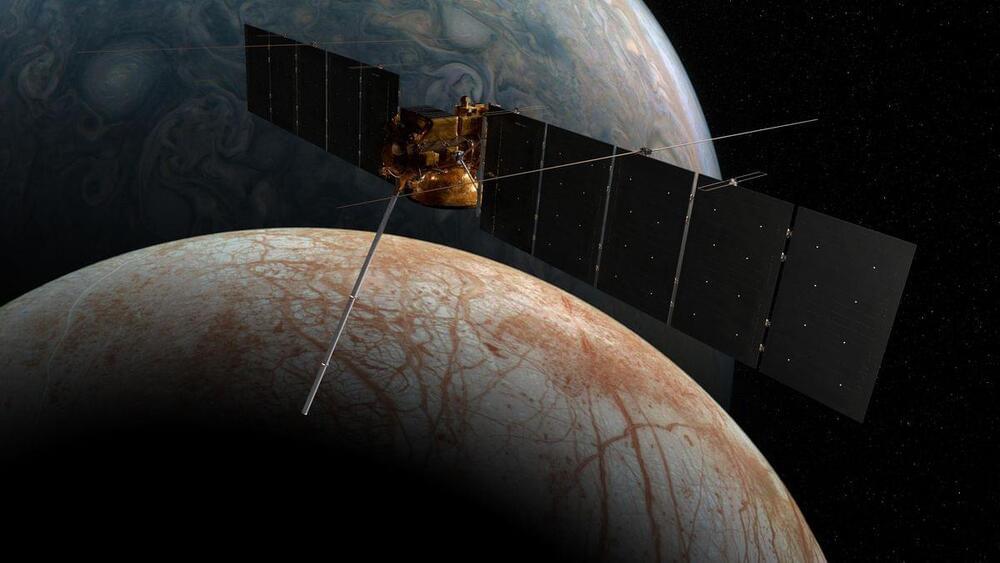
NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft is headed to one of Jupiter’s largest moons. It’s bringing along a microchip filled with human names.


At the most recent H+ Academy discussion and debate on the topic of “anti-transhumanist” writings (video below), several transhumanists suggested that we reclaim “transhumanism” from the obfuscations and misrepresentations of the original meaning of transhumanism as a philosophy and worldview.
How did this happen? Over the years, there have been many “opinions” about what transhumanism is or isn’t. These opinions could be personal interpretations of the philosophy, some of which may or may not be true. While diversity is welcome and new ideas are highly valued, the philosophy of transhumanism does have principles that form the core of its meaning. With a lot of leeway for opinion, interpretations can go in directions that are counter to transhumanism. Some of the more extreme opinions have caused a flood of anti-transhumanist bias and even hate. This is not what we want.
What can we do? We need to make it very clear what transhumanism is and is not. And we need to state this publicly and make it available to everyone.


In today’s column, I am going to walk you through a prominent AI-mystery that has caused quite a stir leading to an incessant buzz across much of social media and garnering outsized headlines in the mass media.
I make use of detective work to try and figure out what the alleged AI breakthrough was at OpenAI and has been claimed to be called Q*, leading supposedly toward AGI.


Inflection claims that its new language model, Inflection-2, outperforms direct competitors such as Google PaLM-2 and Claude 2, and is second only to GPT-4.
The new model is said to be significantly more powerful than its predecessor, Inflection-1, and, according to the startup, demonstrates improved factual knowledge, better style control, and significantly improved reasoning.
Inflection-1 was released in July. It was roughly on par with GPT-3.5 and PaLM-540B. Inflection-2 should now catch up with GPT-4, the company claims.
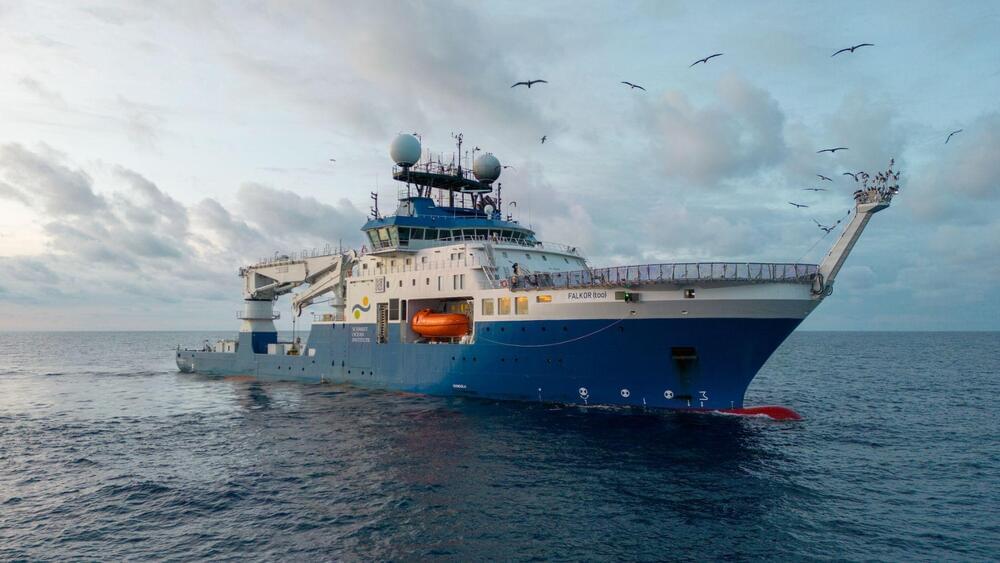

“While there is so much we’ve come to understand, so much remains unknown in our Ocean–and we are thrilled to continue exploring.”
Ocean explorers from the Schmidt Ocean Institute have unveiled a colossal underwater mountain, challenging our perceptions of the ocean’s mysterious depths.
Schmidt Ocean Institute.
This seamount, found in international waters off the coast of Guatemala, stands at a staggering 5,249 feet (1,600 meters), dwarfing the Burj Khalifa, the world’s tallest building. The revelation came during a seafloor mapping expedition to explore the Earth’s least understood frontier aboard the research vessel Falkor (too).

Noise-canceling headphones are designed to block out the ambient noise and let you focus on what you want to hear.
Wirestock, photoschmidt via iStock.
This feature used to be a niche product for a select group of users, primarily frequent air travelers. But now, with technology being more affordable, it has become more vividly seen in many of the current market offerings. Take Apple’s AirPods Pro or AirPods Max, for example, or Sony’s WH 1,000 XM5 or WF 1,000 XM5 series or, say, the Bose Quite Comfort series. There are many options, from affordable to expensive ones, and the ANC performance varies across the price range.

The technique represents an important step in engineering skin grafts, drug testing. A team led by scientists at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute has 3D-printed hair follicles in human skin tissue cultured in the lab. This marks the first time researchers have used the technology to generate hair follicles, which play an important role in skin healing and function.
The finding, published in the journal Science Advances, has potential applications in regenerative medicine and drug testing, though engineering skin grafts that grow hair are still several years away.
“Our work is a proof-of-concept that hair follicle structures can be created in a highly precise, reproducible way using 3D-bioprinting. This kind of automated process is needed to make future biomanufacturing of skin possible,” said Pankaj Karande, Ph.D., an associate professor of chemical and biological engineering and a member of Rensselaer’s Shirley Ann Jackson, Ph.D. Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies, who led the study.
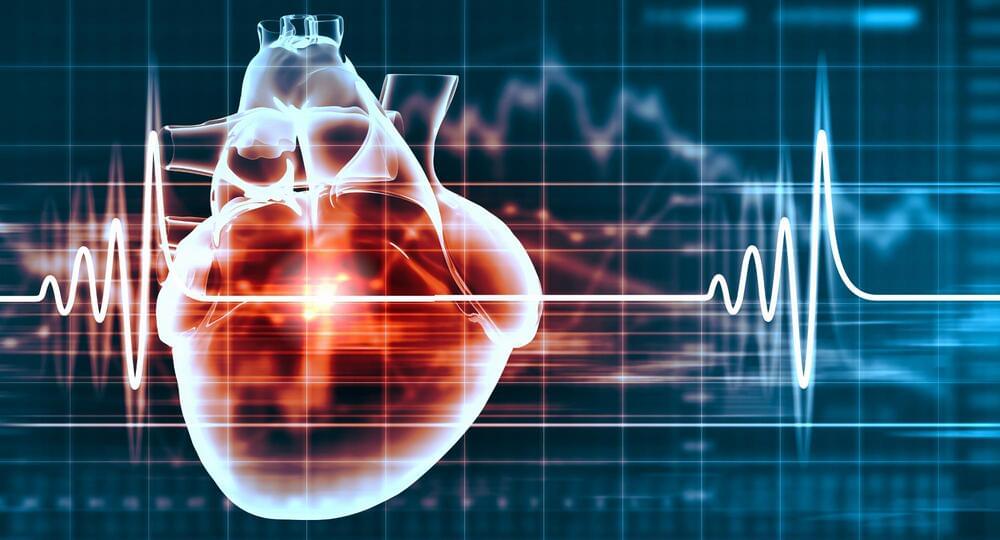
An AI tool that can predict 10-year risk of deadly heart attacks, could transform treatment for patients who undergo CT scans to investigate chest pain, according to British Heart Foundation-funded research presented today at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions in Philadelphia.
In the first real-world trial of the AI tool, it was found to improve treatment for up to 45 per cent of patients. The AI technology could potentially save the lives of thousands with chest pain, who may not have been identified as at risk of a heart attack, and therefore may not have received appropriate treatment to lower their risk. With the technology also found to be cost-effective, the researchers hope it could change the management of patients who are referred for chest pain investigations, across the NHS.
Every year in the UK around 350,000 people have a cardiac CT scan – the standard test to identify any narrowings or blockages in the coronary arteries. In around three quarters of cases, there is no clear sign of significant narrowings, so patients are often reassured and discharged. Unfortunately, many of these people will die from a heart attack in future, because small, undetectable narrowings may break up if they are inflamed, blocking the arteries. Until recently, it was not possible to identify these patients at risk.