Computer science professor Fernanda Viégas believes “dashboards” that disclose AI models’ biases can help laypeople control AI.






Two recent studies due to be presented as posters at the American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2023 between November 11–13 examine how frequent cannabis use could potentially lead to increased chances of cardiology issues, including heart attack, stroke, or heart failure. These studies were conducted by an international team of researchers and holds the potential to help scientists, medical professionals, and the public better understand the long-term health risks associated with cannabis use, specifically pertaining to cardiovascular concerns.
For the first study, which was conducted by the All of Us Research Program, researchers enlisted 156,999 participants who had not experienced heart failure at the time of the study’s enrollment to take part in a survey-based study to evaluate their cannabis use habits and conduct a follow-up survey 45 months later. The results indicated that heart failure emerged with 2,958 (1.88 percent) of the participants during the 48-month study period along with a 34 percent increased risk of emerging heart failure for participants were reported daily cannabis use compared to participants who didn’t use cannabis.
“Our results should encourage more researchers to study the use of marijuana to better understand its health implications, especially on cardiovascular risk,” said Dr. Yakubu Bene-Alhasan, who is a resident physician at Medstar Health and lead author of the study. “We want to provide the population with high-quality information on marijuana use and to help inform policy decisions at the state level, to educate patients and to guide health care professionals.”

In 2008, Dr. Eben Alexander contracted a rare case of bacterial meningitis. As the pathogen wracked his brain, causing it to swell and suffuse with pus, Alexander entered a deep coma. He was not expected to survive. But live he did, and with a tale to tell. For in Alexander’s stricken state, he underwent a near-death experience, a profound out-of-body event. Four years later, the neurosurgeon detailed it in a best-selling book.
“I had no real center of consciousness,” he wrote. “I didn’t know who or what I was or even if I was simply… there, a singular awareness in the midst of a soupy, dark, muddy nothingness…”
More recently, Alexander’s popular account of his near-death experience attracted the attention of Pascal Michael, a PhD student in psychology at the University of Greenwich. Michael met Alexander after seeing him speak at an academic conference and was informed that Alexander had experimented with 5-MeO-DMT, a psychedelic closely related to DMT, secreted from the glands of the Colorado River toad.
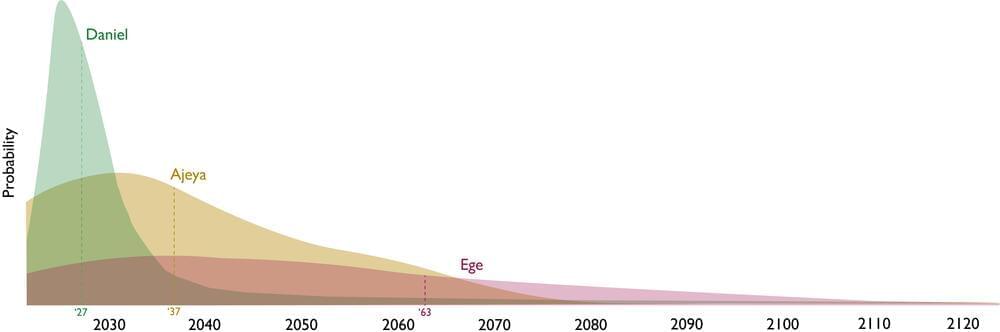
How many years will pass before transformative AI is built? Three people who have thought about this question a lot are Ajeya Cotra from Open Philanthropy, Daniel Kokotajlo from OpenAI and Ege Erdil from Epoch. Despite each spending hundreds of hours investigating this question, they still still disagree substantially about the relevant timescales. For instance, here are their median timelines for one operationalization of transformative AI:
You can see the strength of their disagreements in the graphs below, where they give very different probability distributions over two questions relating to AGI development.
So I invited them to have a conversation about where their disagreements lie, sitting down for 3 hours to have a written dialogue. You can read the discussion below, which I personally found quite valuable.

Apple is developing custom batteries with significantly improved performance that it aims to bring to its devices starting in 2025, ETNews reports.
Apple’s custom battery technology has reportedly been in the works since 2018, with the company actively seeking patents and hiring new personnel related to the project. The company is reportedly seeking to create an “all-new” kind of battery with significantly improved performance by becoming directly involved in its use of materials.