Using single-cell and spatial transcriptomics, human embryonic limb development across space and time and the diversification and cross-species conservation of cells are demonstrated.


The feeling that we belong to something much larger and deeper than ourselves has long been a common human experience. Palaeontologist and Jesuit priest Teilhard de Chardin wrote about “a noosphere” of cognitive realisation evolving towards an “Omega point” of divine planetary spiritualisation. But it is hard to envisage that ever occurring. It is easier to envisage that we belong in an evolving intelligent power that has entered a momentous posthuman dimension though artificial intelligence.
Some futurists believe we are on the way to realising a posthuman world in which we will live on as cyborgs, or in some new embodiment of intelligent power that will absorb and supersede human intelligence. It is no longer fanciful to foresee a future in which we will have everyday interactions with androids that are powered by artificial general intelligence. They will look, move, and seem to think and respond like a human person, be skilled in simulating emotional responses realistically, and greatly out-perform us in mental activities and manual tasks. It may be we will regard them only as tools or mechanical assistants. But from their expression of human-like behaviours we may become attached to them, even to the extent of according them rights. Their design will have to ensure they don’t carry any threat, but will we be able to trust fully that this will remain the case given their technical superiority? And how far can we trust that the military, malicious groups, and rogue states won’t develop androids trained to kill people and destroy property? We know only too well about our human propensity for violent conflict.
It would be ironic if, to gain more power and control over the world, we used our human intelligence to create AI systems and devices which, for all the benefits they bring, end up managing our lives to our detriment, or even controlling us. And irony, as Greek dramatists were well aware, is often a component of fate.

SUMMARY: A soft robot with octopus-inspired sensory and motion capabilities represents significant progress in robotics, offering nimbleness and adaptability in uncertain environments.
Robotic engineers have made a leap forward with the development of a soft robot that closely resembles the dynamic movements and sensory prowess of an octopus. This groundbreaking innovation from an international collaboration involving Beihang University, Tsinghua University, and the National University of Singapore has the potential to redefine how robots interact with the world around them.
The blueprint for this highly adaptable robot draws upon the intelligent, soft-bodied mechanics of an octopus, enabling smooth movements across a variety of surfaces and environments with precision. The sensorized soft arm, lovingly named the electronics-integrated soft octopus arm mimic (E-SOAM), embodies advancements in soft robotics with its incorporation of elastic materials and sophisticated liquid metal circuits that remain resilient under extreme deformation.




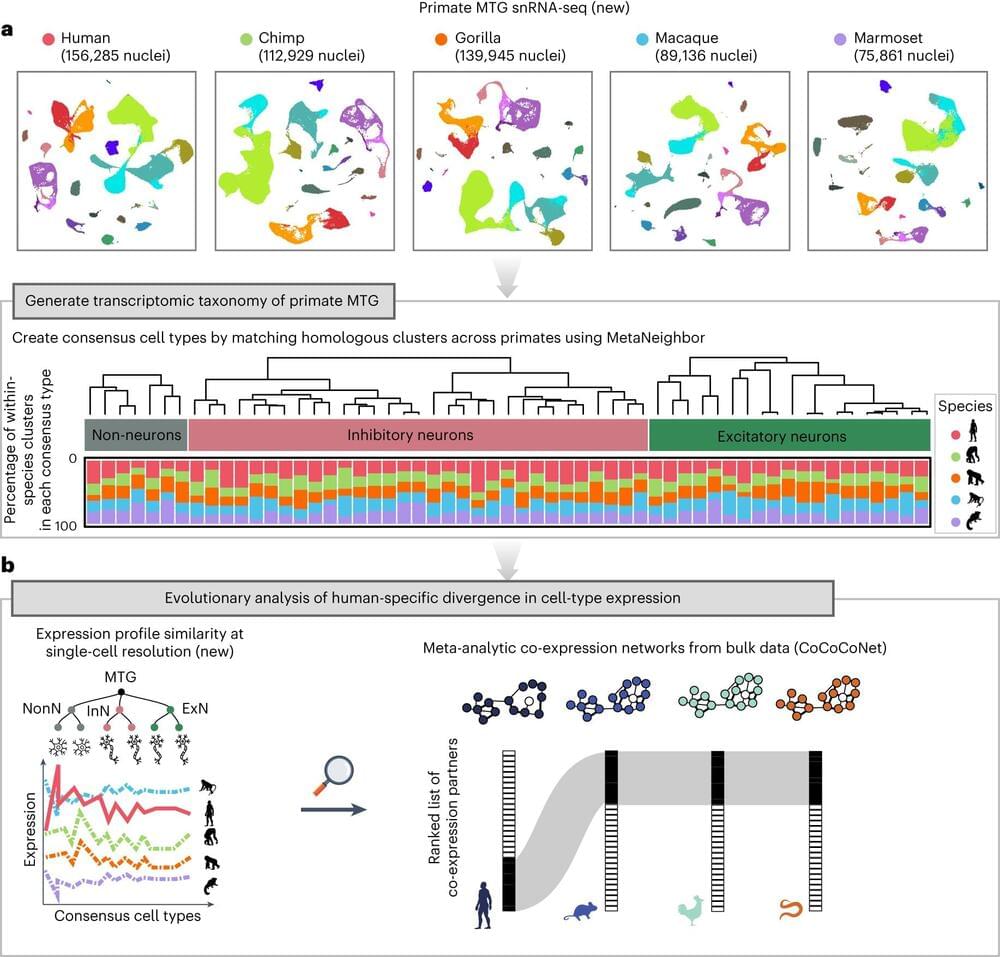
An international team led by researchers at the University of Toronto has uncovered over 100 genes that are common to primate brains but have undergone evolutionary divergence only in humans—and which could be a source of our unique cognitive ability.
The researchers, led by Associate Professor Jesse Gillis from the Donnelly Center for Cellular and Biomolecular Research and the department of physiology at U of T’s Temerty Faculty of Medicine, found the genes are expressed differently in the brains of humans compared to four of our relatives—chimpanzees, gorillas, macaques and marmosets.
The findings, published in Nature Ecology & Evolution, suggest that reduced selective pressure, or tolerance to loss-of-function mutations, may have allowed the genes to take on higher-level cognitive capacity. The study is part of the Human Cell Atlas, a global initiative to map all human cells to better understand health and disease.