Graham Cooks and his team at Purdue University have discovered a chemical process that has exciting implications for people who believe that life could have emerged spontaneously and through natural means. The idea that the building blocks of life started in a primordial ocean now has a competitor: airborne tiny water droplets.
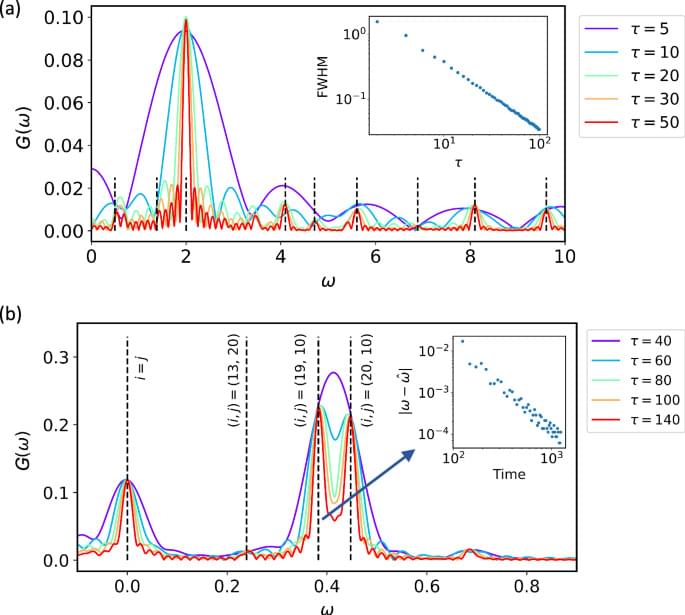
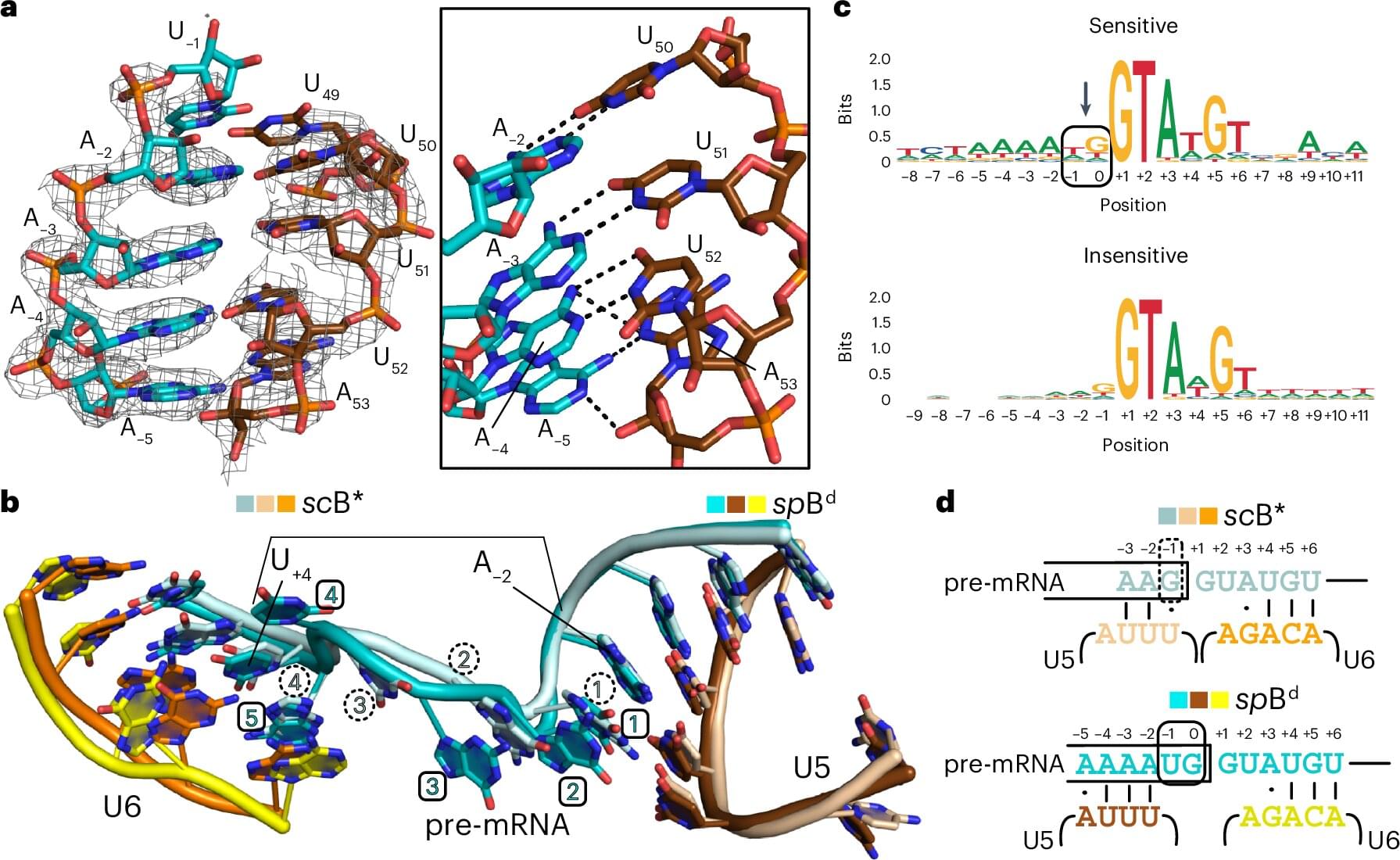
Estimating spectral features of quantum many-body systems has attracted great attention in condensed matter physics and quantum chemistry. To achieve this task, various experimental and theoretical techniques have been developed, such as spectroscopy techniques1,2,3,4,5,6,7 and quantum simulation either by engineering controlled quantum devices8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16 or executing quantum algorithms17,18,19,20 such as quantum phase estimation and variational algorithms. However, probing the behaviour of complex quantum many-body systems remains a challenge, which demands substantial resources for both approaches. For instance, a real probe by neutron spectroscopy requires access to large-scale facilities with high-intensity neutron beams, while quantum computation of eigenenergies typically requires controlled operations with a long coherence time17,18. Efficient estimation of spectral properties has become a topic of increasing interest in this noisy intermediate-scale quantum era21.
A potential solution to efficient spectral property estimation is to extract the spectral information from the dynamics of observables, rather than relying on real probes such as scattering spectroscopy, or direct computation of eigenenergies. This approach capitalises on the basics in quantum mechanics that spectral information is naturally carried by the observable’s dynamics10,20,22,23,24,25,26. In a solid system with translation invariance, for instance, the dynamic structure factor, which can be probed in spectroscopy experiments7,26, reaches its local maximum when both the energy and momentum selection rules are satisfied. Therefore, the energy dispersion can be inferred by tracking the peak of intensities in the energy excitation spectrum.
That statement, now signed by twice as many concerned citizens, warned about the risk of human extinction from AI, which was perhaps a bit of an overreach, because … well, extinction? Come on! That’s just a movie with Arnold Schwarzenegger.
What they should have warned about was jobs — the redundancy and destitution of most of humanity, unless there’s some kind of universal income funded by taxes on robots.
What no-one talks about, as the AI revolution unfolds in stock market hype and scientific gung-ho, is what they’re all really trying to do.
Ibogaine—a psychoactive plant derivative—has attracted attention for its anti-addictive and anti-depressant properties. But ibogaine is a finite resource, extracted from plants native to Africa like the iboga shrub (Tabernanthe iboga) and the small-fruited voacanga tree (Voacanga africana). Further, its use can lead to irregular heartbeats, introducing safety risks and an overall need to better understand how its molecular structure leads to its biological effects.
In a study appearing in Nature Chemistry, researchers at the University of California, Davis Institute for Psychedelics and Neurotherapeutics (IPN) report the successful total synthesis of ibogaine, ibogaine analogs and related compounds from pyridine—a relatively inexpensive and widely available chemical.
The team’s strategy enabled the synthesis of four naturally occurring ibogaine-related alkaloids as well as several non-natural analogs. Overall yields ranged from 6% to 29% after only six or seven steps, a marked increase in efficiency from previous synthetic efforts to produce similar compounds.
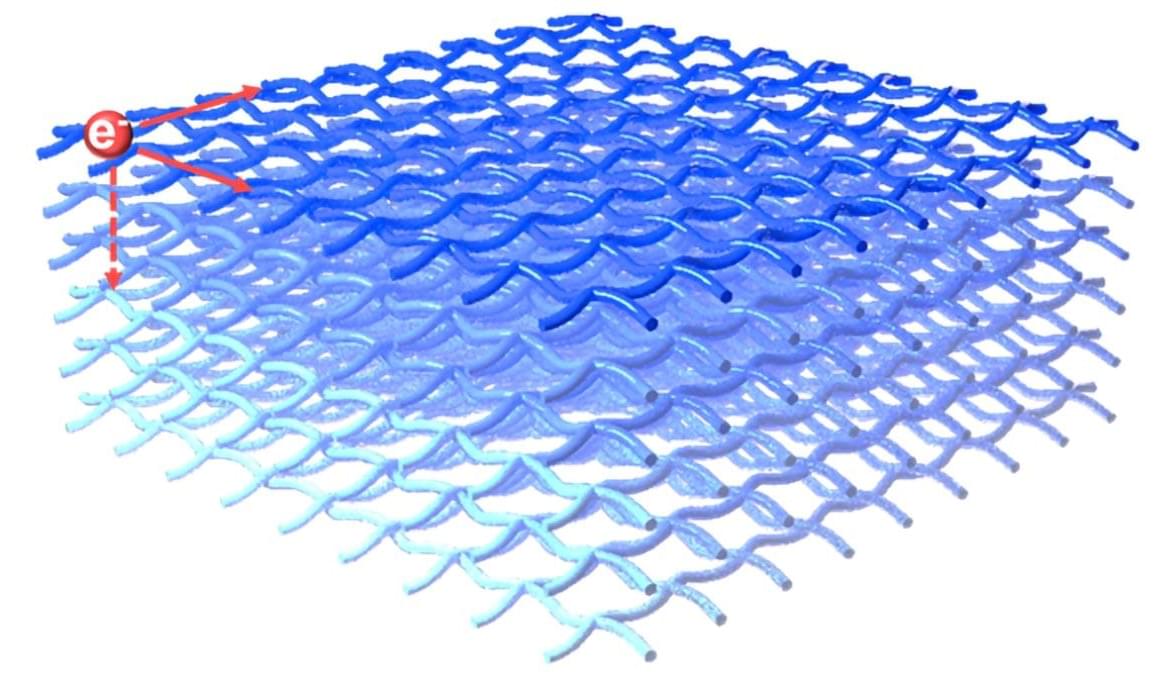
Engineering researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have achieved breakthroughs in multi-material 3D printing through the power of capillary action. The LLNL team printed lattice structures with a series of custom-designed unit cells to selectively absorb fluid materials and precisely direct them into patterns – making it possible to fabricate complex structures with unprintable materials or materials with vastly different properties.
According to the researchers, the technique, featured in Advanced Materials Technologies, would help engineers design and optimize structures for properties like extreme strength-to-weight ratios, large surface areas, or precision deformation.
“By decoupling some of the printing and patterning techniques, you could achieve some complex multi-material structures, and you wouldn’t always have to be able to print the material,” said Hawi Gemeda, Materials Engineering Division (MED) staff engineer at LLNL and the paper’s lead author.
Imagine a world where the act of observation itself holds the key to solving our most complex problems, a world where the very fabric of reality becomes a canvas for computation. This is the tantalizing promise of Observational Computation (OC), a radical new paradigm poised to redefine the very nature of computation and our understanding of the universe itself.
Forget silicon chips and algorithms etched in code; OC harnesses the enigmatic dance of quantum mechanics and the observer effect, where the observer and the observed are inextricably intertwined. Instead of relying on traditional processing power, OC seeks to translate computational problems into carefully crafted observer-environment systems. Picture a quantum stage where potential solutions exist in a hazy superposition, like ghostly apparitions waiting for the spotlight of observation to solidify them into reality.
By meticulously designing these “observational experiments,” we can manipulate quantum systems, nudging them towards desired outcomes. This elegant approach offers tantalizing advantages over our current computational methods. Imagine harnessing the inherent parallelism of quantum superposition for exponentially faster processing, or tapping into the natural energy flows of the universe for unprecedented energy efficiency.
A complex molecular machine, the spliceosome, ensures that the genetic information from the genome, after being transcribed into mRNA precursors, is correctly assembled into mature mRNA. Splicing is a basic requirement for producing proteins that fulfill an organism’s vital functions. Faulty functioning of a spliceosome can lead to a variety of serious diseases.
Researchers at the Heidelberg University Biochemistry Center (BZH) have succeeded for the first time in depicting a faulty “blocked” spliceosome at high resolution and reconstructing how it is recognized and eliminated in the cell. The research was published in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology.
The genetic information of all living organisms is contained in DNA, with the majority of genes in higher organisms being structured in a mosaic-like manner. So the cells are able to “read” the instructions for building proteins stored in these genetic mosaic particles, they are first copied into precursors of mRNA, or messenger RNA. The spliceosome then converts them into mature, functional mRNA.
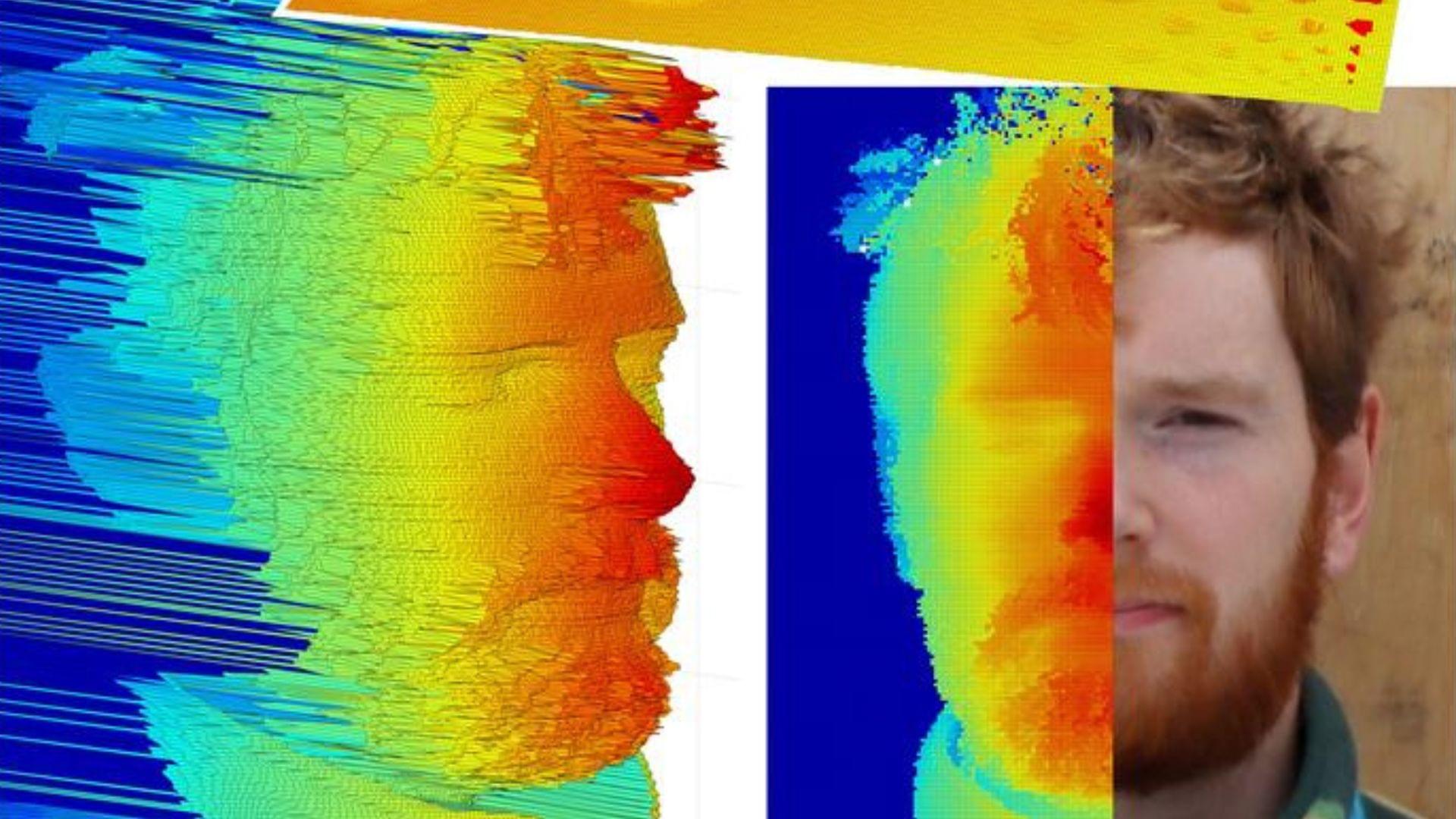
LiDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, works by measuring the time it takes for a laser pulse to travel to an object and back. This time-of-flight measurement reveals the distance, and by scanning across an area, a 3D image is created.
This new tech utilizes a superconducting nanowire single-photon detector (SNSPD), an ultrasensitive detector developed by the MIT and NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
A research team has developed a revolutionary two-dimensional polyaniline (2DPANI) crystal that overcomes major conductivity limitations in polymers. Its unique multilayered structure allows metallic charge transport, setting the stage for new applications in electronics and materials science.
An international team of researchers has successfully created a multilayered two-dimensional polyaniline (2DPANI) crystal, demonstrating exceptional conductivity and a unique ability to transport charge in a metallic-like manner. Their findings were published on February 5 in Nature.