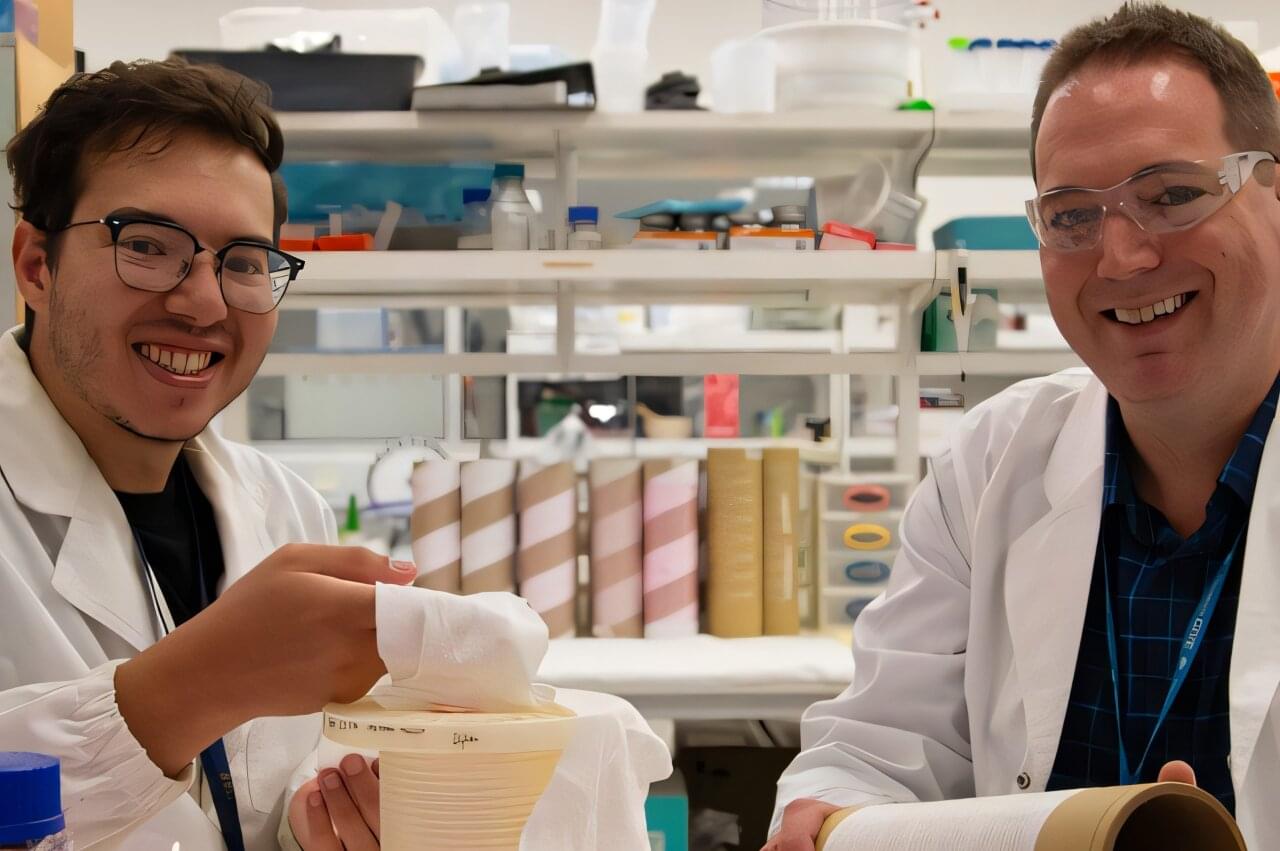
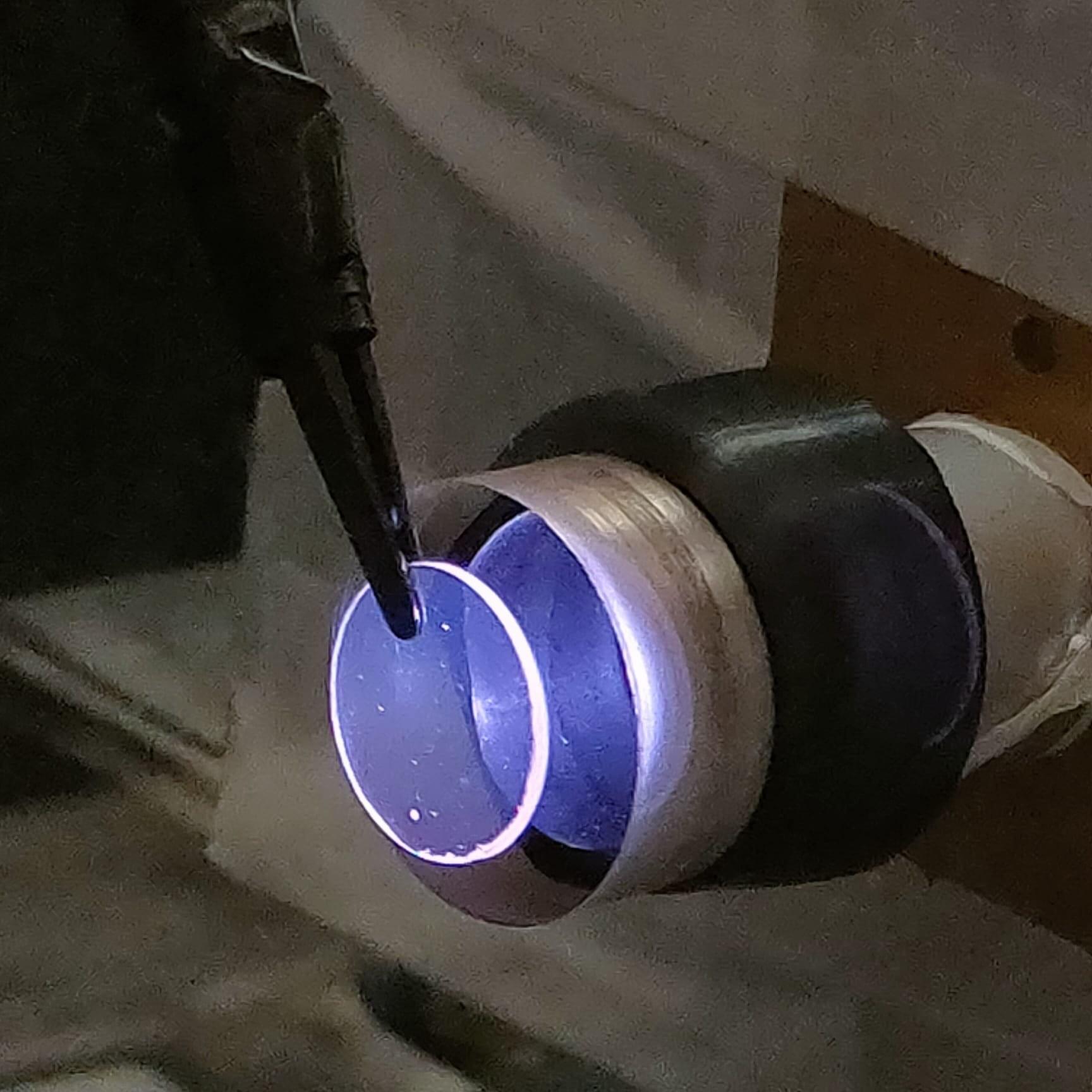
Dr. Ben Allardyce and Ph.D. candidate Mr. Martin Zaki from Deakin’s Institute for Frontier Materials (IFM) have delivered a world first in next-generation materials research. Silkworm silk is a protein-based fiber with mechanical properties rivaling petroleum-derived synthetic fibers, yet spun using a fraction of the energy. Despite decades of research, aspects of natural silkworm spinning remain a mystery.
Published in Advanced Materials, the IFM discovery takes researchers one step closer to solving this mystery by wet-spinning a new class of silk that produces fibers that outperform natural silk.
This research, led by Dr. Allardyce and Mr. Zaki, with expert input from Sheffield University’s Professor Chris Holland, involves sidestepping degumming—a commonplace industrial process—and experimenting with dissolving whole silk fibers.