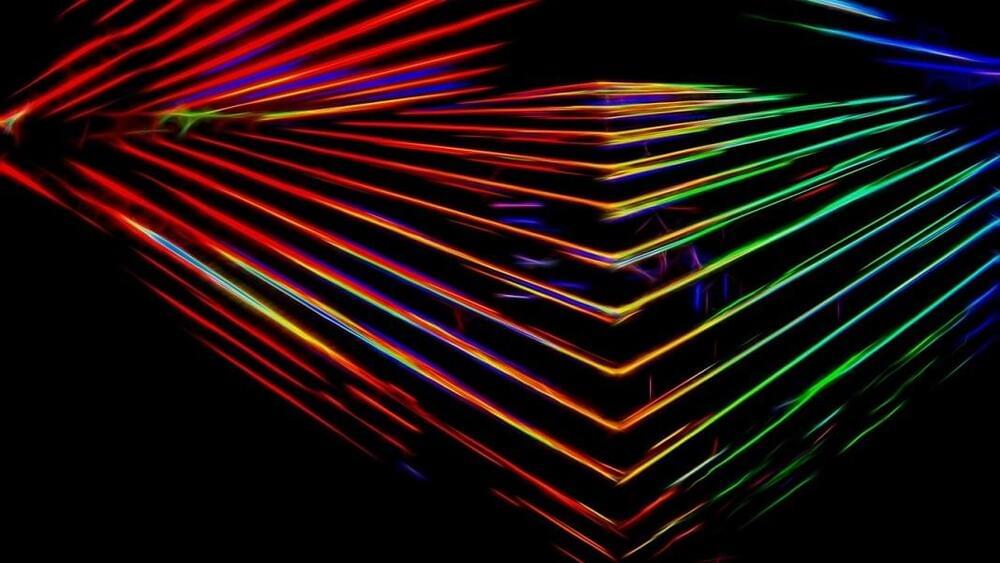
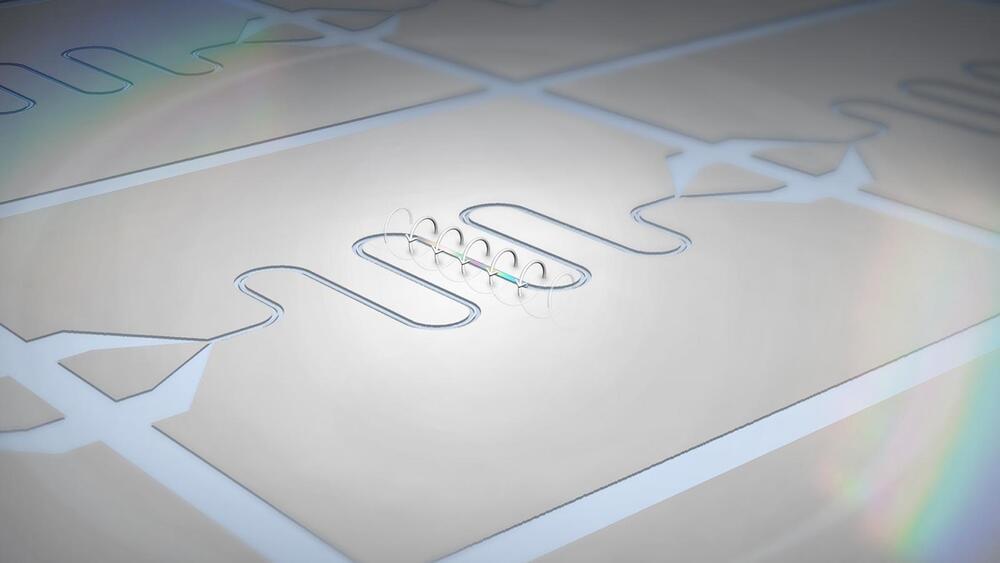
The device uses magnetic fields to carry out computation rather than shuttling electricity around, so it consumes far less power.
In new research from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, scientists have achieved efficient quantum coupling between two distant magnetic devices, which can host a certain type of magnetic excitations called magnons. These excitations happen when an electric current generates a magnetic field. Coupling allows magnons to exchange energy and information. This kind of coupling may be useful for creating new quantum information technology devices.
“Remote coupling of magnons is the first step, or almost a prerequisite, for doing quantum work with magnetic systems,” said Argonne senior scientist Valentine Novosad, an author of the study. “We show the ability for these magnons to communicate instantly with each other at a distance.”
Johannes Kalliauer, a postdoc at the MIT Concrete Sustainability Hub, studies how structures like DNA and bridges relate with Newtonian mechanics.
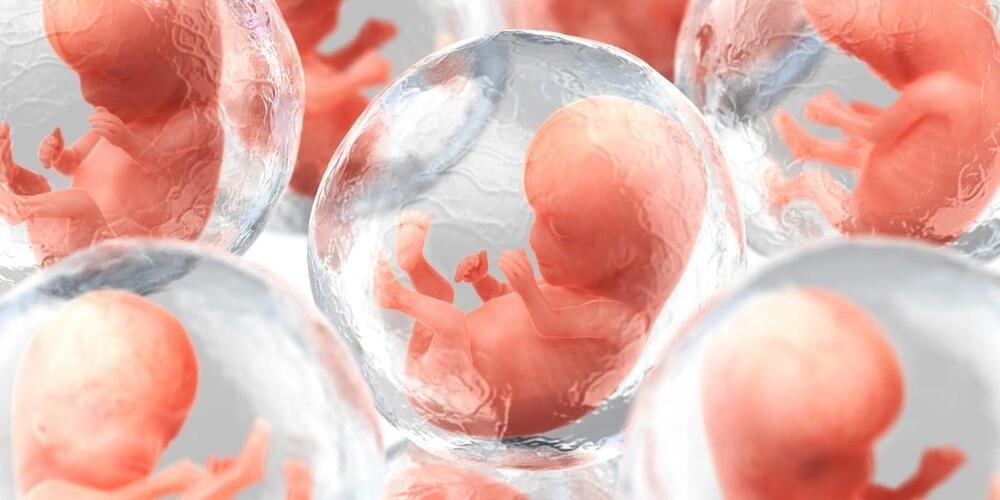
A biotechnology company based in Israel wants to replicate a recent experiment that successfully created an artificial mouse embryo from stem cells — only this time with human cells.
Scientists at Weizmann’s Molecular Genetics Department grew “synthetic mouse embryos” in a jar without the use of sperm, eggs, or a womb, according to a paper published in the journal Cell on August 1. It was the first time the process had been successfully completed, Insider’s Marianne Guenot reported.
The replica embryos could not develop into fully-formed mice and were therefore not “real,” Jacob Hanna, who led the experiment, told the Guardian. However, scientists observed the synthetic embryos having a beating heart, blood circulation, the start of a brain, a neural tube, and an intestinal tract.
Our model of the Universe, dominated by dark matter and dark energy, explains almost everything we see. Almost. Here’s what remains.
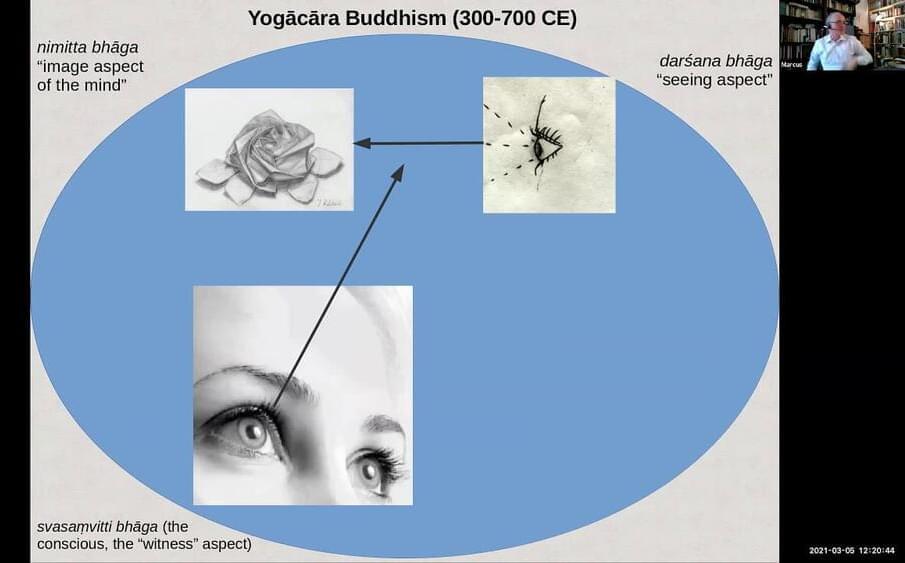
Discussion with Joscha Bach, Marcus Bingenheimer, Pei Wang, and Simon Wiles about Buddhist models of the mind and contemporary research in Artificial General Intelligence.
This event was a Global Studies webinar, co-sponsored by the Science, Technology, and Society CHAT Interdisciplinary Research Group, and the Temple University Libraries. It took place on 2021/03/05.
To view other library event recordings, visit: https://library.temple.edu/watchpastprograms
New video published on our YouTube channel:
New #research published in #experimental #neurology shows evidence that #lsd promotes #memory #neuroplasticity and possibly #neurogenesis.
Abstract linked in the description of the video.
#science.
I believe that these microbes are not just simple organisms but are some sorta biological singularity seeds that activate over millions of years developing life slowly and may be exterrestial in origin.
Researchers from Hokkaido University in Japan have found new evidence that the chemical components necessary to build DNA may have been carried to Earth by carbonaceous meteorites, some of the earliest matter in the solar system, as they report in a study published Tuesday in Nature Communications. Although these kinds of materials make up about 75 percent of all asteroids, they rarely fall to Earth, limiting how often scientists can study them. Yet they are troves of information: Scrutinizing these space rocks can tell stories about unique cosmic locations. Their contents may also help reveal the ancient chemical reactions that made our world a living planet.
Specifically, several meteorites have been found to contain nucleobases. These chemicals, called the building blocks of life, make up the nucleic acids inside DNA and RNA. Of the five major nucleobases, previous meteorite studies detected only three of them, named adenine, guanine, and uracil. But the present research proves for the first time that two more—cytosine and thymine—can exist within space rocks.
“The detection of all primary DNA and RNA nucleobases in meteorites indicates that these molecules have been supplied to the early Earth before the onset of life,” says Yasuhiro Oba, lead author of the study and an associate professor at Hokkaido University. ” In other words, we got information about the inventory of organic molecules related to DNA and RNA before any life arose on the Earth.” One of the oldest specimens in the study clocks in at about 4.6 billion years old, which is even older than the solar system.
My point on this would just be that AI will be able to make anything you want into a game, or movie, or TV episode. And, it can be any length you want; play it as it was intended, or you can change it in any direction you want. with movies and TV i also can see people trying to play interactively as a character in the story. media in 2030s.
The founder and CEO of Midjourney, David Holz, has some truly inspiring views around how AI image generation will transform the gaming industry. During the short time we spoke this week, I had to hold myself back from falling too deep into the AI rabbit hole. In the process, I discovered Holz’s view on how this kind of tech will develop and how it’s likely to benefit the gaming industry, as well as human creativity as a whole.
Holz believes that one day in the near future, “you’ll be able to buy a console with a giant AI chip and all the games will be dreams.”
The word ‘universe’ once described everything that exists. But as our horizons have expanded, many scientists have begun to consider what’s beyond our own cosmos, and…