Strategy using genetically engineered T cells would attack cancer while sparing healthy blood stem cells.
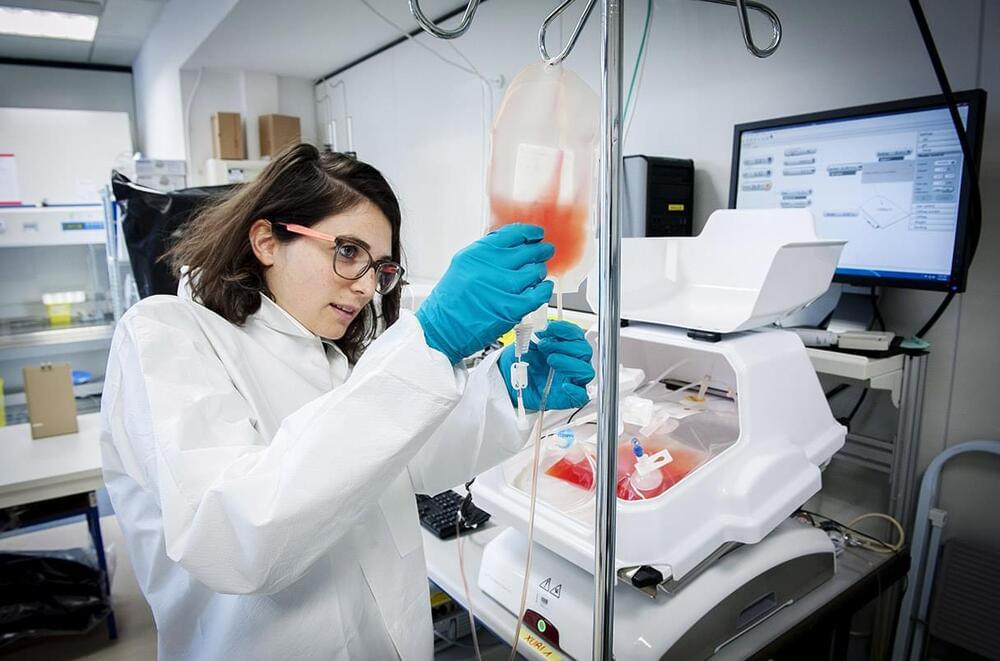


The research paper reviews the potential benefits of marine plasmalogens, a type of glycerophospholipid, in combating age-related diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. These compounds, abundant in marine resources, could improve lipid metabolism and reduce oxidative stress, offering a new avenue for improving the quality of life in aging populations.

Infamous Chisel is described as a collection of multiple components that’s designed with the intent to enable remote access and exfiltrate information from Android phones.
Besides scanning the devices for information and files matching a predefined set of file extensions, the malware also contains functionality to periodically scan the local network and offer SSH access.
“Infamous Chisel also provides remote access by configuring and executing TOR with a hidden service which forwards to a modified Dropbear binary providing a SSH connection,” the Five Eyes (FVEY) intelligence alliance said.

Artificial intelligence (AI) has been helping humans in IT security operations since the 2010s, analyzing massive amounts of data quickly to detect the signals of malicious behavior. With enterprise cloud environments producing terabytes of data to be analyzed, threat detection at the cloud scale depends on AI. But can that AI be trusted? Or will hidden bias lead to missed threats and data breaches?
Bias can create risks in AI systems used for cloud security. There are steps humans can take to mitigate this hidden threat, but first, it’s helpful to understand what types of bias exist and where they come from.
Today marks nine months since ChatGPT was released, and six weeks since we announced our AI Start seed fund. Based on our conversations with scores of inception and early-stage AI founders, and hundreds of leading CXOs (chief experience officers), I can attest that we are definitely in exuberant times.
In the span of less than a year, AI investments have become de rigueur in any portfolio, new private company unicorns are being created every week, and the idea that AI will drive a stock market rebound is taking root. People outside of tech are becoming familiar with new vocabulary.
Large language models. ChatGPT. Deep-learning algorithms. Neural networks. Reasoning engines. Inference. Prompt engineering. CoPilots. Leading strategists and thinkers are sharing their view on how it will transform business, how it will unlock potential, and how it will contribute to human flourishing.


To flourish, one must retain wonder throughout life. Formal education often beats wonder out of us by teaching us that learning is a chore. But learning and experiencing wonder, these represent among the greatest gifts life has to offer.
“While wandering down the path of wonder, I briefly escape the world of separation and enter the world of unity.”


Since its public launch last year, the artificially intelligent chatbot ChatGPT has simultaneously wowed and frightened the world with its deep knowledge, its surprising empathy, and its undeniable potential to change the world in unforeseen, possibly miraculous or calamitous, ways. Now, it’s making it possible to digitally resurrect the dead in the form of chatbots trained on data of the deceased.
Developed by OpenAI, ChatGPT is an AI program called a large language model. Trained on more than 300 billion words from all sorts of sources on the Internet, ChatGPT responds to prompts from humans by predicting the word it should use next based on both its training and the prompt. The result is a stream of communication that’s both informative and human-like. ChatGPT has passed difficult tests, written scientific papers, and convinced many Microsoft scientists that it actually can understand language and utilize reason.
ChatGPT and other large language models can also receive more specific training to shape their responses. Programmer Jason Rohrer realized that he can create chatbots that emulate specific people by feeding ChatGPT examples of how they communicate and details of their lives. He started off with Star Trek’s Mr. Spock, as any good nerd would. He next launched a website called Project December, which allows paying customers to input all sorts of data and information and make their own personalized chatbots, even ones based upon deceased friends and family.
At 14, Anton received an old laptop that changed everything. Now he’s using AI to help himself and others achieve their potential.
Neither keyboards nor voice-to-text work well for Anton, a developer with cerebral palsy. He uses AI and LLMs to pursue his passion for programming and shows others how they can harness these technologies to accomplish more.