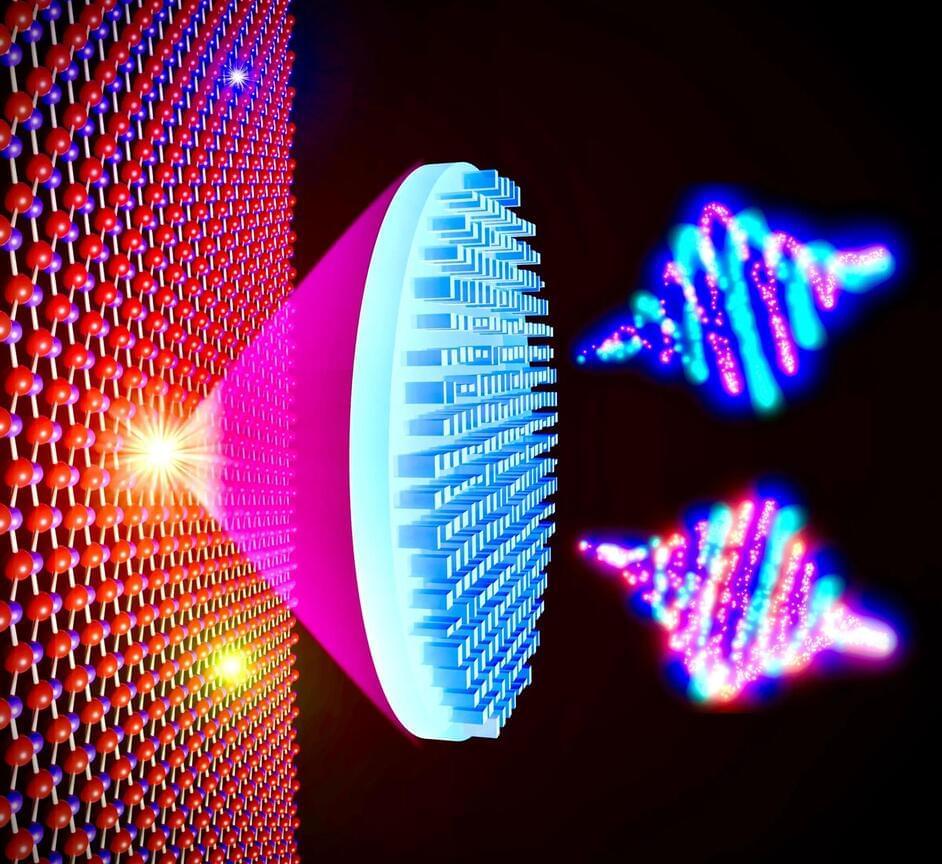
Scientists have developed a multifunctional metalens capable of structuring quantum emissions from single photon.
A photon is a particle of light. It is the basic unit of light and other electromagnetic radiation, and is responsible for the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature. Photons have no mass, but they do have energy and momentum. They travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, and can have different wavelengths, which correspond to different colors of light. Photons can also have different energies, which correspond to different frequencies of light.