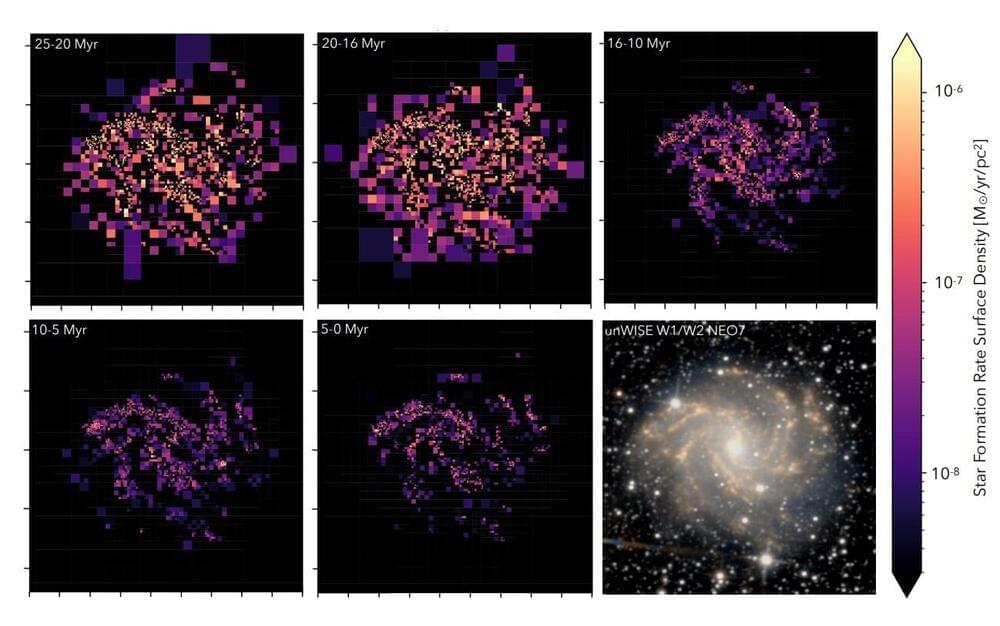
Astronomers from the University of Washington in Seattle and elsewhere have conducted Hubble Space Telescope (HST) observations of the nearby Fireworks Galaxy. Results of the observational campaign, presented July 10 on the preprint server arXiv, yield crucial insights into the recent star formation history of this galaxy.
Discovered in 1,798, the Fireworks Galaxy (also known as NGC 6946) is a nearby face-on star forming spiral galaxy located some 25.5 million light years away. The galaxy has a size of 87,300 light years and its name was coined due to an unusually large number of supernovae observed in it—about ten times more than in the Milky Way.
Although many studies of the Fireworks Galaxy have been conducted to date, its star formation rate (SFR) is not well constrained, estimated to be between three and 12 solar masses per year. This discrepancy is mainly due to the diverse methods of measuring star formation rate and the wide range of different distances used.