Microsoft is going to update its services agreement very soon and rival Mozilla is relentlessly questioning the Redmond giant about its true intentions with user data regarding AI services.



Global worming?
Scientists recently revived microscopic creatures frozen for 46,000 years in the Siberian permafrost.
The ancient nematodes, better known as roundworms, are able to shut their bodies down in unsuitable environments — a process called anabiosis.
This comprehensive study explores ChatGPT’s ability to answer questions about diabetes, comparing it to human experts in a Danish diabetes center. While familiar users could more often spot the AI-generated answers, the research underscores the need for rigorous evaluation and safe integration of AI in healthcare.
Like biomarker tests, germline testing can help doctors determine the best treatments for patients, but such testing may also help identify people whose family members should be offered testing for potential cancer-causing gene changes.
Guidelines recommend that germline testing be offered to all people with male breast cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, and metastatic prostate cancer. For other cancers with lower likelihood of harmful inherited mutations, recommendations for germline testing vary.
But new findings from a study that is examining the extent of testing for germline mutations among people diagnosed with cancer in California and Georgia between 2013 and 2019 found that germline testing rates are still low. Among the more than 1.3 million people in the study, only about 93,000, or 6.8%, underwent germline genetic testing through March 31, 2021, according to findings published July 3 in JAMA.
A new cancer therapy developed by Purdue University researchers attacks tumors by tricking cancer cells into absorbing a snippet of RNA that naturally blocks cell division. As reported in Oncogene, tumors treated with the new therapy did not increase in size over the course of a 21-day study, while untreated tumors tripled in size over the same time period. The paper is tiled “A first-in-class fully modified version of miR-34a with outstanding stability, activity, and anti-tumor efficacy.”
Cancer can begin almost anywhere in the human body. It is characterized by cells that divide uncontrollably and that may be able to ignore signals to die or stop dividing, and even evade the immune system. The therapy, tested in mouse models, combines a delivery system that targets cancer cells with a specially modified version of microRNA-34a, a molecule that acts “like the brakes on a car,” slowing or stopping cell division, said Andrea Kasinski, lead author and the William and Patty Miller Associate Professor of biological sciences at Purdue University.
In addition to slowing or reversing tumor growth, the targeted microRNA-34a strongly suppressed the activity of at least three genes—MET, CD44 and AXL—known to drive cancer and resistance to other cancer therapies, for at least 120 hours. The results indicate that the patent-pending therapy, the newest iteration in more than 15 years of work targeting microRNA to destroy cancer, could be effective on its own and in combination with existing drugs when used against cancers that have built drug resistance.

After a certain age, approximately 40% of people experience some degree of hearing loss. While age-related hearing loss is most prevalent in adults over the age of 65, it can start occurring far earlier than that, when people are in their 40s or 50s.
Despite their widespread use, existing diagnostic techniques might be unable to detect earlier signs of hearing loss, such as the loss of the ability to hear speech in crowded or noisy environments. Some researchers have thus been trying to devise viable techniques to detect subtler forms of hearing loss, so that they can be addressed early, before they are irreparable.
To this end, two neuroscientists at the Rotman Research Institute in Canada have recently been exploring the relationship between effortful listening and eye movements. Their most recent paper, published in The Journal of Neuroscience, suggests eye movements tend to decrease while young adults are placing greater effort in trying to hear speech.
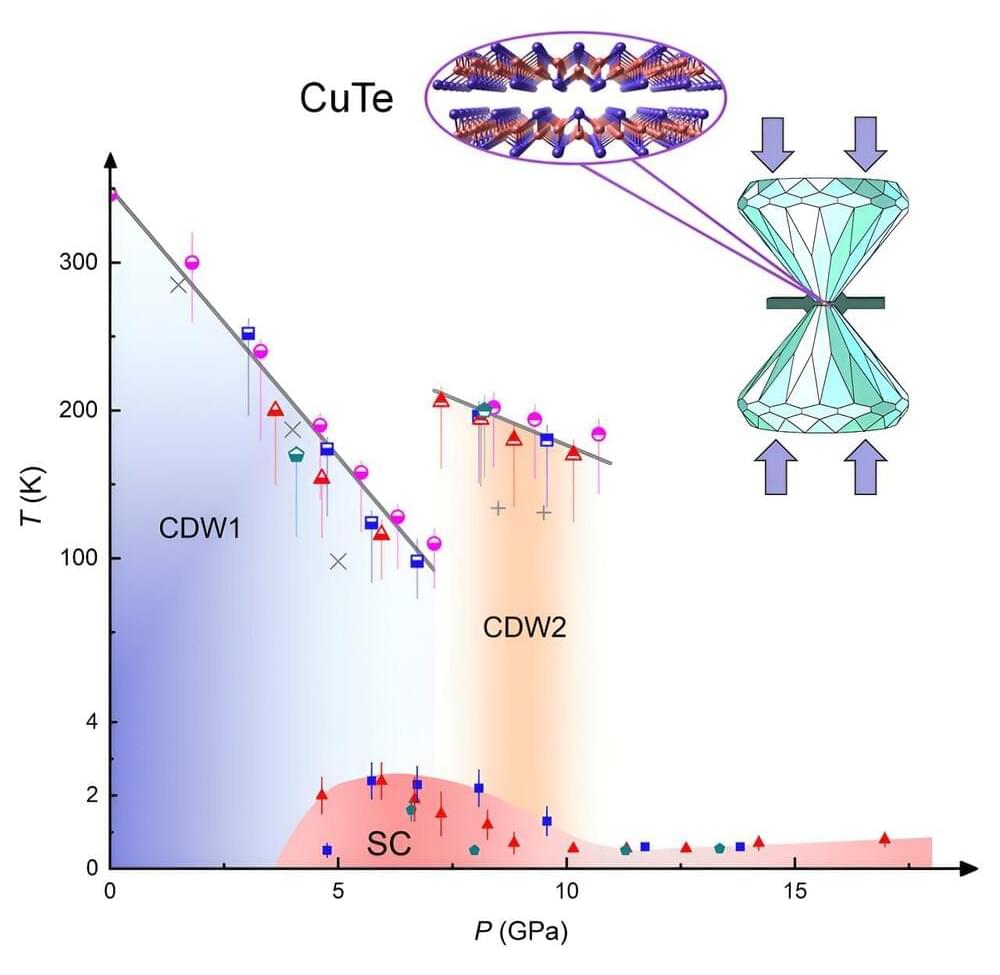
In a study published in Matter, researchers led by Prof. Yang Zhaorong and Prof. Hao Ning from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences found that the quasi-one-dimensional charge density wave (CDW) material cupric telluride (CuTe) provides a rare and promising platform for the study of multiple CDW orders and superconductivity under high pressure.
The interplay between superconductivity and CDW has always been one of the central issues in the research of condensed matter physics. While theory generally predicts that they compete with each other, superconductivity and CDW can manifest complex relationships under external stimuli in practical materials. Additionally, recent research in the superconducting cuprates and the Kagome CsV3Sb5 has found that superconductivity interacts with multiple CDW orders. However, in the above two systems, there are some other quantum orders in the phase diagrams, which hinders a good understanding of the interplay between superconductivity and multiple CDWs.
In this study, the researchers provided solid evidence for a second CDW order in the quasi-one-dimensional CDW material CuTe under high pressure. In addition, they found that superconductivity can be induced and that it has complex relationships with the native and emergent CDW orders.
To assist humans during their day-to-day activities and successfully complete domestic chores, robots should be able to effectively manipulate the objects we use every day, including utensils and cleaning equipment. Some objects, however, are difficult to grasp and handle for robotic hands, due to their shape, flexibility, or other characteristics.
These objects include textile-based cloths, which are commonly used by humans to clean surfaces, polish windows, glass or mirrors, and even mop the floors. These are all tasks that could be potentially completed by robots, yet before this can happen robots will need to be able to grab and manipulate cloths.
Researchers at ETH Zurich recently introduced a new computational technique to create visual representations of crumpled cloths, which could in turn help to plan effective strategies for robots to grasp cloths and use them when completing tasks. This technique, introduced in a paper pre-published on arXiv, was found to generalize well across cloths with different physical properties, and of different shapes, sizes and materials.
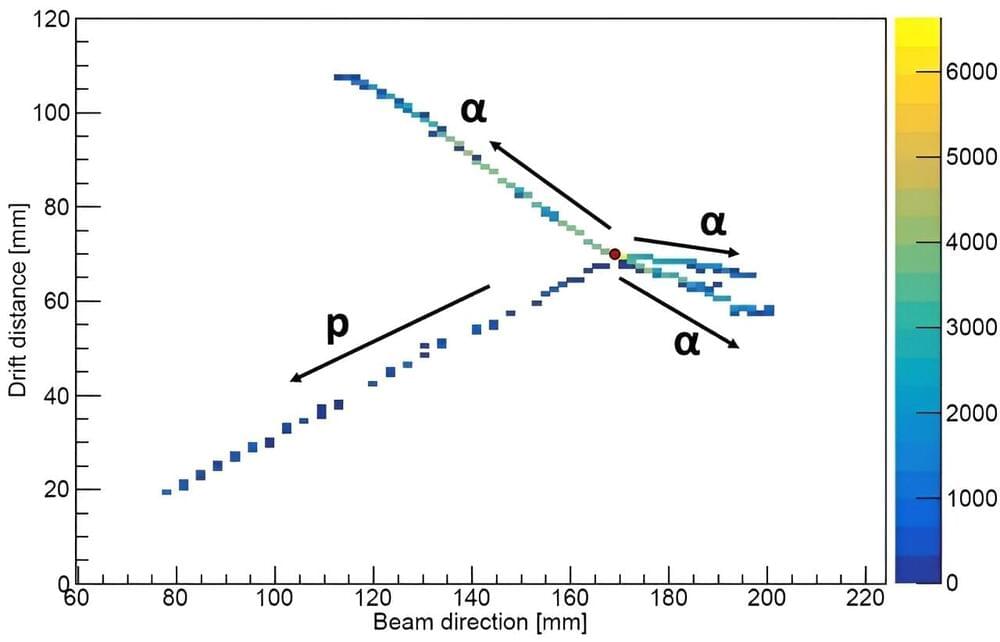
Not all of the material around us is stable. Some materials may undergo radioactive decay to form more stable isotopes. Scientists have now observed a new decay mode for the first time. In this decay, a lighter form of oxygen, oxygen-13 (with eight protons and five neutrons), decays by breaking into three helium nuclei (an atom without the surrounding electrons), a proton, and a positron (the antimatter version of an electron).
Scientists observed this decay by watching a single nucleus break apart and measuring the breakup products. The study is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Scientists have previously observed interesting modes of radioactive decay following the process called beta-plus decay. This is where a proton turns into a neutron and emits some of the produced energy by emitting a positron and an antineutrino. After this initial beta-decay, the resulting nucleus can have enough energy to boil off extra particles and make itself more stable.
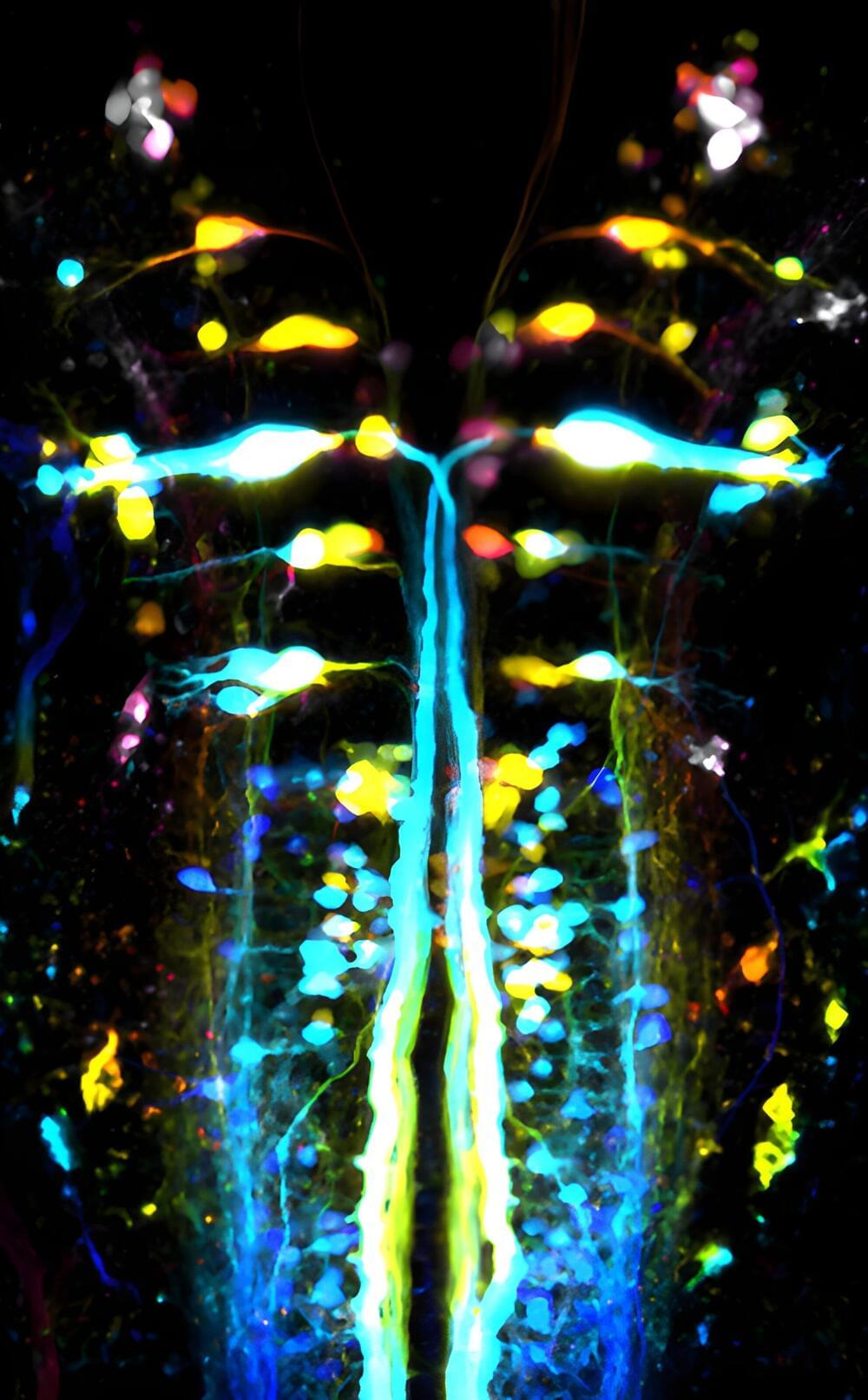
Walking is a complex mechanism involving both automatic processes and conscious control. Its dysfunction can have multiple, sometimes extremely subtle causes, within the motor cortex, brain stem, spinal cord, or muscles. At Paris Brain Institute, Martin Carbo-Tano, Mathilde Lapoix, and their colleagues in the “Spinal Sensory Signaling” team, led by Claire Wyart (Inserm), have focused on a specific component of locomotion: forward propulsion.
In a study published in Nature Neuroscience, they show that it involves a region classically called the mesencephalic locomotor region, which controls the vigor and speed of movement and transmits the nervous message to the spinal cord via control neurons located in the brainstem.
This new mapping carried out in zebrafish corroborates recent studies in mice. It could eventually be extended to humans—helping to understand how movement control circuits can malfunction, in Parkinson’s disease notably.