Samsung ended its Unpacked event with a teaser showing a new Galaxy Ring.
Details on the Galaxy Ring are still slim.


AI becomes the decoder to predict treatment response.
Believe it or not, some types of cancers can grow resistant to chemotherapy.
Deciphering when cancer might toughen up against chemotherapy is pretty tricky. Even though researchers and doctors notice some hints and clues about resistance, predicting the exact moment is a bit like trying to hit a bullseye with a blindfold.
But in what could be a game-changer, scientists at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine revealed today in a study that a high-tech machine learning tool might just figure out when cancer is going to give the cold shoulder to chemotherapy.
The European Commission has officially signed an agreement to develop a new program to connect the various assets of EU-member state military forces.
LATACC will boost European military collaboration, focusing on rapid response and tech innovation in ‘high-intensity’ conflicts.

Caltech’s Space Solar Power Demonstrator (SSPD-1) was launched into space one year ago.
After nearly a year in orbit, Caltech’s Space Solar Power Demonstrator (SSPD-1) reached its end of mission.

As the Roman Space Telescope prepares for launch, it joins a cadre of upcoming missions, including the European Space Agency’s Euclid mission and the Vera C. Rubin Observatory. Together, these endeavors are poised to reshape our understanding of dark matter, providing valuable data to refine simulations and deepen our comprehension of the universe’s large-scale structure.
In conclusion, NASA’s Roman Space Telescope stands on the precipice of a groundbreaking exploration into the gaps between stars, promising to unveil new dimensions of the cosmos and potentially solve the longstanding mystery of dark matter, NASA release claims.
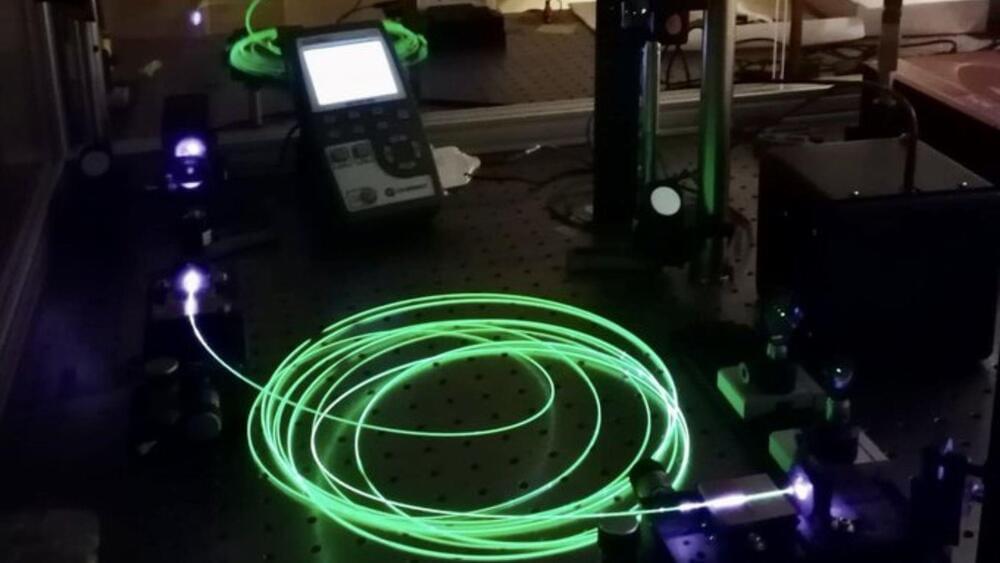

The research project demonstrated a power output of 20 watts using a fiber-optic laser and aims to increase this to kilowatts in the future.
The main goal of the WiPTherm project was to create an innovative wireless energy transfer system that could recharge energy storage components on micro and nano-sized satellites.
The IFIMUP was tasked with developing thermoelectric sensors capable of absorbing light at 1,550 nm and using them to charge energy storage devices.
After three years of work, the consortium tested their technologies at the São Jacinto airbase in Aveiro, a city on the Portuguese west coast. During this display, the research team succeeded in generating 20 watts of power output using a fiber optic laser and directed it to the sensors.
