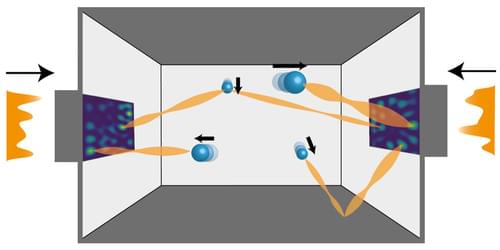
Researchers predict that the “scattering matrix” of a collection of particles could be used to slow the particles down, potentially allowing for the cooling of significantly more particles than is possible with current techniques.
When light travels through an environment containing many particles, information about the collective motion of the particles gets added to the light. This information leaves a measurable signature on a quantity known as the scattering matrix. Now researchers from the Vienna University of Technology predict that the information in this matrix could be used to alter the speeds of the particles [1, 2]. The team says that, if experimentally realized, the technique could allow scientists to study the collective quantum behavior of more particles than is possible with current techniques.
Researchers have long been fascinated with using light to slow down or even freeze the motion of a collection of particles. One motivation is that cooled particles can be isolated from outside influences in order to study quantum behaviors such as entanglement. To date, researchers have simultaneously cooled one or two particles, but they have struggled to scale techniques to cool additional particles.