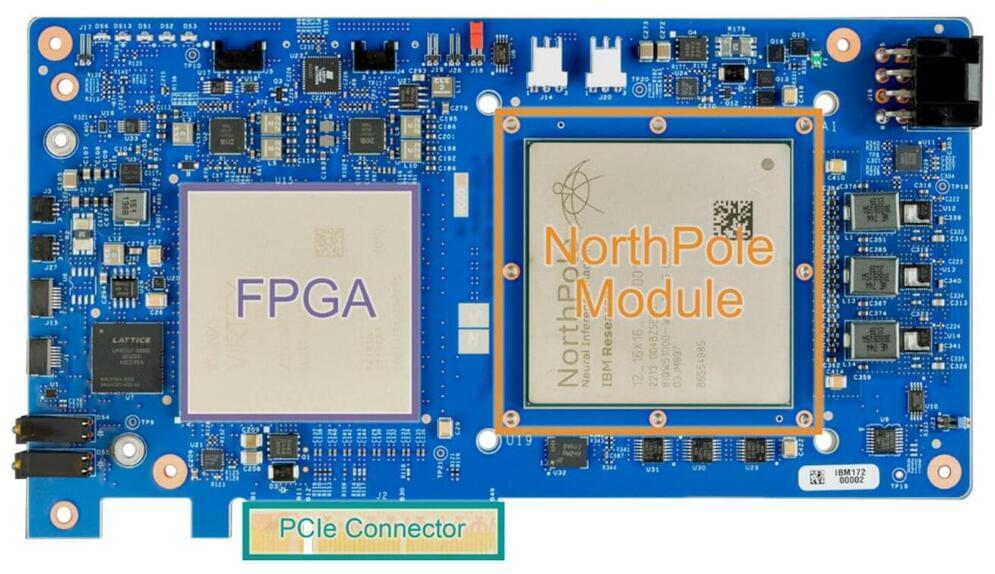
A large team of computer scientists and engineers at IBM Research has developed a dedicated computer chip that is able to run AI-based image recognition apps 22 times as fast as chips that are currently on the market.
In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes the ideas that went into developing the chip, how it works and how well it performed when tested. Subramanian Iyer and Vwani Roychowdhury, both at the University of California, Los Angeles, have published a Perspective piece in the same journal issue, giving an in-depth analysis of the work by the team in California.
As AI-powered applications become mainstream tools used by professionals and amateurs alike, scientists continue work to make them better. One way to do that, Iyer and Roychowdhury note, is to move toward an “edge” computer system in which the data is physically closer to the AI applications that are using them.