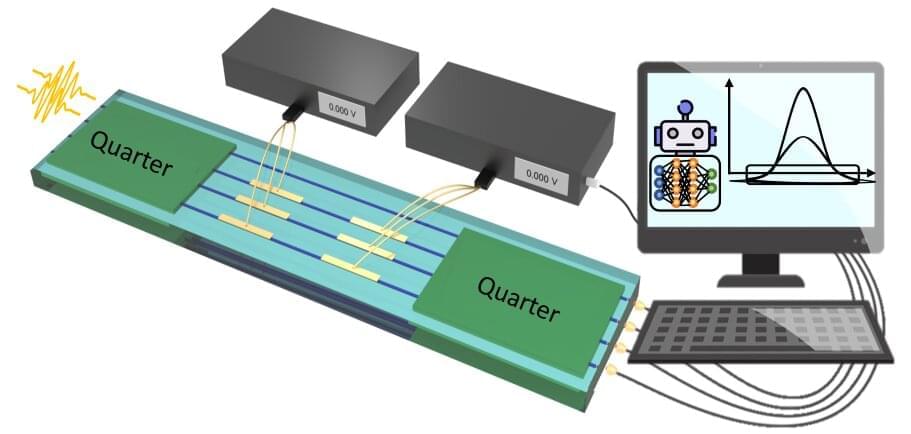
Quantum sensing represents one of the most promising applications of quantum technologies, with the aim of using quantum resources to improve measurement sensitivity. In particular, sensing of optical phases is one of the most investigated problems, considered key to developing mass-produced technological devices.
Optimal usage of quantum sensors requires regular characterization and calibration. In general, such calibration is an extremely complex and resource-intensive task—especially when considering systems for estimating multiple parameters, due to the sheer volume of required measurements as well as the computational time needed to analyze those measurements. Machine-learning algorithms present a powerful tool to address that complexity. The discovery of suitable protocols for algorithm usage is vital for the development of sensors for precise quantum-enhanced measurements.
A particular type of machine-learning algorithm known as “reinforcement learning” (RL) relies on an intelligent agent guided by rewards: Depending on the rewards it receives, it learns to perform the right actions to achieve the desired optimization. The first experimental realizations using RL algorithms for the optimization of quantum problems have been reported only very recently. Most of them still rely on prior knowledge of the model describing the system. What is desirable is instead a completely model-free approach, which is possible when the agent’s reward does not depend on the explicit system model.