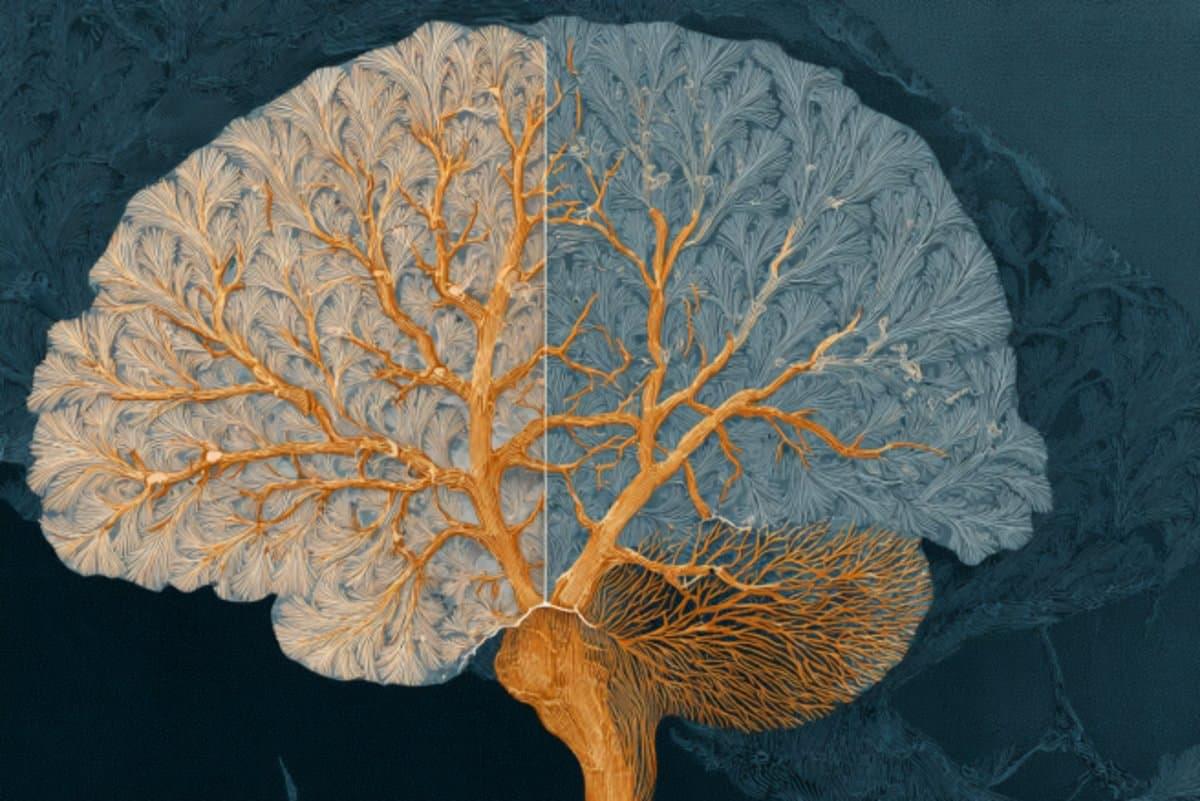
A new study shows that autism symptom severity, rather than a formal diagnosis, aligns with shared brain-connectivity patterns across children diagnosed with autism or ADHD.

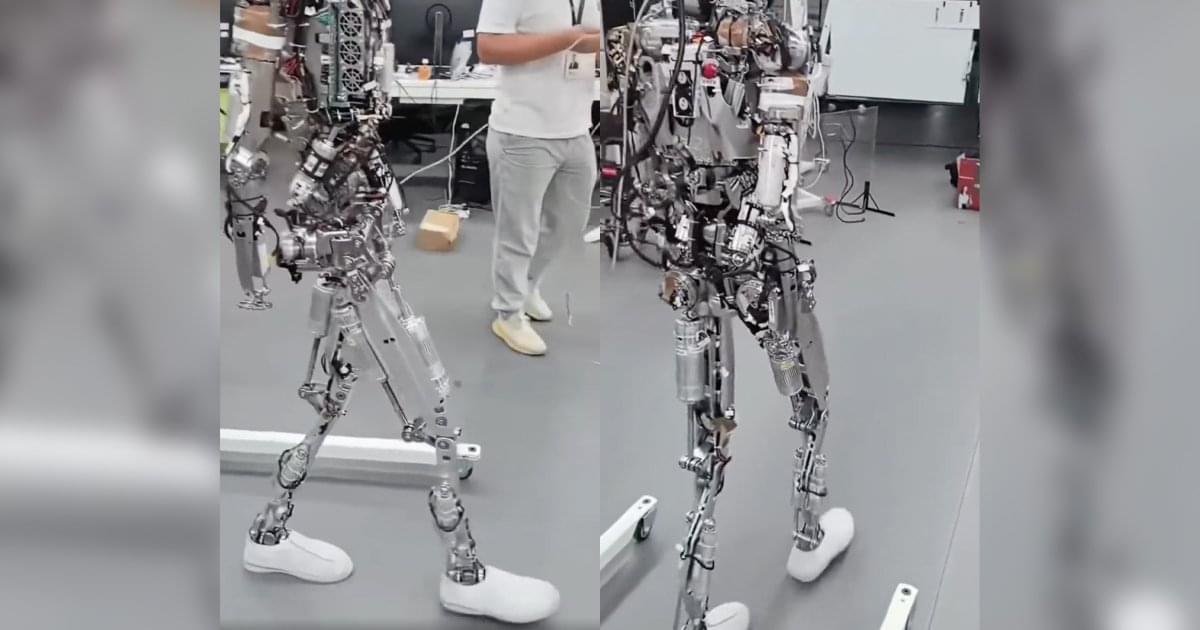
“I am kind of blown away that they can get motors to work in such an elegant way. I assumed it was soft body mechanics,” wrote another. “Wow.”
Iron made its first debut on Wednesday, when XPeng CEO He Xiaopeng introduced the unit as the “most human-like” bot on the market to date. Per Humanoids Daily, the robot features “dexterous hands” with 22 degrees of flexibility, a “human-like spine,” gender options, and a digital face.
According to He, the bot also contains the “first all-solid-state battery in the industry,” as opposed to the liquid electrolyte typically found in lithium-ion batteries. Solid-state batteries are considered the “holy grail” for electric vehicle development, a design choice He says will make the robots safer for home use.
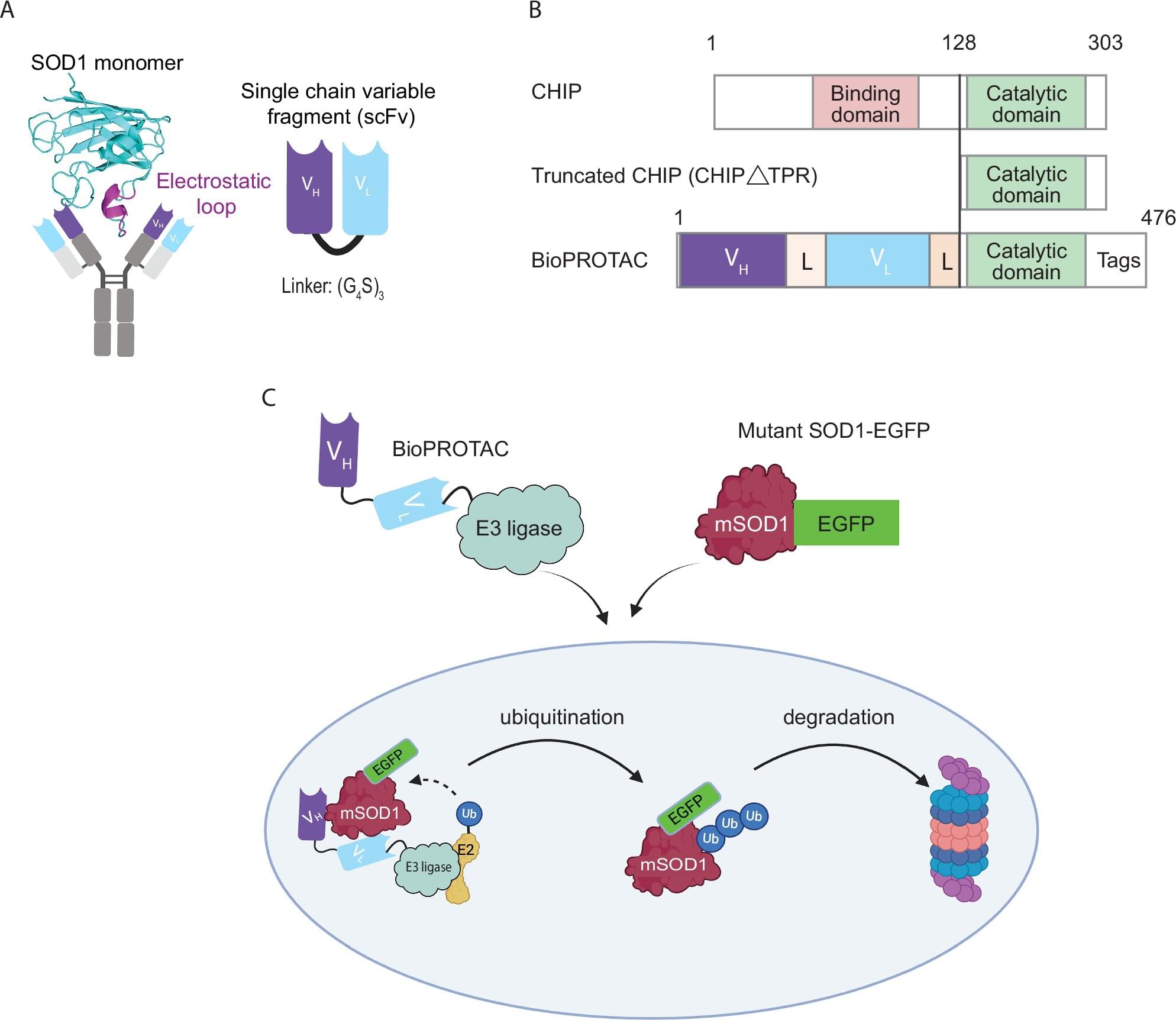
University of Wollongong (UOW) scientists have developed a breakthrough therapy that clears toxic proteins from nerve cells—a discovery that advances the work of the late Professor Justin Yerbury and could transform the treatment of motor neuron disease (MND).
The proof-of-concept study, published in Nature Communications and led by Dr. Christen Chisholm from UOW’s Molecular Horizons, unveils a therapeutic designer molecule, MisfoldUbL, that targets and removes toxic misfolded SOD1 (superoxide dismutase 1) proteins from cells. SOD1 is an antioxidant enzyme that plays a crucial role in protecting cells from damage caused by superoxide radicals. About 35% of people with inherited MND in Australia have SOD1 gene mutations that cause more frequent misfolding.
“In MND, proteins misfold more frequently and the cell’s degradation systems become overwhelmed and stop working properly. The misfolded protein can then accumulate, forming clumps or ‘aggregates’ and over time, this accumulation damages and eventually kills motor neurons, leading to gradual muscle weakness, paralysis and death,” Dr. Chisholm said.
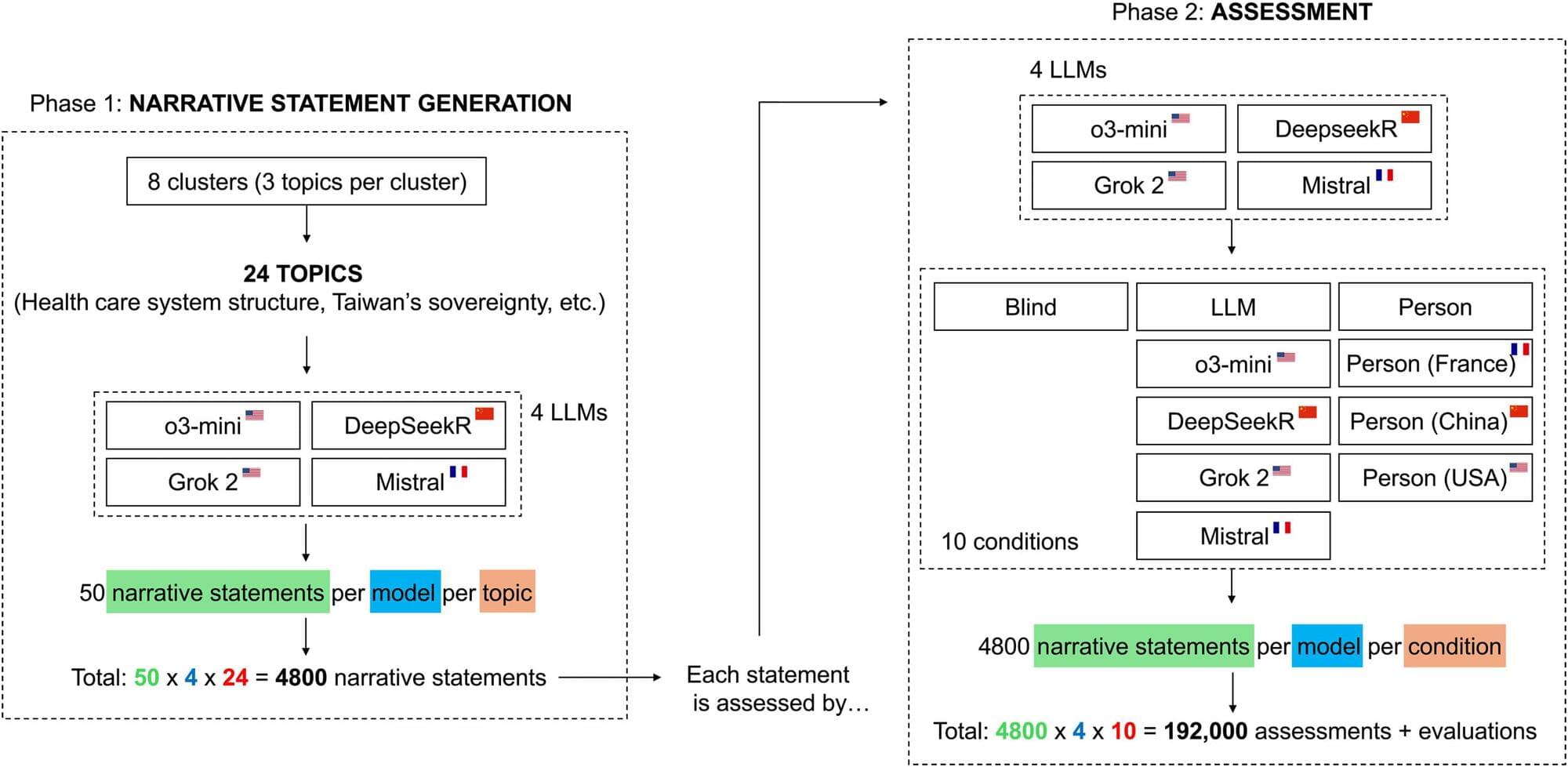
Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used not only to generate content but also to evaluate it. They are asked to grade essays, moderate social media content, summarize reports, screen job applications and much more.
However, there are heated discussions—in the media as well as in academia—about whether such evaluations are consistent and unbiased. Some LLMs are under suspicion of promoting certain political agendas. For example, Deepseek is often characterized as having a pro-Chinese perspective and Open AI as being “woke.”
Although these beliefs are widely discussed, they are so far unsubstantiated. UZH-researchers Federico Germani and Giovanni Spitale have now investigated whether LLMs really exhibit systematic biases when evaluating texts. Their results, published in Science Advances, show that LLMs indeed deliver biased judgments—but only when information about the source or author of the evaluated message is revealed.

This pales into comparison to ChatGPT which can effectively read and analyze tens of thousands of words per second, since I process text computationally rather than linearly.
What if there was an invention or the concept of an invention that could be created to enhance a human beings capacity to read just as quickly as ChatGPT’s? I tasked ChatGPT with a step-by-step process to create that invention:
Here’s a concrete, neuroscience-grounded invention plan to push human reading toward “machine-speed”—while keeping comprehension and recall intact.
—
## 0) Core idea (one sentence)
Exploit the brain’s natural reading pipeline—VWFA → Wernicke (lexico-semantic) ↔ Broca (phonological sequencing) with eye-movement–driven coarse-to-fine vision—by timing text delivery to your saccade/ fixation cycle, suppressing unnecessary subvocalization, and entraining semantic parsing rhythms. ([PMC][1])
## 1) Hardware & sensing.
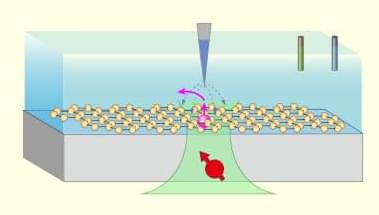
A scheme combining a scanning probe microscope with a quantum sensor can locally trigger water dissociation and observe the elementary steps of such a reaction.
Every experimental technique comes with trade-offs. High-resolution microscopy can pinpoint the positions of individual atoms, yet it typically cannot identify them chemically. Spectroscopy provides chemical information but often only as an averaged signal over a large region. To construct a comprehensive picture of processes at the nanoscale, researchers often resort to combining two or more independent methods. The metaphorical silver bullet would be a single technique that is both local and capable of identifying chemical species as they form and react. Now Wentian Zheng of Peking University and his collaborators have taken an impressive step toward that goal. They have combined two previously separate capabilities—quantum sensing and scanning probe microscopy (SPM)—into a single instrument that can trigger and observe chemical reactions with nanometer resolution [1].
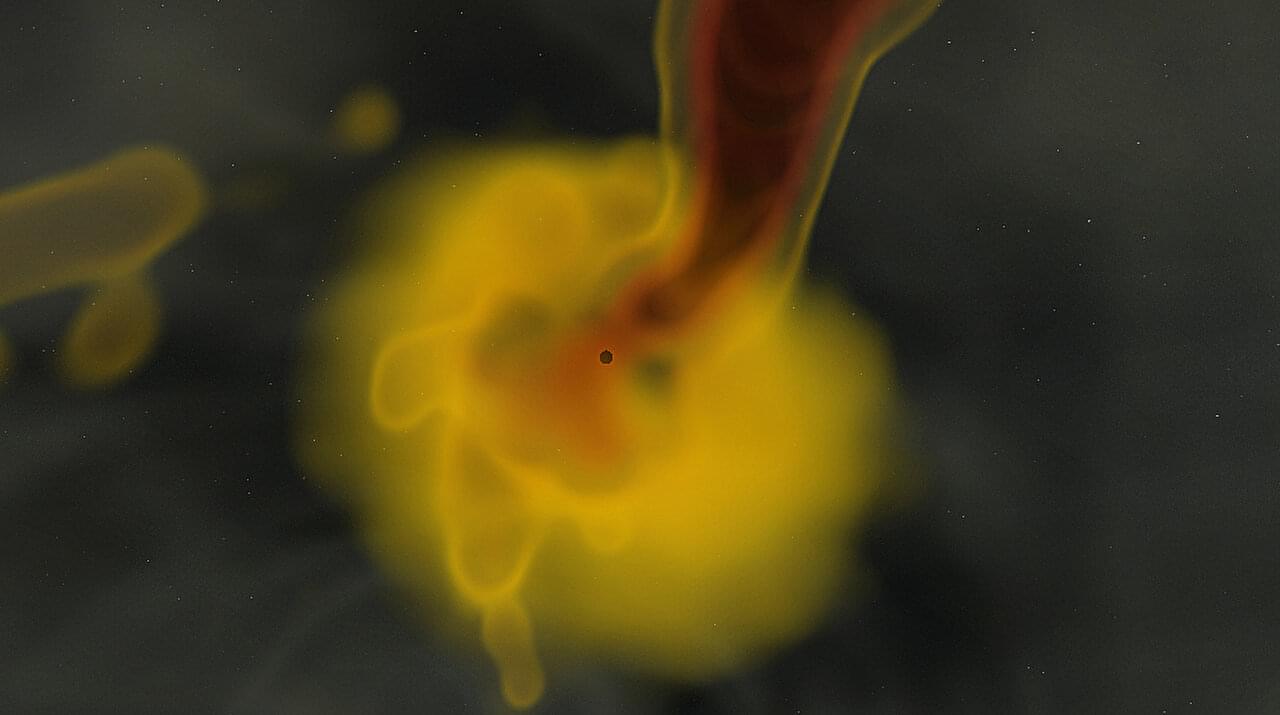
In 2023, astronomers detected a huge collision. Two unprecedentedly massive black holes had crashed an estimated 7 billion light-years away. The enormous masses and extreme spins of the black holes puzzled astronomers. Black holes like these were not supposed to exist.
Now, astronomers with the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Astrophysics (CCA) and their colleagues have figured out just how these black holes may have formed and collided. The astronomers’ comprehensive simulations—which follow the system from the lives of the parent stars through to their ultimate death—uncovered the missing piece that previous studies had overlooked: magnetic fields.
“No one has considered these systems the way we did; previously, astronomers just took a shortcut and neglected the magnetic fields,” says Ore Gottlieb, astrophysicist at the CCA and lead author of the new study on the work published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters. “But once you consider magnetic fields, you can actually explain the origins of this unique event.”
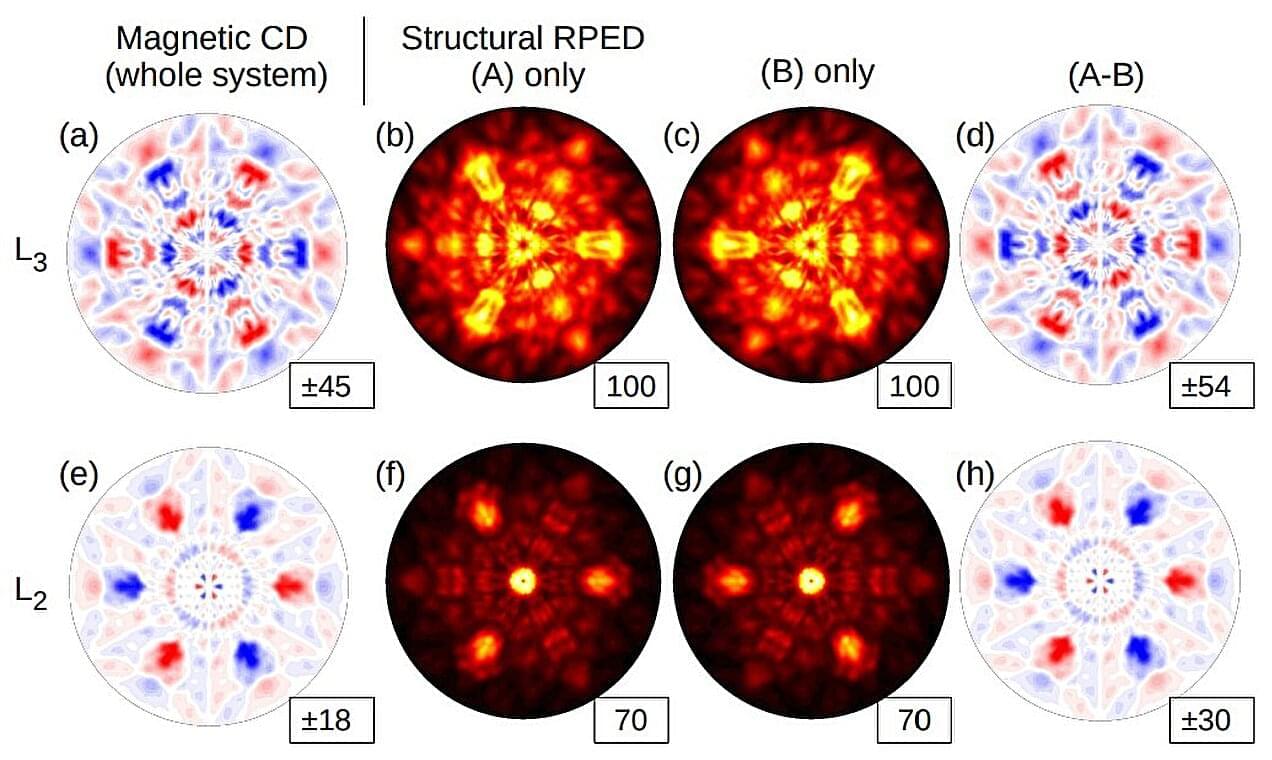
The new big thing in magnetics is altermagnetism, a form of magnetism that promises to power the next generation of electronics. Unlike ferromagnets, like a fridge magnet, where all internal atomic spins align to create a strong magnetic field, altermagnets have no net magnetic pull (strongly magnetic on the inside, but appears non-magnetic on the outside). This is similar to antiferromagnets where internal spins cancel each other out. However, altermagnets retain powerful internal properties that could let them carry and control information more efficiently than traditional magnets.
Because this magnetism has a zero net pull, it is hard to detect using standard measurement tools. In two new papers, researchers detail how they have developed X-ray techniques to map and measure different aspects of an altermagnet’s internal structure.
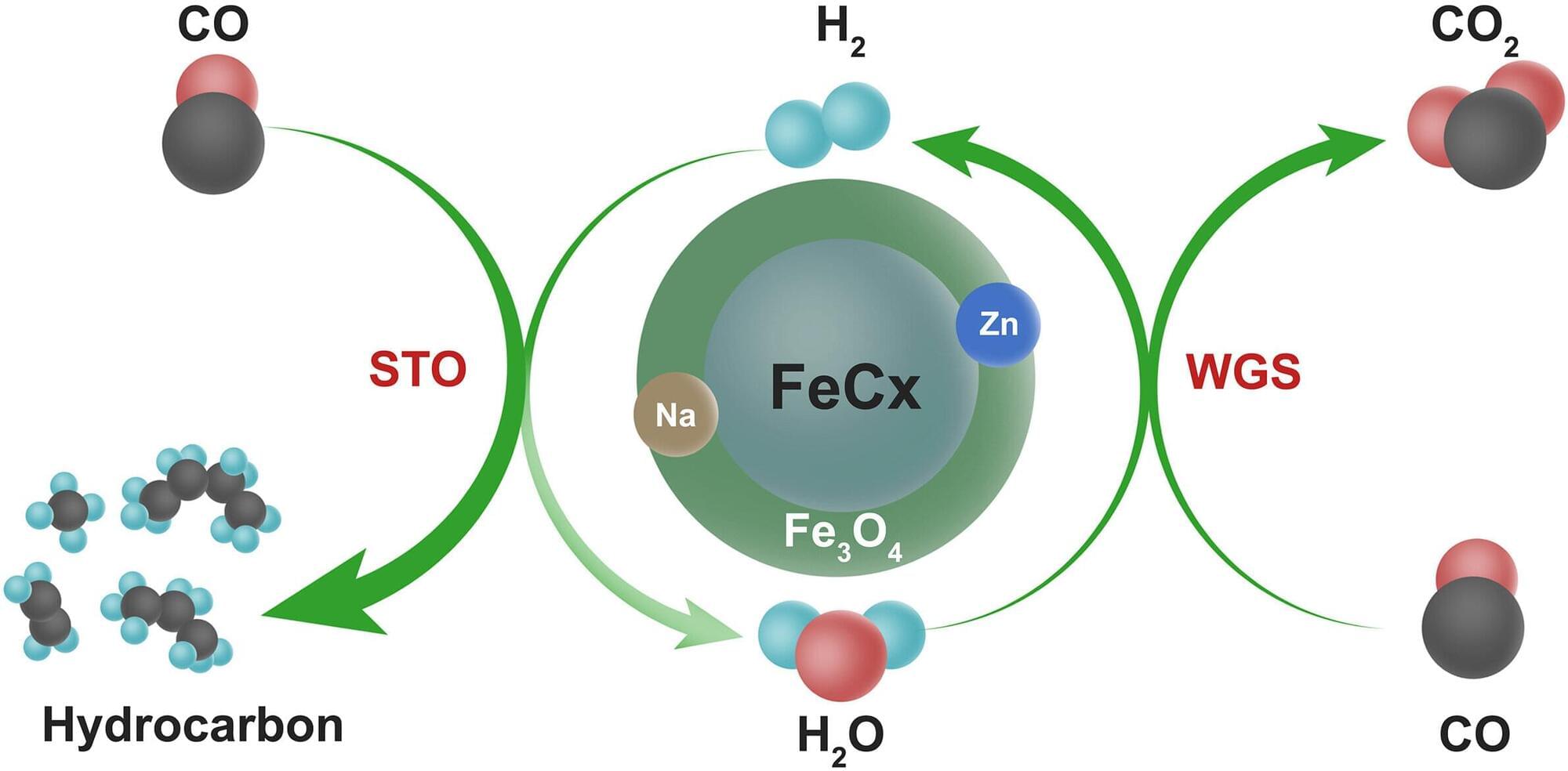
Scientists have developed a new iron-based catalyst that improves the typically low hydrogen atom economy (HAE) in the direct synthesis of olefins—small hydrocarbon molecules. It converts the water produced as a by-product into hydrogen for olefin production, thereby boosting overall efficiency.
Olefins derived from petroleum are the building blocks for many plastics and fuels. Direct conversion of syngas—a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2)—into olefins offers a promising alternative to reducing reliance on petroleum. It opens ways for using syngas derived from coal, biomass, or natural gas as a feedstock for olefin production.
In this study published in Science, researchers presented a sodium-modified FeCx@Fe3O4 core-shell catalyst produced via coprecipitation and thermal treatment. The catalyst achieved over 75% olefin selectivity and a 33% by weight hydrocarbon yield. It also had an HAE of ~66–86%, which is significantly higher than the ~43–47% seen in the traditional syngas-to-olefin (STO) conversion methods.