Imagine that you have a secret decoder ring that you can use to decipher a secret message with important clues about things around you: where they came from, why they are there, and what will become of them in the future. Now imagine that the secret decoder ring is actually a sensor that can be flown in space to unravel secrets about the matter in the solar system. Where did this matter originate, how did it become energized, and how could it impact humans living on Earth and traveling in space?
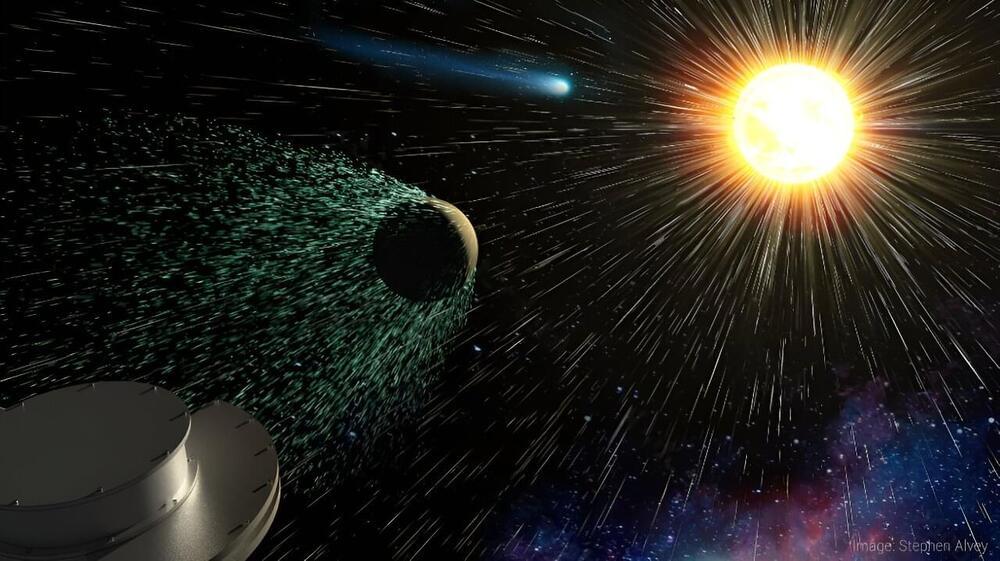
The Solar Wind Pickup Ion Composition Energy Spectrometer (SPICES) is like a decoder ring for the plasma (gas consisting of electrically charged particles) in the solar system. It has the potential to reveal important information about how the sun behaves and interacts with planets and their atmospheres, and how the solar system is impacted by its own motion through interstellar space.
The universe is mostly made of hydrogen, but the elements that make up life as well as the planets, comets, and many other celestial bodies are heavier than hydrogen. In fact, these heavier elements, although not as abundant, can hold the key to understanding how numerous processes in the universe work. In our solar system, these “heavy elements”—which are called “heavy ions” when they are electrically charged—can help us trace plasma to its origin at planets, comets, the sun and solar atmosphere, and even to interstellar space.