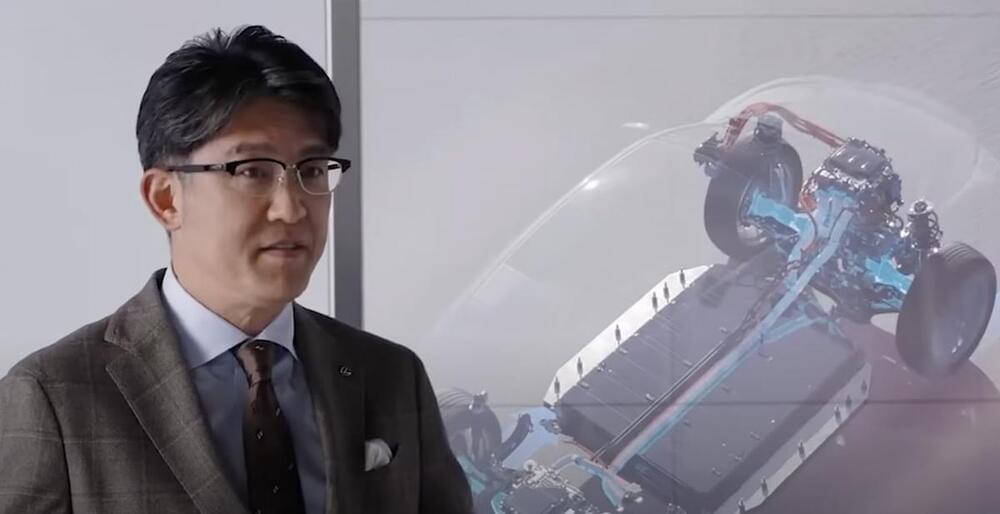
In a world that seems inexorably drawn towards an all-electric future, Toyota has consistently taken a different road. The Japanese automaker remains skeptical about an exclusive reliance on electric vehicles (EVs). While it’s true that Toyota has some exciting EVs in the pipeline for the upcoming year, they are also actively exploring alternative energy sources. However, a recent development could potentially turn the tables on the EV revolution — an ammonia-powered engine for passenger vehicles.
Also, to read: