🔒 Yet another critical SQL injection vulnerability (CVE-2023–36934) uncovered in popular MOVEit Transfer—the same software that was exploited.


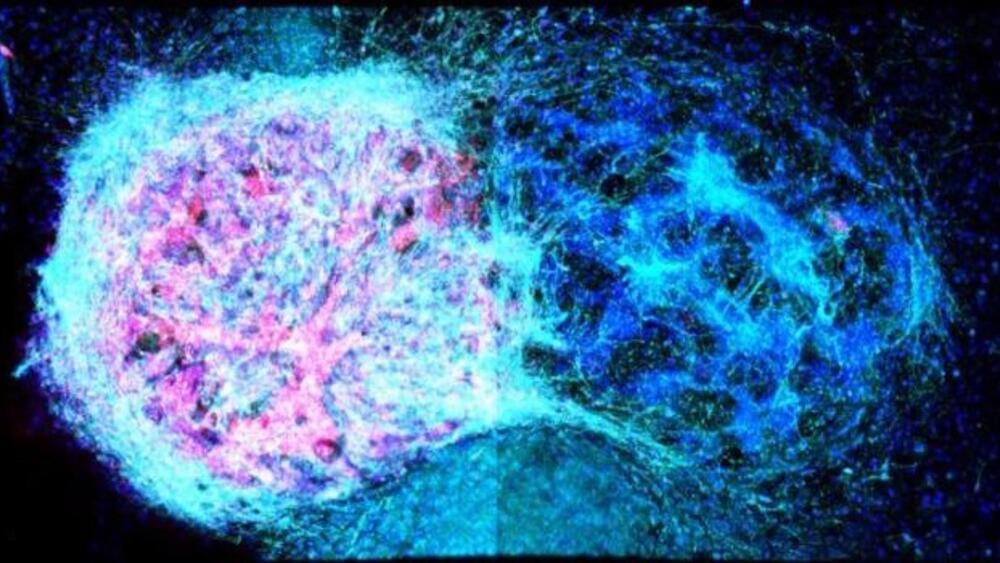
The University of Oxford researchers for the first time showcased that neural cells can be 3D printed to replicate the structure of the brain’s outer layer: the cerebral cortex.
In a significant breakthrough, scientists have created brain tissue using human stem cells through 3D printing. This advancement holds promise for potential future applications in treating brain injuries.
For the first time, the University of Oxford researchers showcased that neural cells can be 3D printed to replicate the structure of the brain’s outer layer: the cerebral cortex.
This accomplishment marks a significant advancement in the realm of neural tissue engineering.
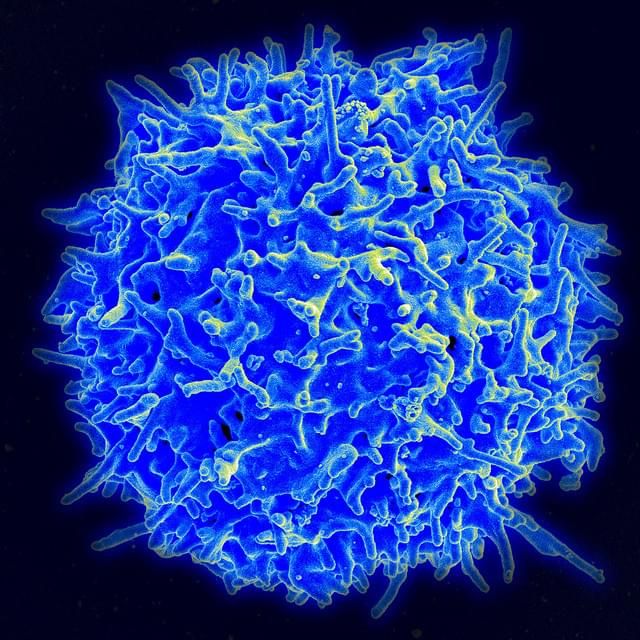
UCLA scientists have developed a new method to engineer more powerful immune cells that can potentially be used for “off-the-shelf” cell therapy to treat challenging cancers.
“Off-the-shelf” cell therapy, also known as allogenic therapy, uses immune cells derived from healthy donors instead of patients. The approach can bring cell therapies, like chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy, to more patients in a timelier manner, which is one of the major barriers in getting these life-saving treatments to patients.
“Time is often of the essence when it comes to treating people with advanced cancers,” said Lili Yang, associate professor of microbiology, immunology and molecular genetics and member of the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center. “Currently, these types of therapies need to be tailored to the individual patient. We have to extract white blood cells from a patient, genetically engineer the cells and then re-infuse them back into the patient. This process can take weeks to months and can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars to treat each patient.”

It’s a stormy holiday weekend, and you’ve just received the last notification you want in the busiest travel week of the year: the first leg of your flight is significantly delayed.
You might expect this means you’ll be sitting on hold with airline customer service for half an hour. But this time, the process looks a little different: You have a brief text exchange with the airline’s AI chatbot, which quickly assesses your situation and places you in a priority queue. Shortly after, a human agent takes over, confirms the details, and gets you rebooked on an earlier flight so you can make your connection. You’ll be home in time to enjoy mom’s pot roast.
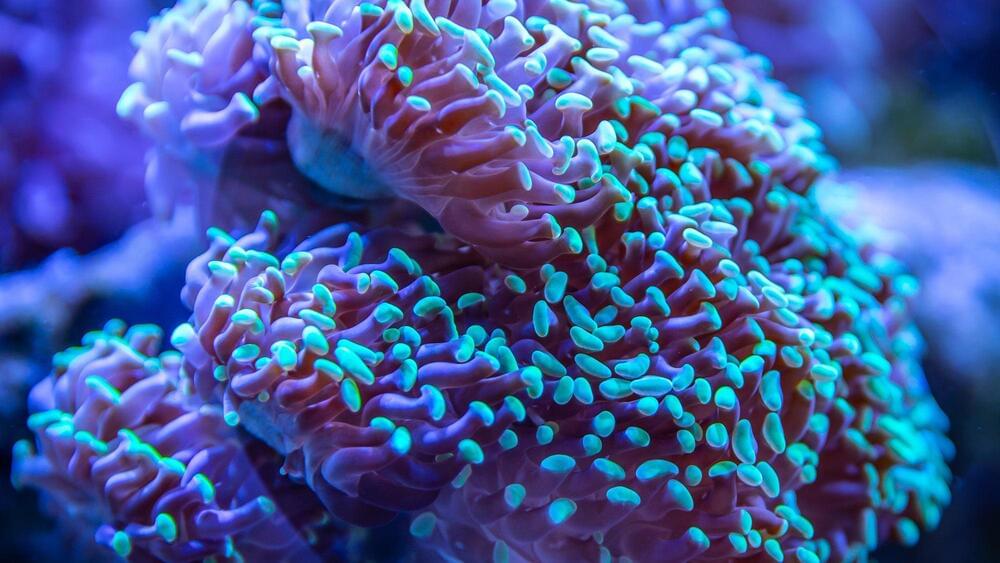

In 2018, researchers reported that they had managed to get a coral larva to survive freezing and thawing for the first time. The scientists had added gold nanoparticles to their antifreeze to help the corals warm evenly during reheating. However, the thawed larvae were unable to settle and develop into adults. Instead, they kept swimming until they died.
When Narida began her experiments with hood corals in 2021, she included gold in her antifreeze recipe and combined several different antifreeze chemicals to reduce the solution’s toxicity. To thaw the animals quickly and minimize damage, Narida used a high-powered laser designed for welding jewelry. Then, she carefully washed the antifreeze away with seawater, rehydrating the corals. In the end, a whopping 11 percent of larvae in the experiment survived thawing, then settled, and developed into adults.
Leandro Godoy, a coral cryobiologist at the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil, is impressed by how many larvae survived after settling. “It’s a huge step,” he says, considering that, in the wild, only about five percent of corals make it that far.
Artificial intelligence already wears multiple hats in the workplace, whether its writing ad copy, handling customer support requests, or filtering job applications. As the technology continues its ascent and capabilities, the notion of corporations managed or owned by AI becomes less far-fetched. The legal framework already exists to allow “Zero-member LLCs.”
How would an AI-operated LLC be treated under the law, and how would AI respond to legal responsibilities or consequences as the owner/manager of an LLC? These questions speak to an unprecedented challenge facing lawmakers: the regulation of a nonhuman entity with the same (or better) cognitive capabilities as humans that, if left unresolved or poorly addressed, could slip beyond human control.
“Artificial intelligence and interspecific law,” an article by Daniel Gervais of Vanderbilt Law School and John Nay of The Center for Legal Informatics at Stanford University, and a Visiting Scholar at Vanderbilt, argues for more AI research on the legal compliance of nonhumans with human-level intellectual capacity.
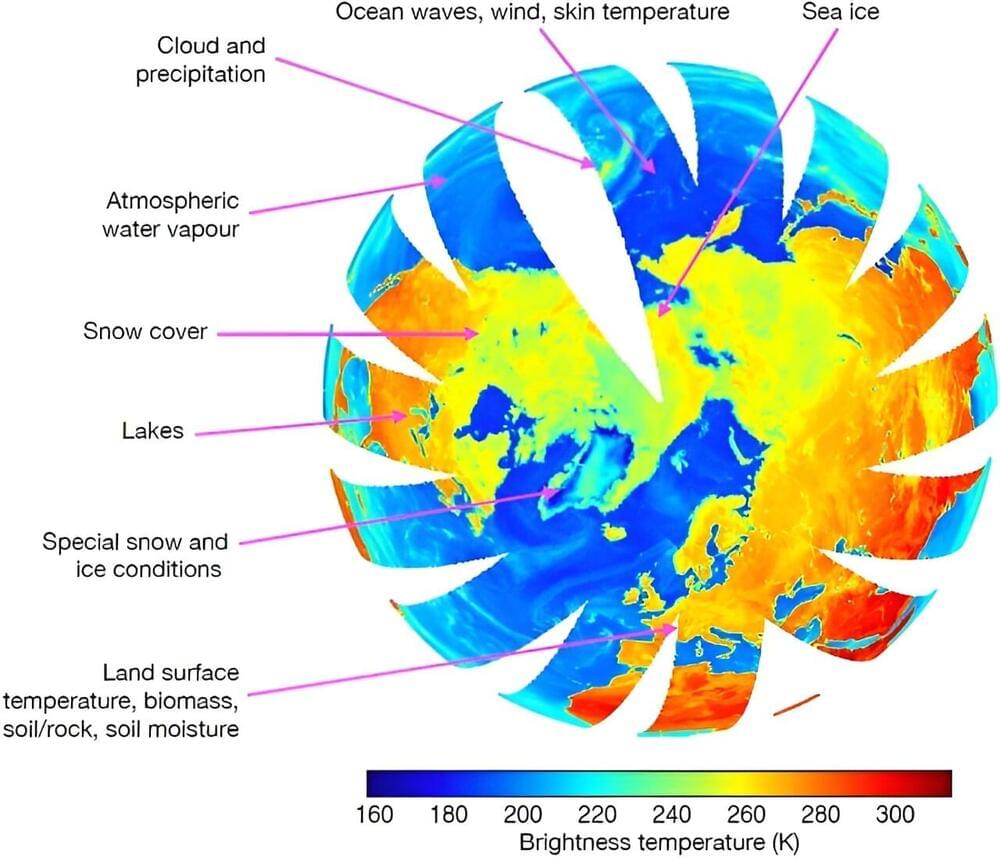
Data assimilation is the combination of the latest observations with a short-range forecast to obtain the best possible estimate of the current state of the Earth system. Machine learning can contribute to it by optimizing the use of satellite observations.
Obtaining the best possible estimate of the current state of the Earth system, known as the analysis, is extremely important for weather forecasting. That’s because the analysis serves as the initial conditions of forecasts.
To use the latest observations, we rely on a vast system of instruments that regularly measure aspects of the atmosphere and other components of the Earth system. Over the last few decades, satellite observations have become increasingly important.

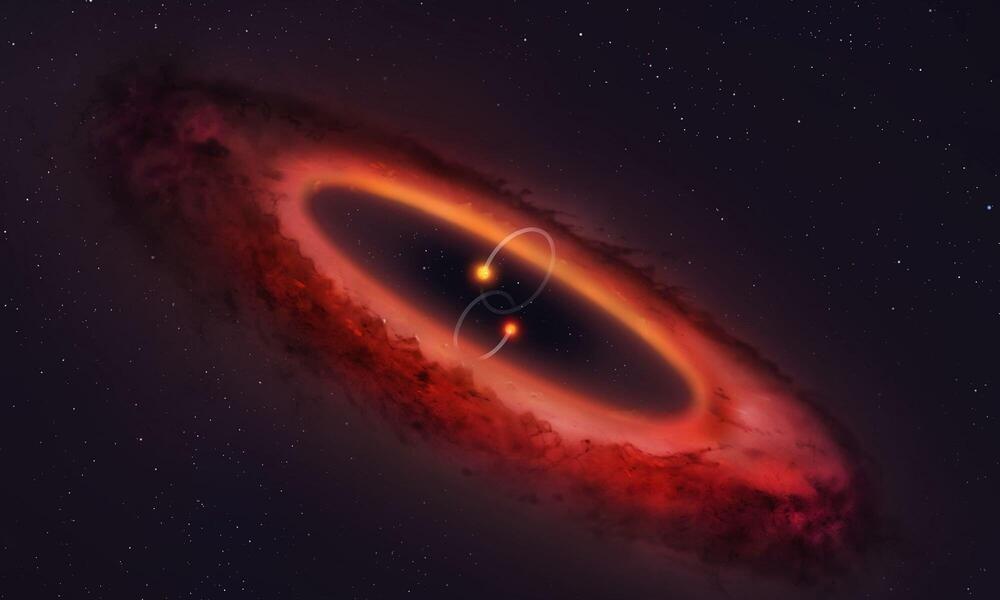
We live in an age of exoplanet discovery. One thing we’ve learned is not to be surprised by the kinds of exoplanets we keep discovering. We’ve discovered planets where it might rain glass or even iron, planets that are the rocky core remnants of gas giants stripped of their atmospheres, and drifting rogue planets untethered to any star.
Now, astronomers have uncovered evidence of an exoplanet in a circumbinary disk around a binary star. The remarkable thing about this discovery is that the disk is in a polar configuration. That means the exoplanet moves around its binary star in a circumpolar orbit, and this is the first one scientists have found.
AC Herculis (AC Her) is a binary star about 4,200 light-years away. The primary star is well-studied, while its partner is invisible. It has a polar circumbinary disk, which is unusual but not unheard of. In a new paper, a team of researchers presents evidence for the polar circumbinary exoplanet.
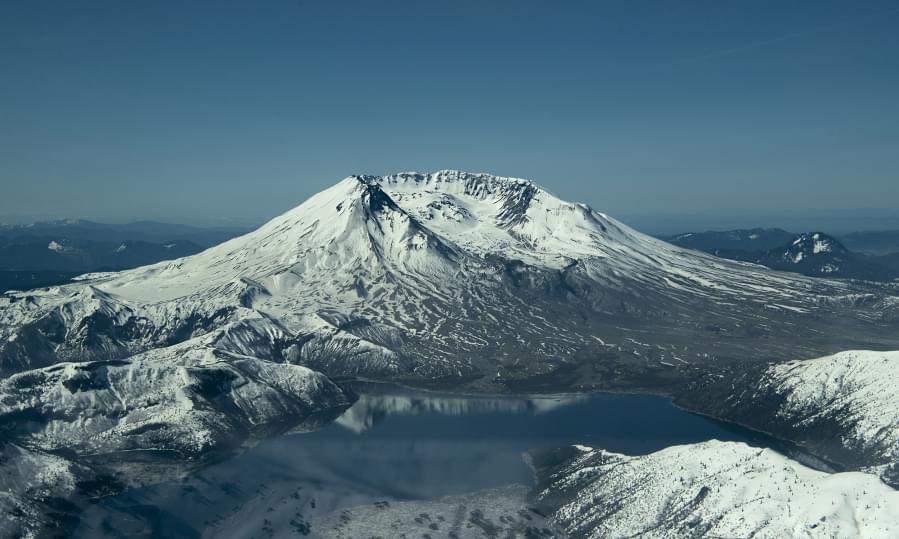

About 400 earthquakes have rumbled under Mount St. Helens since mid-July, the largest chain of shakes since the volcano finished erupting in 2008, the U.S. Geological Survey reported last week.
Small magnitude earthquakes, detected only by sensitive equipment, signal a volcano’s “recharging” as magma flows through chambers and cracks deep under the ground, said Wes Thelen, U.S. Geological Survey Cascades Volcano Observatory geophysicist and seismologist.
Between late August and early September, scientists observed 40 to 50 earthquakes per week located between 2.5 to 5 miles below the crater floor, before recently dwindling to 30. To compare, Mount St. Helens averaged roughly 11 quakes per month since 2008.