The apparent equivalence of gravitational mass to inertial mass is a remarkable and beautiful feature of the cosmos, with a deep implication, says Chanda Prescod-Weinstein


The apparent equivalence of gravitational mass to inertial mass is a remarkable and beautiful feature of the cosmos, with a deep implication, says Chanda Prescod-Weinstein

Everyone knows that arithmetic is true: 2 + 2 = 4.
But surprisingly, we don’t know why it’s true.
By stepping outside the box of our usual way of thinking about numbers, my colleagues and I have recently shown that arithmetic has biological roots and is a natural consequence of how perception of the world around us is organised.

A study that peered into live mouse brains suggests for nearly 70 years we’ve been targeting the wrong neurons in our design of antipsychotic drugs.
Untangling the vast web of brain cells and determining how drugs work upon them is a tough task. Using a miniature microscope and fluorescent tags, a team of researchers led by Northwestern University neuroscientist Seongsik Yun discovered that effective antipsychotic drugs cling to a different type of brain cell than scientists originally thought.
Just like research suggesting depression might not be a chemical imbalance in serotonin levels, our understanding of schizophrenia treatments may need a rethink if widely-used antipsychotics are targeting different neurons than expected.

Computer simulations confirm that the African Superplume causes the unusual deformations and rift-parallel seismic anisotropy detected below the East African Rift System.
Continental rifting involves a combination of stretching and fracturing that penetrates deep within the Earth, explains geophysicist D. Sarah Stamps. This process pertains to the elongation of the lithosphere, Earth’s rigid outer layer. As it becomes more taut, the lithosphere’s upper sections undergo brittle changes, leading to rock fractures and earthquakes.
Stamps, who studies these processes by using computer modeling and GPS.
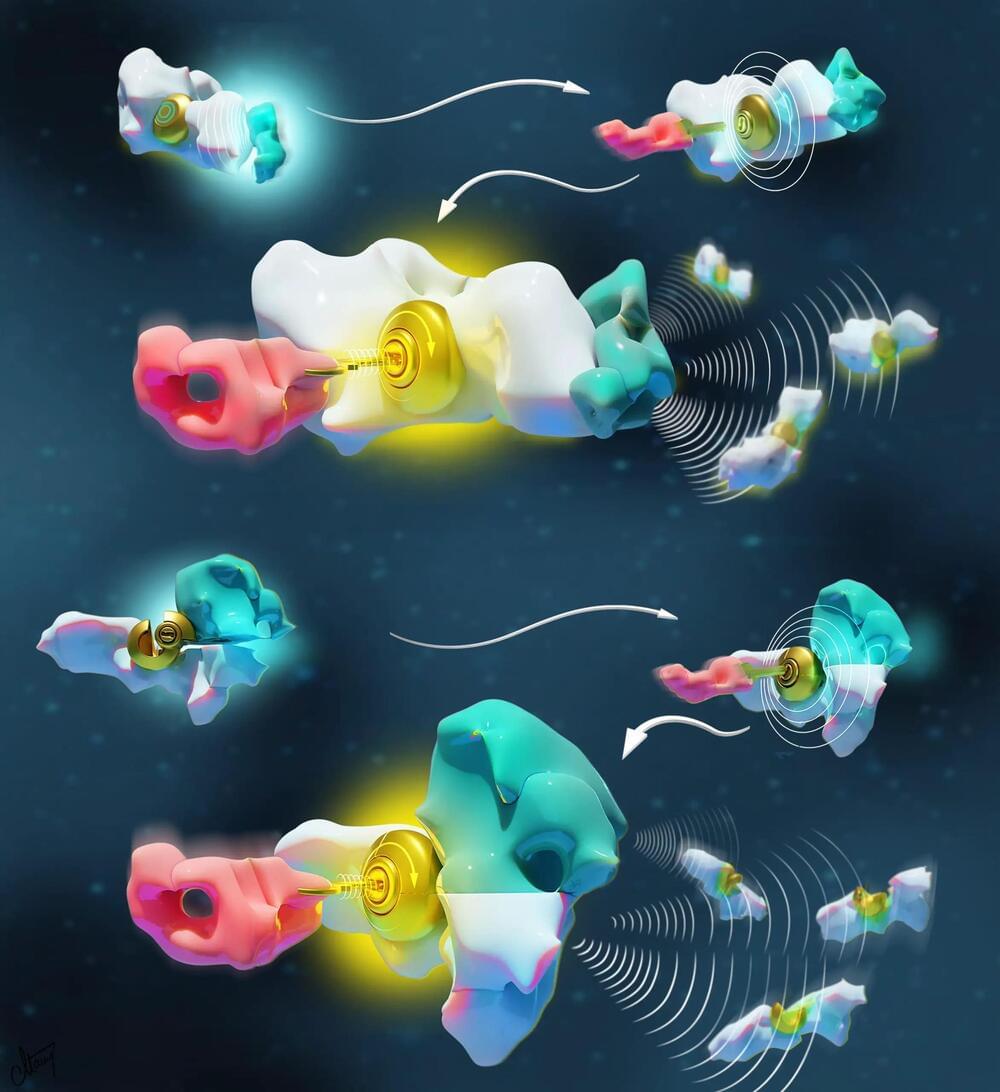
Canadian researchers at the University of Montreal have successfully recreated and mathematically confirmed two molecular languages at the origin of life.
Their groundbreaking findings, recently published in the Journal of American Chemical Society, pave the way for advancements in nanotechnologies, offering potential in areas like biosensing, drug delivery, and molecular imaging.
Living organisms are made up of billions of nanomachines and nanostructures that communicate to create higher-order entities able to do many essential things, such as moving, thinking, surviving, and reproducing.

Psychedelics are known for inducing altered states of consciousness in humans by fundamentally changing our normal pattern of sensory perception, thought and emotion. Research into the therapeutic potential of psychedelics has increased significantly in the last decade.
While this research is important, I have always been more intrigued by the idea that psychedelics can be used as a tool to study the neural basis of human consciousness in laboratory animals. We ultimately share the same basic neural hardware with other mammals, and possibly some basic aspects of consciousness, too. So by examining what happens in the brain when there’s a psychedelically induced change in conscious experience, we can perhaps glean insights into what consciousness is in the first place.
We still don’t know a lot about how the networks of cells in the brain enable conscious experience. The dominating view is that consciousness somehow emerges as a collective phenomenon when the dispersed information processing of individual neurons (brain cells) is integrated as the cells interact.
Elon Musk delves into the groundbreaking potential of Neuralink, a revolutionary venture aimed at interfacing with the human brain to tackle an array of brain-related disorders. Musk envisions a future where Neuralink’s advancements lead to the resolution of conditions like autism, schizophrenia, memory loss, and even spinal cord injuries.
Elon Musk discusses the transformative power of Neuralink, highlighting its role in restoring motor control after spinal cord injuries, revitalizing brain function post-stroke, and combating genetically or trauma-induced brain diseases. Musk’s compelling insights reveal how interfacing with neurons at an intricate level can pave the way for repairing and enhancing brain circuits using cutting-edge technology.
Discover the three-layer framework Musk envisions: the primary layer akin to the limbic system, the more intelligent cortex as the secondary layer, and the potential tertiary layer where digital superintelligence might exist. Musk’s thought-provoking perspective raises optimism about the coexistence of a digital superintelligence with the human brain, fostering a harmonious relationship between these layers of consciousness.
Elon Musk emphasises the urgency of Neuralink’s mission, stressing the importance of developing a human brain interface before the advent of digital superintelligence and the elusive singularity. By doing so, he believes we can mitigate existential risks and ensure a stable future for humanity and consciousness as we navigate the uncharted territories of technological evolution.
For more insights, visit EM360tech.com:
https://em360tech.com/tech-news.
#AI #superintelligence #machinelearning.
Researchers have found in a new study that statin use was associated with significant reduction in the risk of osteoporotic fractures among general older population.
Research author Dr Seo said, “Statin users experienced a decline in risk of major osteoporotic fractures, hip fractures and vertebral fractures.”
The study has been published in Osteoporosis International entitled Age-and dose-dependent effect of statin use on the risk of osteoporotic fracture in older adults.