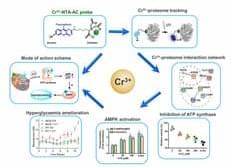
Recently, a research team led by Professor Hongzhe SUN from the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, The University of Hong Kong, has published a paper in Nature Communications.
The researchers found that, chromium(III) (Cr(III)), a nutritional supplement, can enhance cells’ ability to metabolise glucose by regulating ATP synthase activity. This process improves mitochondrial deformation caused by high glucose levels and significantly boosts glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic mice. To uncover the protein targets of Cr(III) and elucidate the molecular mechanism, the team has developed a fluorescent probe for detecting transient metal-protein interactions, achieving a high spatiotemporal resolution tracking of the Cr(III) proteome in HepG2 cells. This led to the identification of Cr(III)-binding proteins within cells. The team then revealed that Cr(III) replaces magnesium ions (Mg2+) in ATP synthase, reduces ATP synthase activity, and activates the downstream AMPK pathway, resulting in improved glucose metabolism. This study provides a novel concept for hypoglycaemic research.
“Although Cr(III) compounds have long been used as a nutritional supplement for diabetes treatment, weight loss and muscle development, its protein target and mechanism of action remain concealed for over half a century. We used a novel fluorescent probe, along with other chemical biology approaches, to uncover the long-standing scientific problem of the biological chemistry of Cr(III) and discovered that Cr(III) targets ATP synthase to regulate glucose,” commented Professor Sun.