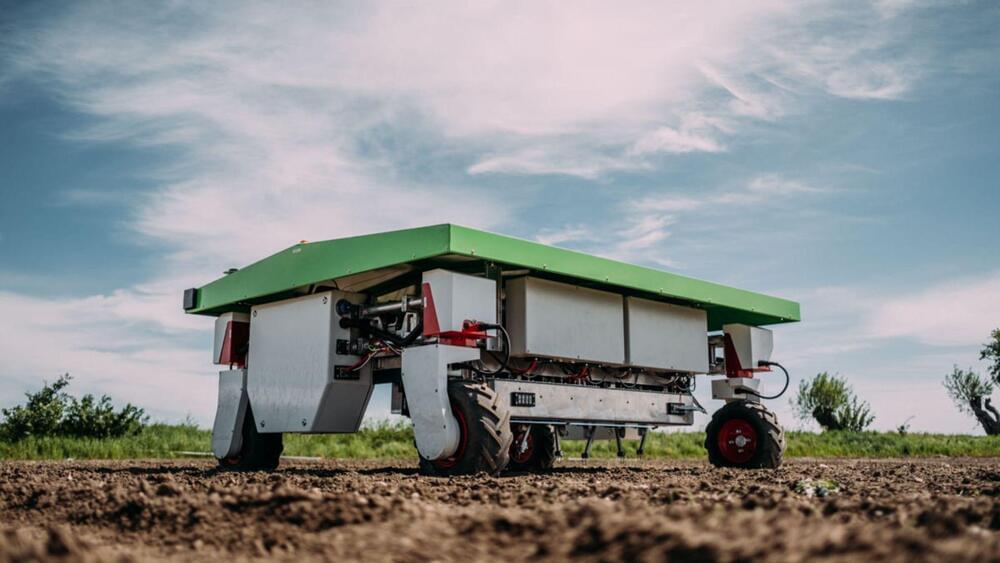
Now you can sit back and relax in your easy chair as your garden is weeded.
Ekobot.
As anyone who has tended to a garden knows, weeding is time-consuming and energy-draining. Scale it up to a farm, and it becomes a logistical nightmare. Traditional herbicides, though efficient, pose potential threats to people, animals, and the environment.