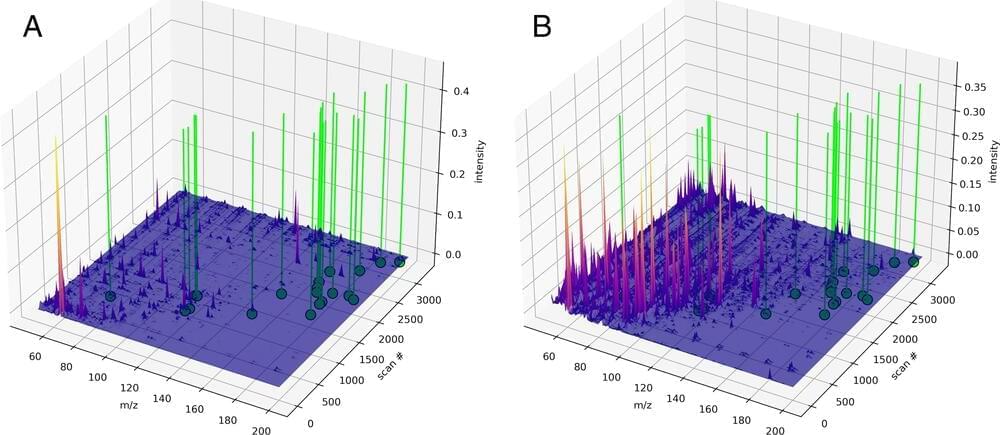
The search for definitive biosignatures—unambiguous markers of past or present life—is a central goal of paleobiology and astrobiology. We used pyrolysis–gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry to analyze chemically disparate samples, including living cells, geologically processed fossil organic material, carbon-rich meteorites, and laboratory-synthesized organic compounds and mixtures. Data from each sample were employed as training and test subsets for machine-learning methods, which resulted in a model that can identify the biogenicity of both contemporary and ancient geologically processed samples with ~90% accuracy. These machine-learning methods do not rely on precise compound identification: Rather, the relational aspects of chromatographic and mass peaks provide the needed information, which underscores this method’s utility for detecting alien biology.