Traveling to faraway places is a great way to seek out new experiences, but jet lag can be an unpleasant side effect. Adjusting to a new time zone is often accompanied by fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and a host of other problems that can turn an otherwise exciting adventure into a miserable trip.
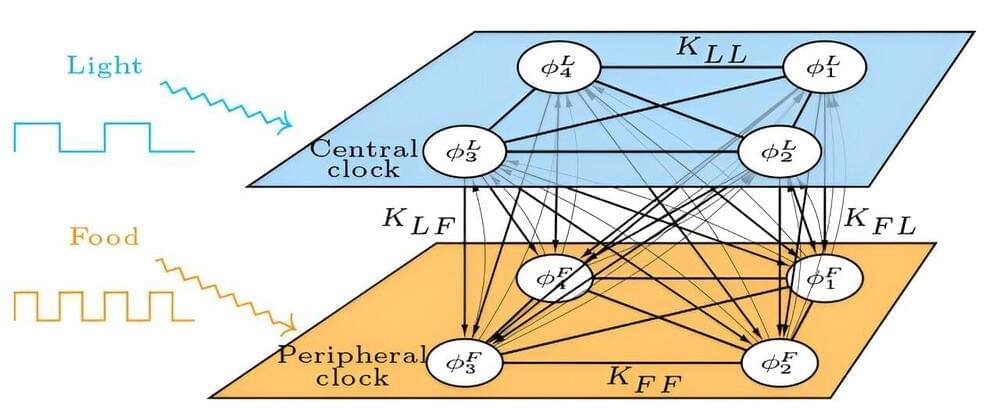
Jet lag is caused by a difference between the circadian system —the body’s internal clock—and the surrounding environment. Around the turn of the century, scientists began to recognize that the body has multiple internal clocks, calibrated in different ways, and that jet lag-like symptoms can result when these clocks drift out of sync with each other. This can happen in several ways and grows more prevalent with age.
A team of scientists from Northwestern University and the Santa Fe Institute developed a theoretical model to study the interactions between multiple internal clocks under the effects of aging and disruptions like jet lag. The article, “A minimal model of peripheral clocks reveals differential circadian re-entrainment in aging,” appeared in the journal Chaos on Sept. 5, 2023.