Could information be the stuff of which everything is made? Information seems so abstract, not a substance or a thing, so how could it be the building blocks of reality? There are ways and reasons how information can literally be reality, some scientists claim, and their ideas are revolutionary.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Sean Carroll — Is Information the Foundation of Reality?
Could information be the stuff of which everything is made? Information seems so abstract, not a substance or a thing, so how could it be the building blocks of reality? There are ways and reasons how information can literally be reality, some scientists claim, and their ideas are revolutionary.

Some Uber and Lyft drivers have learned they can make more money if they’re pickier about who they serve
Ken, a 36-year-old Uber and Lyft driver in Houston, drives about four to five hours per day — in addition to his full-time analyst job — to supplement his income. Last year, he earned a combined $25,000 driving for Uber and Lyft from about 2,000 trips, according to screenshots of earnings documents viewed by Business Insider.
While he accepts most rides, he said he prioritizes trips that pay at least $0.80 to $1.00 per mile, excluding vehicle expenses — a ride’s base pay and distance are displayed on the app. He also tries to avoid trips that take him too far out of Houston because he worries he won’t be able to find trips for the ride back. He calls these “empty miles.”
“I have seen a 50-mile trip that only $20 was offered,” Ken previously told Business Insider. “I wouldn’t be doing that.” He asked that his last name not be included for fear of professional repercussions.

The Importance of the Earth’s Atmosphere in Creating the Large storms that Affect Satellite Communications
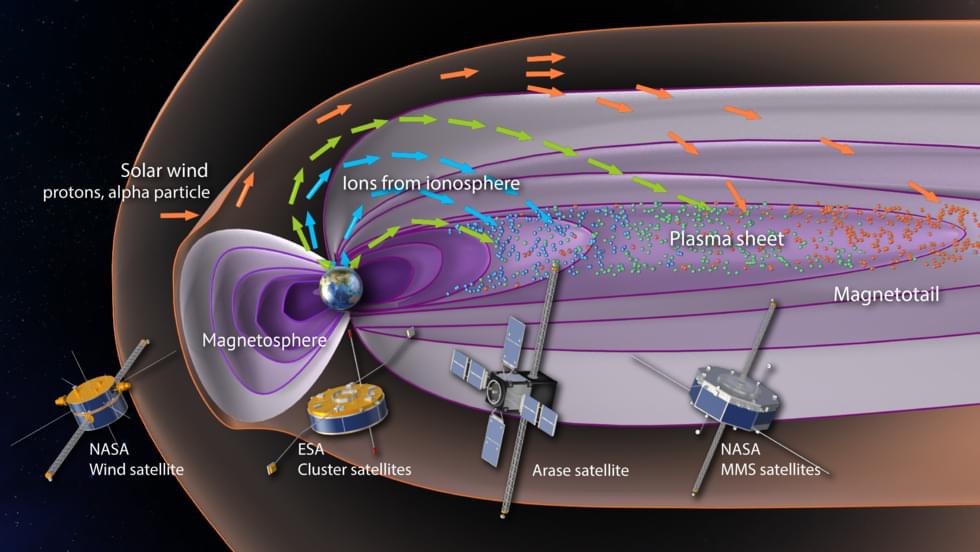
A study from an international team led by researchers from Nagoya University in Japan and the University of New Hampshire in the United States has revealed the importance of the Earth’s upper atmosphere in determining how large geomagnetic storms develop. Their findings reveal the previously underestimated importance of the Earth’s atmosphere. Understanding the factors that cause geomagnetic storms is important because they can have a direct impact on the Earth’s magnetic field such as causing unwanted currents in the power grid and disrupting radio signals and GPS. This research may help predict the storms that will have the greatest consequences.
Scientists have long known that geomagnetic storms are associated with the activities of the Sun. Hot charged particles make up the Sun’s outer layer, the one visible to us. These particles flow out of the Sun creating the ‘solar wind’, and interact with objects in space, such as the Earth. When the particles reach the magnetic field surrounding our planet, known as the magnetosphere, they interact with it. The interactions between the charged particles and magnetic fields lead to space weather, the conditions in space that can affect the Earth and technological systems such as satellites.
An important part of the magnetosphere is the magnetotail. The magnetotail is the part of the magnetosphere that extends away from the Sun, in the direction of the solar wind flow. Inside the magnetotail is the plasma sheet region, which is full of charged particles (plasma). The plasma sheet is important because it is the source region for the particles that get into the inner magnetosphere, creating the current that causes geomagnetic storms.

Developing ‘Indoor Solar’ to Power the Internet of Things
From Wi-Fi-connected home security systems to smart toilets, the so-called Internet of Things brings personalization and convenience to devices that help run homes. But with that comes tangled electrical cords or batteries that need to be replaced. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Energy Materials have brought solar panel technology indoors to power smart devices. They show which photovoltaic (PV) systems work best under cool white LEDs, a common type of indoor lighting.
Indoor lighting differs from sunlight. Light bulbs are dimmer than the sun. Sunlight includes ultraviolet, infrared and visible light, whereas indoor lights typically shine light from a narrower region of the spectrum. Scientists have found ways to harness power from sunlight, using PV solar panels, but those panels are not optimized for converting indoor light into electrical energy.
Some next-generation PV materials, including perovskite minerals and organic films, have been tested with indoor light, but it’s not clear which are the most efficient at converting non-natural light into electricity; many of the studies use various types of indoor lights to test PVs made from different materials. So, Uli Würfel and coworkers compared a range of different PV technologies under the same type of indoor lighting.
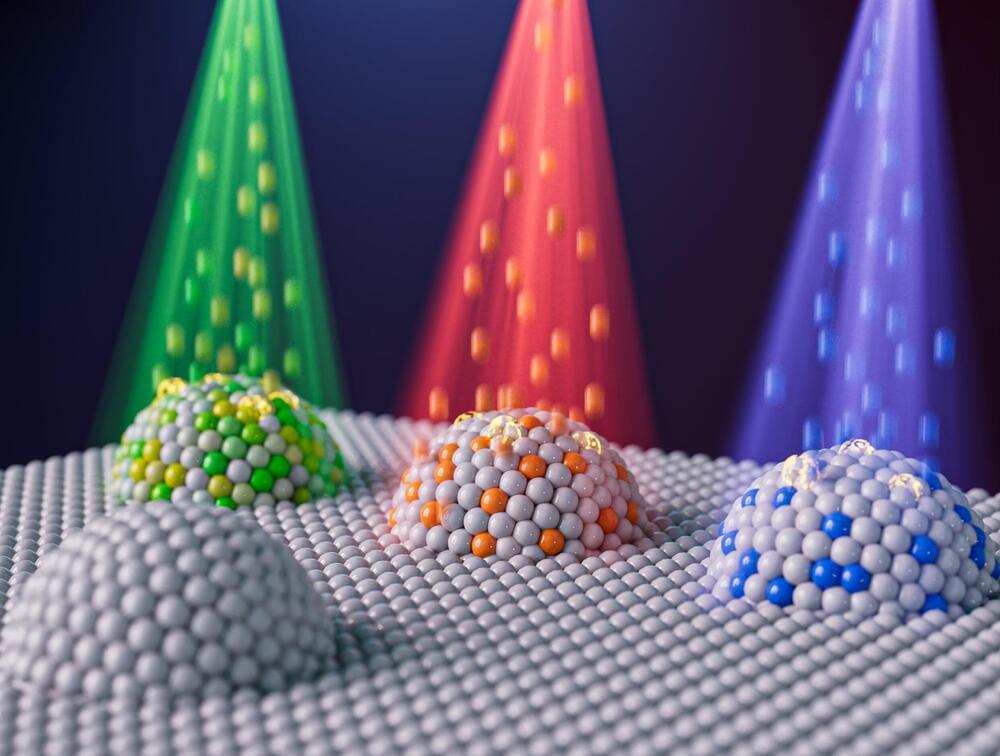
Researchers engineer nanoparticles using ion irradiation to advance clean energy, fuel conversion
MIT researchers and colleagues have demonstrated a way to precisely control the size, composition, and other properties of nanoparticles key to the reactions involved in a variety of clean energy and environmental technologies. They did so by leveraging ion irradiation, a technique in which beams of charged particles bombard a material.
They went on to show that nanoparticles created this way have superior performance over their conventionally made counterparts.
“The materials we have worked on could advance several technologies, from fuel cells to generate CO2-free electricity to the production of clean hydrogen feedstocks for the chemical industry [through electrolysis cells],” says Bilge Yildiz, leader of the work and a professor in MIT’s Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering and Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
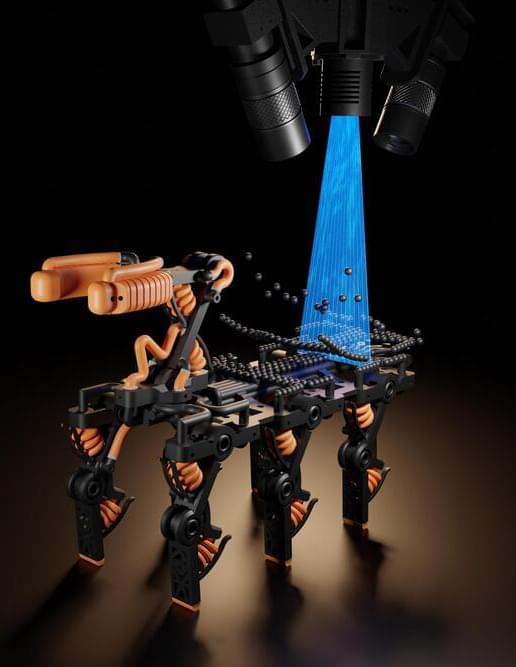

This 3D printer can watch itself fabricate objects
With 3D inkjet printing systems, engineers can fabricate hybrid structures that have soft and rigid components, like robotic grippers that are strong enough to grasp heavy objects but soft enough to interact safely with humans.
These multimaterial 3D printing systems utilize thousands of nozzles to deposit tiny droplets of resin, which are smoothed with a scraper or roller and cured with UV light. But the smoothing process could squish or smear resins that cure slowly, limiting the types of materials that can be used.
Researchers from MIT, the MIT spinout Inkbit, and ETH Zurich have developed a new 3D inkjet printing system that works with a much wider range of materials. Their printer utilizes computer vision to automatically scan the 3D printing surface and adjust the amount of resin each nozzle deposits in real time to ensure no areas have too much or too little material.
