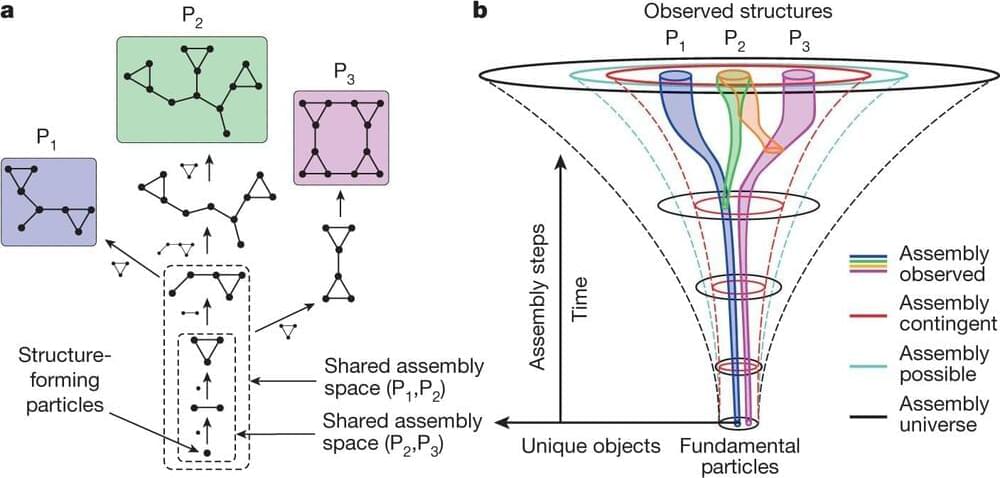
In October, a paper titled “Assembly theory explains and quantifies selection and evolution” appeared in the journal Nature. The authors—a team led by Lee Cronin at the University of Glasgow and Sara Walker at Arizona State University—claim their theory is an “interface between physics and biology” which explains how complex biological forms can evolve.
The paper provoked strong responses. On the one hand were headlines like “Bold New ” Theory of Everything’ Could Unite Physics And Evolution”
On the other were reactions from scientists. One evolutionary biologist tweeted after multiple reads I still have absolutely no idea what [this paper] is doing. Another said I read the paper and I feel more confused […] I think reading that paper has made me forget my own name.