We humans are obsessed with speed. We bred the fastest horse when we first started riding. We looked for ways to put insanely powerful engines in our cars when we first started building them.


We humans are obsessed with speed. We bred the fastest horse when we first started riding. We looked for ways to put insanely powerful engines in our cars when we first started building them.
A new North Carolina State University study, performed in collaboration with battery testing researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, shows that extremely short pulses from a high-powered laser can cause tiny defects in lithium-ion battery materials—defects that can enhance battery performance.
The technique, called nanosecond pulsed laser annealing, lasts for only 100 nanoseconds and is generated by the same type of laser used in modern-day eye surgeries. Researchers tested the technique on graphite, a material widely used in lithium-ion battery anodes, or positive electrodes. They tested the technique in batches of 10 pulses and 80 pulses and compared the differences in current capacity; power is calculated by multiplying voltage by current.
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in portable electronic devices and electric cars. With further improvements, these batteries could have a major impact on transportation and as storage devices for renewable energy sources like wind and solar.

One of the most interesting stars in the Milky Way is still serving up more than its fair share of intrigue.
In October 2020, SGR 1935+2154, the magnetar responsible for spitting out radio signals never before detected in our home galaxy, unexpectedly slowed down.
Now, scientists believe the rotational slowdown could be evidence of a volcano-like eruption on its surface, spewing material out into space that altered the star’s environment enough to decelerate the spinning of the planet minutely.

A team of researchers has reduced the size of a laser-based mass spectrometer to optimize its use for future life-detection missions.

Experiments reveal a hydrodynamic analog of an important effect in quantum optics called superradiance.
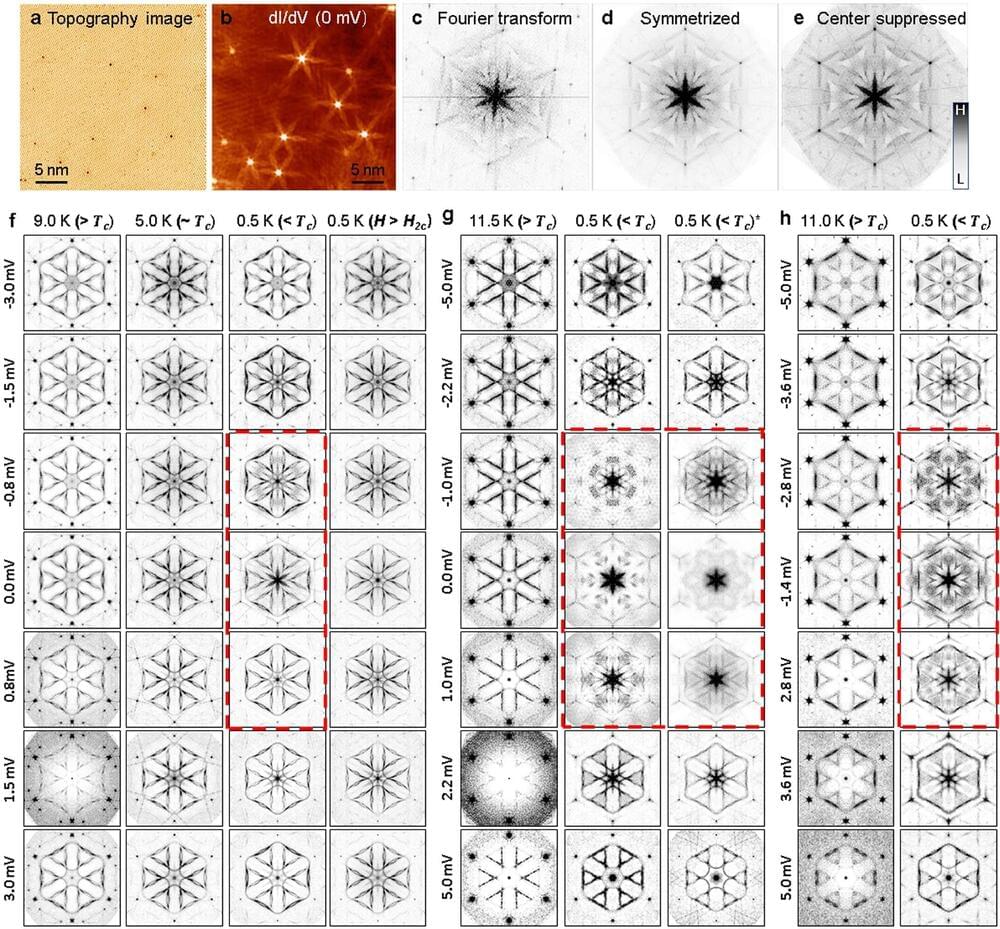
The University of Tennessee’s physicists have led a scientific team that found silicon—a mainstay of the soon-to-be trillion-dollar electronics industry—can host a novel form of superconductivity that could bring rapidly emerging quantum technologies closer to industrial scale production.
The findings are reported in Nature Physics and involve electron theft, time reversal, and a little electronic ambidexterity.
Superconductors conduct electric current without resistance or energy dissipation. Their uses range from powerful electromagnets for particle accelerators and medical MRI devices to ultrasensitive magnetic sensors to quantum computers. Superconductivity is a spectacular display of quantum mechanics in action on a macroscopic scale. It all comes down to the electrons.
A certain amount of noise is inherent in any quantum system. For instance, when researchers want to read information from a quantum computer, which harnesses quantum mechanical phenomena to solve certain problems too complex for classical computers, the same quantum mechanics also imparts a minimum level of unavoidable error that limits the accuracy of the measurements.
Scientists can effectively get around this limitation by using “parametric” amplification to “squeeze” the noise—a quantum phenomenon that decreases the noise affecting one variable while increasing the noise that affects its conjugate partner. While the total amount of noise remains the same, it is effectively redistributed. Researchers can then make more accurate measurements by looking only at the lower-noise variable.
A team of researchers from MIT and elsewhere has now developed a new superconducting parametric amplifier that operates with the gain of previous narrowband squeezers while achieving quantum squeezing over much larger bandwidths. Their work is the first to demonstrate squeezing over a broad frequency bandwidth of up to 1.75 gigahertz while maintaining a high degree of squeezing (selective noise reduction). In comparison, previous microwave parametric amplifiers generally achieved bandwidths of only 100 megahertz or less.
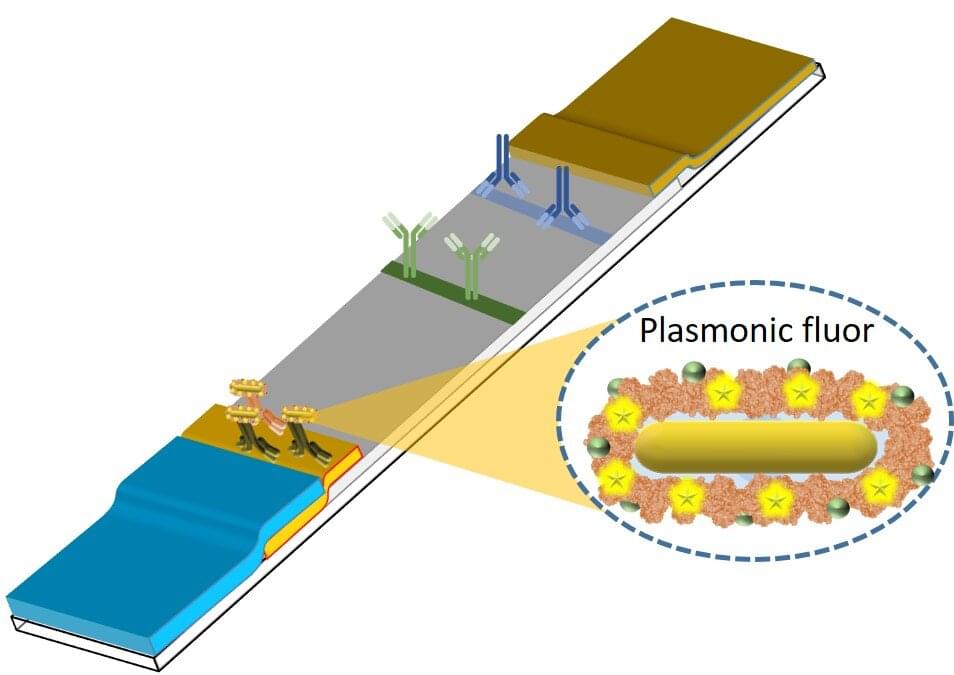
When Srikanth Singamaneni and Guy Genin, both professors of mechanical engineering and materials science at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, established a new collaboration with researchers from the School of Medicine in late 2019, they didn’t know the landscape of infectious disease research was about to shift dramatically. In a conference room overlooking Forest Park on a beautiful fall day, the team had one goal in mind: tackle the biggest infectious disease problem facing the world right then.
“Srikanth and I had a vision of a simple, quantitative diagnostic tool, so we connected with infectious disease physicians here at WashU and asked them, ‘What are the most important questions that could be answered if you could get really detailed information cheaply at the point of care?’” said Genin, the Harold and Kathleen Faught Professor of Mechanical Engineering.
“Greg Storch told us that one of the most important challenges facing the field of infectious disease is finding a way to figure out quickly if a patient has a bacterial infection and should get antibiotics or has a viral infection, for which antibiotics will not be effective.”

In a new Nature Energy study, engineers report progress toward lithium-metal batteries that charge quickly—as fast as an hour. This fast charging is thanks to lithium metal crystals that can be seeded and grown—quickly and uniformly—on a surprising surface. The trick is to use a crystal growing surface that lithium officially doesn’t “like.” From these seed crystals grow dense layers of uniform lithium metal. Uniform layers of lithium metal are of great interest to battery researchers because they lack battery-performance-degrading spikes called dendrites. The formation of these dendrites in battery anodes is a longstanding roadblock to fast-charging ultra-energy-dense lithium-metal batteries.
This new approach, led by University of California San Diego engineers, enables charging of lithium-metal batteries in about an hour, a speed that is competitive against today’s lithium-ion batteries. The UC San Diego engineers, in collaboration with UC Irvine imaging researchers, published this advance aimed at developing fast-charging lithium-metal batteries on Feb. 9, 2023, in Nature Energy.
To grow lithium metal crystals, the researchers replaced the ubiquitous copper surfaces on the negative side (the anode) of lithium-metal batteries with a lithiophobic nanocomposite surface made of lithium fluoride (LiF) and iron (Fe). Using this lithiophobic surface for lithium deposition, lithium crystal seeds formed, and from these seeds grew dense lithium layers—even at high charging rates. The result was long-cycle-life lithium-metal batteries that can be charged quickly.

Scientists are deploying robots on the campus of University of Texas at Austin to see how they interact with the community.