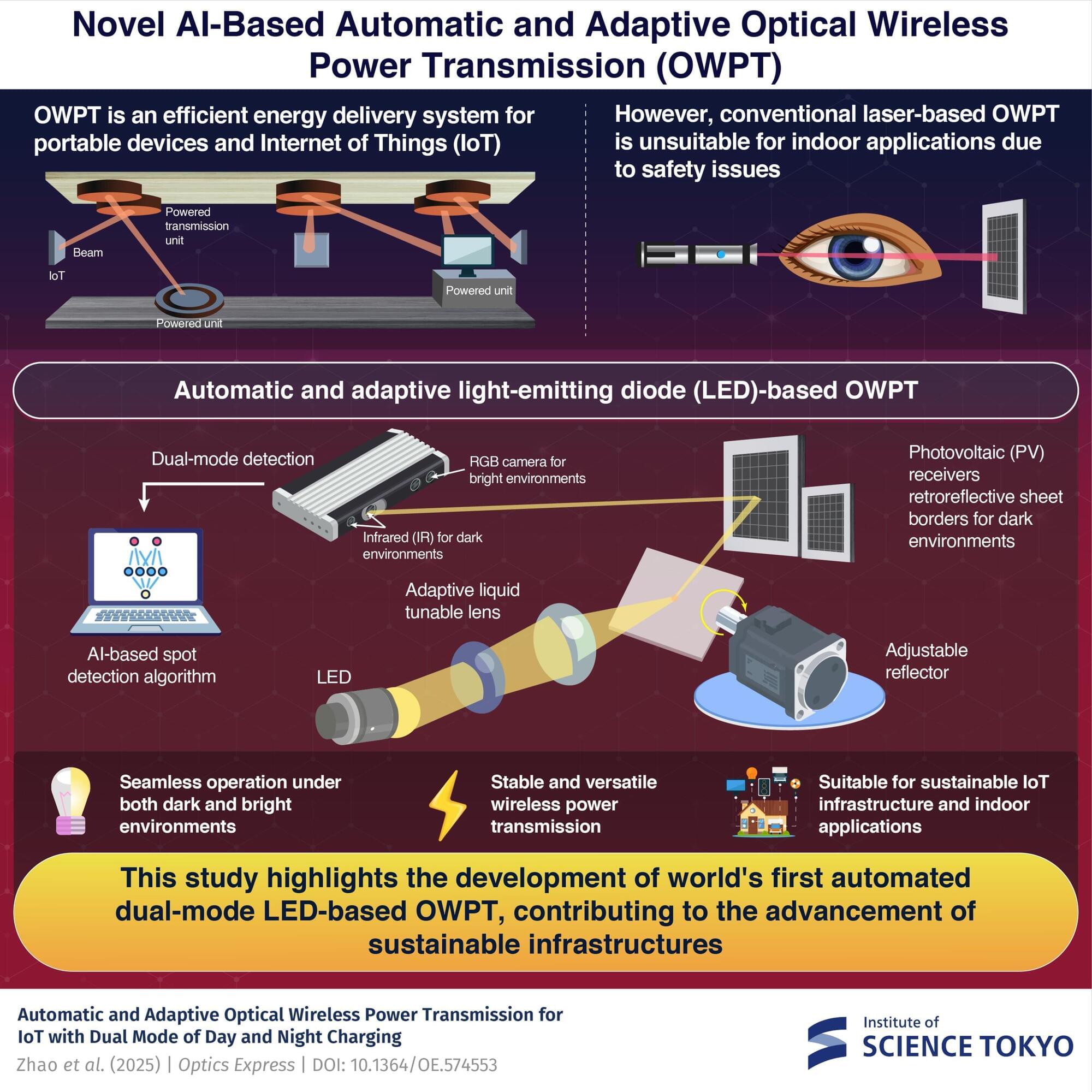
The world’s first automatic and adaptive, dual-mode light-emitting diode (LED)-based optical wireless power transmission system, that operates seamlessly under both dark and bright lighting conditions, has been developed by scientists at Science Tokyo. The system, along with artificial intelligence-powered image recognition, can efficiently power multiple devices in order without interruption. Because it is LED-based, it offers a low-cost and safe solution ideal for building sustainable indoor Internet of Things infrastructure.
With the rapid development of Internet of Things (IoT), the demand for efficient and flexible power solutions is also increasing. Traditional power delivery methods, such as batteries and cable connections, have many drawbacks. Batteries need frequent charging and replacement, while cables restrict device mobility.
Optical wireless power transmission (OWPT) is an emerging technology that can address these limitations. In OWPT, energy is transmitted through free space, without physical wires, by converting electricity to light, transmitting it, and then reconverting light back into electrical power using photovoltaic (PV) receivers.