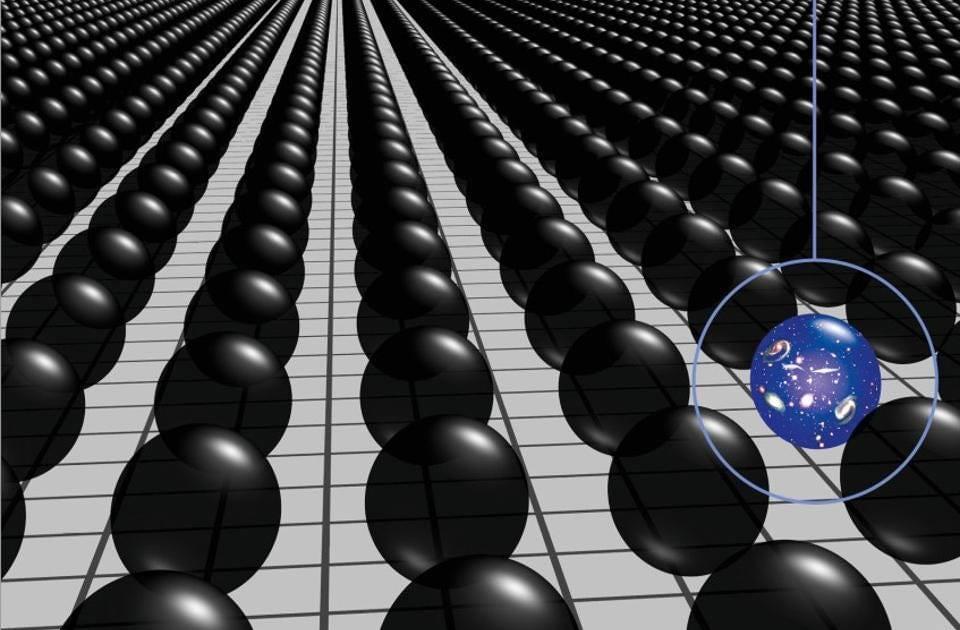
A wild, compelling idea without a direct, practical test, the Multiverse is highly controversial. But its supporting pillars sure are stable.



SpaceX’s Starship can seemingly get Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) clearance for its second flight test as early as next month.
What Happened: “We’re working well with them and have been in good discussions. Teams are working together and I think we’re optimistic sometime next month,” Acting FAA Administrator Polly Trottenberg said on Wednesday, as reported by Reuters.
Earlier this week, CEO Elon Musk confirmed that SpaceX has implemented all the fixes demanded by the FAA for Starship ahead of its second flight test.

Among the ideas discussed was whether there should be an independent agency to oversee certain aspects of the rapidly-developing technology, how companies could be more transparent and how the United States can stay ahead of China and other countries.
“The key point was really that it’s important for us to have a referee,” said Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla and X, during a break in the daylong forum. “It was a very civilized discussion, actually, among some of the smartest people in the world.”
Schumer will not necessarily take the tech executives’ advice as he works with colleagues on the politically difficult task of ensuring some oversight of the burgeoning sector. But he invited them to the meeting in hopes that they would give senators some realistic direction for meaningful regulation.

Meta is reportedly planning to train a new model that it hopes will be as powerful as OpenAI’s latest and greatest chatbot.
Meta has been snapping up AI training chips and building out data centers in order to create a more powerful new chatbot it hopes will be as sophisticated as OpenAI’s GPT-4, according to * The Wall Street Journal.* The company reportedly plans to begin training the new large language model early in 2024, with CEO Mark Zuckerberg evidently pushing for it to once again be free for companies to create AI tools with.
The *Journal *writes that Meta has been buying more Nvidia H100 AI-training chips and is beefing up its infrastructure so that, this time around, it won’t need to rely on Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform to train the new chatbot. The company reportedly assembled a group earlier this year to build the model, with the goal of speeding up the creation of AI tools that can emulate human expressions. company aims to release its new model next year.
The versatile robot will help create a virtual representation of the facilities.
In a first for the UK’s National Trust, Boston Dynamics’ robotic dog Spot is being used to survey two Cold War weapons testing sites located in Orford Ness, Suffolk.
This is according to a report by the *BBC* published on Thursday.
Spot, a versatile quadruped robot, has drawn a lot of interest as well as clients in recent years for its cutting-edge capabilities and its many potential uses.
## Efficiency and speed.
The machine has been designed to tackle a variety of tasks with efficiency and speed. Its lightweight and agile design allow it to navigate rough terrains, climb stairs, and function effectively both indoors and outdoors.
Spot can change its speed and posture to adjust to different environments, can execute dynamic movements and can trot, walk, and crawl.
Naked mole rats are rodents that are about the size of a mouse with a key difference, aside from having no fur — they’re extremely long-lived — reaching ages of around 40 years old. For comparison, lab mice live an average of about three and a half years. To explain their extensive lifespans, researchers have sought to pinpoint how naked mole rats evade the onset of age-related diseases like cancer. In doing so, they’ve identified a form of gelatinous substance called hyaluronan, which has anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties. Now, the question of whether the benefits of the naked mole rat’s abundant levels of this form of hyaluronan — called high molecular mass hyaluronic acid (HMM-HA) — can be exported to other species has recently drawn attention.
Published in Nature, Gorbunova and colleagues from the University of Rochester show that genetically modifying mice to harbor an enzyme that produces HMM-HA extends their lifespan. The researchers go on to show that increasing HMM-HA reduces the prevalence of cancer. Additionally, the nmrHAS2 gene improves the healthspan of mice by countering physiological dysfunction, as measured with a frailty score. These findings provide the first evidence that genes from long-lived species can be exported to other species, perhaps conferring benefits to humans one day.
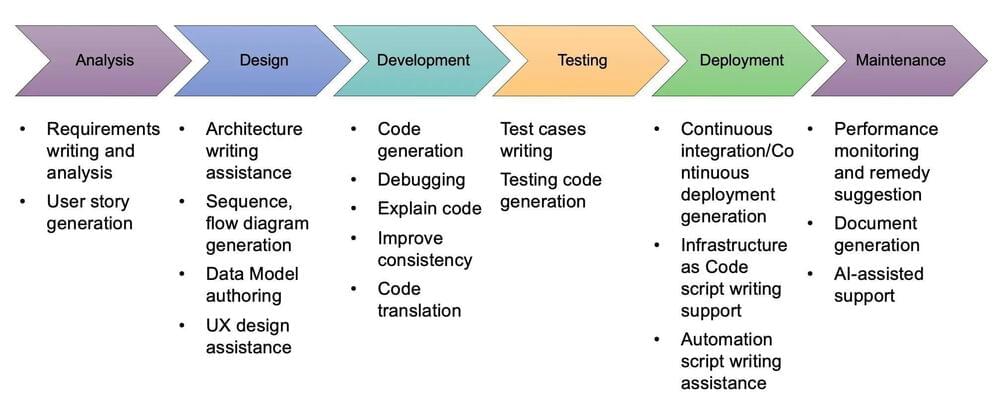
“Here is how Generative AI can help in the Overall Generative AI in Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) stages. Overall, we want to treat Generative AI as senior developer/architect with more accessibility.
- Requirements gathering: ChatGPT can significantly simplify the requirements gathering phase by building quick prototypes of complex applications. It also can minimize the risks of miscommunication in the process since the analyst and customer can align on the prototype before proceeding to the build phase.
- Design: DALL-E, another deep learning model developed by OpenAI to generate digital images from natural language descriptions, can contribute to the design of applications. In addition to providing user interface (UI) templates for common use cases, it also may eventually be deployed to ensure that the design of a given application meets regulatory criteria such as accessibility.
- Build: ChatGPT has the capability to generate code in different languages. It could be used to supplement developers by writing small components of code, thus enhancing the productivity of developers and software quality. It even can enable citizen developers to write code without the knowledge of programming language.
- Test: ChatGPT has a major role in the testing phase. It can be used to generate various test cases and to test the application just by giving prompts in natural language. It can be leveraged to fix any vulnerabilities that could be identified through processes such as Dynamic Code Analysis (DCA) and perform chaos testing to simulate worst-case scenarios to test the integrity of the application in a faster and cost-effective way.
- Maintenance: ChatGPT can significantly improve First Contact Resolution (FCR) by helping clients with basic queries. In the process, it ensures that issue resolution times are significantly reduced while also freeing up service personnel to focus their attention selectively on more complex cases.
https://medium.com/mlearning-ai/generative-ai-in-software-de…90e466eb91
