Microsoft launched an Android version of the app earlier this week.



Zeekr 7 received 51,569 orders in 40 days prior launch.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount Links: Telomere, Epigenetic Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7x…
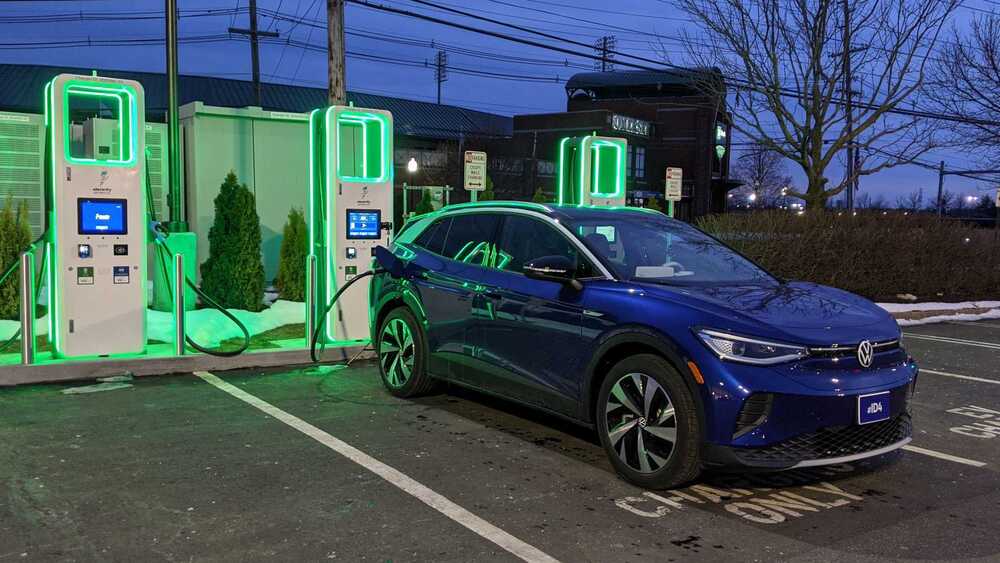

After a year of record electric vehicle sales, waves of people are spending their first winter with an all-electric car for the first time. They’d do well to pay attention to these five tips for charging in cold weather from the Electrify America charging network.
EVs, just like any other vehicles, operate the best in a certain window of temperatures, outside of which their energy consumption range or charging might be negatively affected.
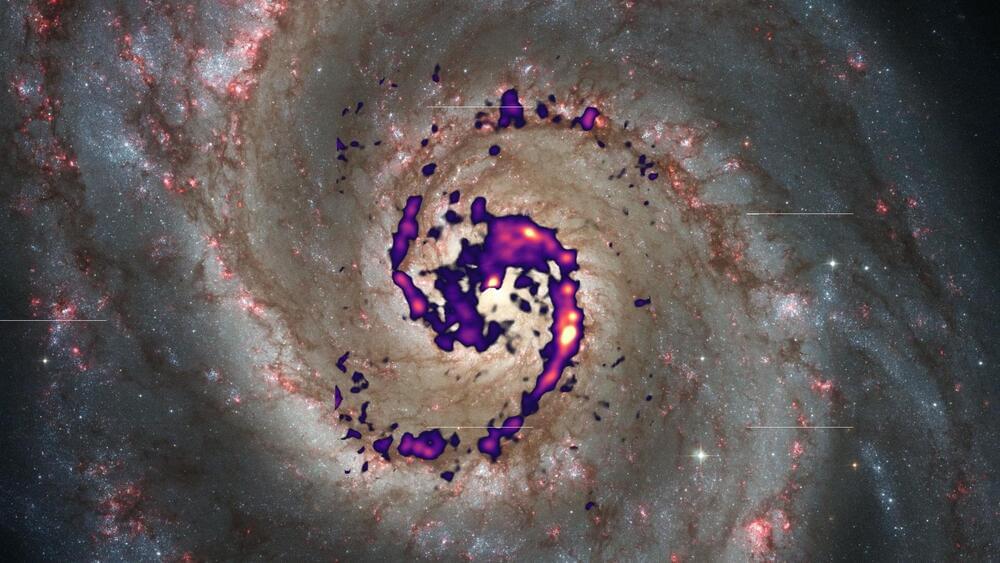

An international research team led by the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA) and involving the University of Bonn has mapped the cold, dense gas of future star nurseries in one of our neighboring galaxies with an unprecedented degree of detail. The data will enable the researchers for the first time to mount an in-depth study of the conditions that exist within the gas during the early stages of star formation outside the Milky Way at the scale of individual star-forming regions.
Their findings have now been published in Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Paradoxically, hot stars begin to form in some of the coldest regions of the universe, specifically in thick clouds of gas and dust that straddle entire galaxies. “To investigate the early phases of star formation, where gas gradually condenses to eventually produce stars, we must first identify these regions,” says Sophia Stuber, a doctoral student at the MPIA in Heidelberg and the first author of the research paper.
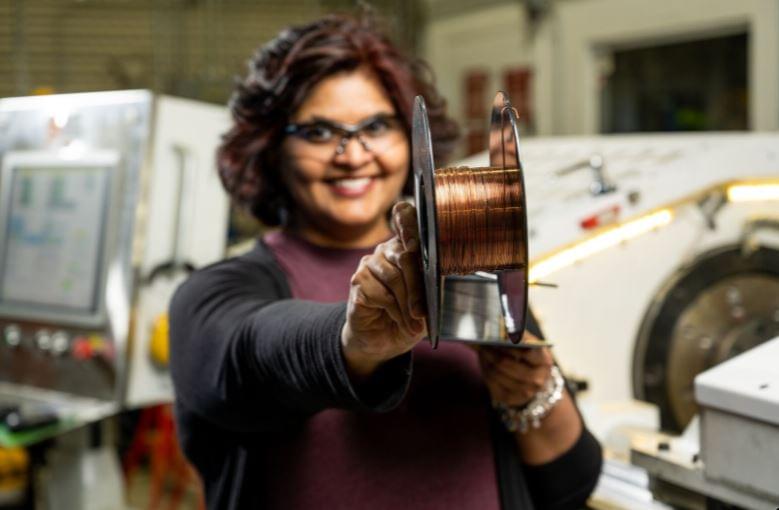

A common carbon compound is enabling remarkable performance enhancements when mixed in just the right proportion with copper to make electrical wires. It’s a phenomenon that defies conventional wisdom about how metals conduct electricity.
The findings, reported in the journal Materials & Design, could lead to more efficient electricity distribution to homes and businesses, as well as more efficient motors to power electric vehicles and industrial equipment. The team has applied for a patent for the work, which was supported by the Department of Energy (DOE) Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies Office.
Materials scientist Keerti Kappagantula and her colleagues at DOE’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory discovered that graphene, single layers of the same graphite found in pencils, can enhance an important property of metals called the temperature coefficient of resistance.
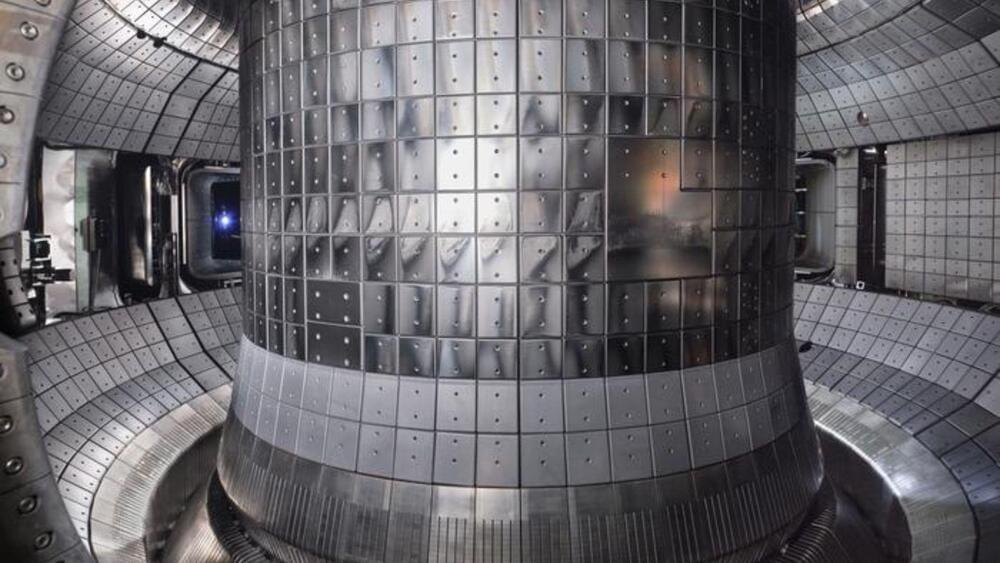
KSTAR, the Korea Institute of Fusion Energy’s (KFE) artificial Sun, has completed a significant modification that would allow it to function for longer periods at higher temperatures. KSTAR stands for Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research, an advanced nuclear fusion reactor constructed in 2007.
The development in this regard involved the installation of its newly developed tungsten divertors, “allowing it to operate for extended periods sustaining high-temperature plasma over the 100 million degrees,” according to a statement by the institute.
The team claimed they could complete a plasma experiment with the reactor equipped with the new divertor on December 21. In 2021, KSTAR set a new record by running at one million degrees and maintaining super-hot plasma for 30 seconds.
Jason Banta, vice president of AMD, believes that integrating AI into computers will make them more personal, more secure, and better able to understand what users want.
Banta predicts wider adoption of AI-enabled laptops by 2024, with a “major inflection point” starting in 2025. The biggest challenge will be scaling down models to run efficiently on laptops.
In general, Banta expects to see a shift from cloud AI applications to smaller models that run directly on computers in real-time and can be trained locally.