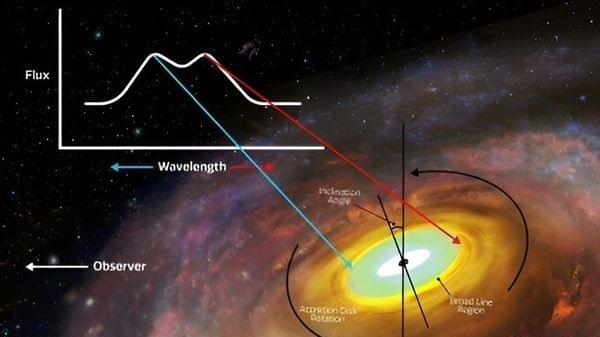
An active supermassive black hole is one of the greatest wonders in the cosmos.
A dense, invisible object that can be billions of times the mass of our Sun is surrounded by a vast, churning disk and torus of material, blazing with light as it swirls down onto the black hole center. But how big do these structures grow?
For the first time, an unambiguous detection of near-infrared light reveals the outskirts of the massive accretion disk surrounding a supermassive black hole hundreds of millions times our Sun’s mass, in a galaxy called III Zw 002 some 1.17 billion light-years away.