Computer and AI giant rolls out machine using ‘Heron’ chips using subatomic particles instead of ones and zeros.


Meet Thousands of Lonely Women. Forget About Loneliness. Let Yourself Be Happy.
Genome and Structure:
HIV’s genome is a 9.7 kb linear positive-sense ssRNA.1 There is a m7G-cap (specifically the standard eukaryotic m7GpppG as added by the host’s enzymes) at the 5’ end of the genome and a poly-A tail at the 3’ end of the genome.2 The genome also has a 5’-LTR and 3’-LTR (long terminal repeats) that aid its integration into the host genome after reverse transcription, that facilitate HIV genetic regulation, and that play a variety of other important functional roles. In particular, it should be noted that the integrated 5’UTR contains the HIV promoter called U3.3,4
HIV’s genome translates three polyproteins (as well as several accessory proteins). The Gag polyprotein contains the HIV structural proteins. The Gag-Pol polyprotein contains (within its Pol component) the enzymes viral protease, reverse transcriptase, and integrase. The Gag-Pol polyprotein is produced via a −1 ribosomal frameshift at the end of Gag translation. Because of the lower efficiency of this frameshift, Gag-Pol is synthesized 20-fold less frequently than Gag.5 The frameshift’s mechanism depends upon a slippery heptanucleotide sequence UUUUUUA and a downstream RNA secondary structure called the frameshift stimulatory signal (FSS).6 This FSS controls the efficiency of the frameshift process.
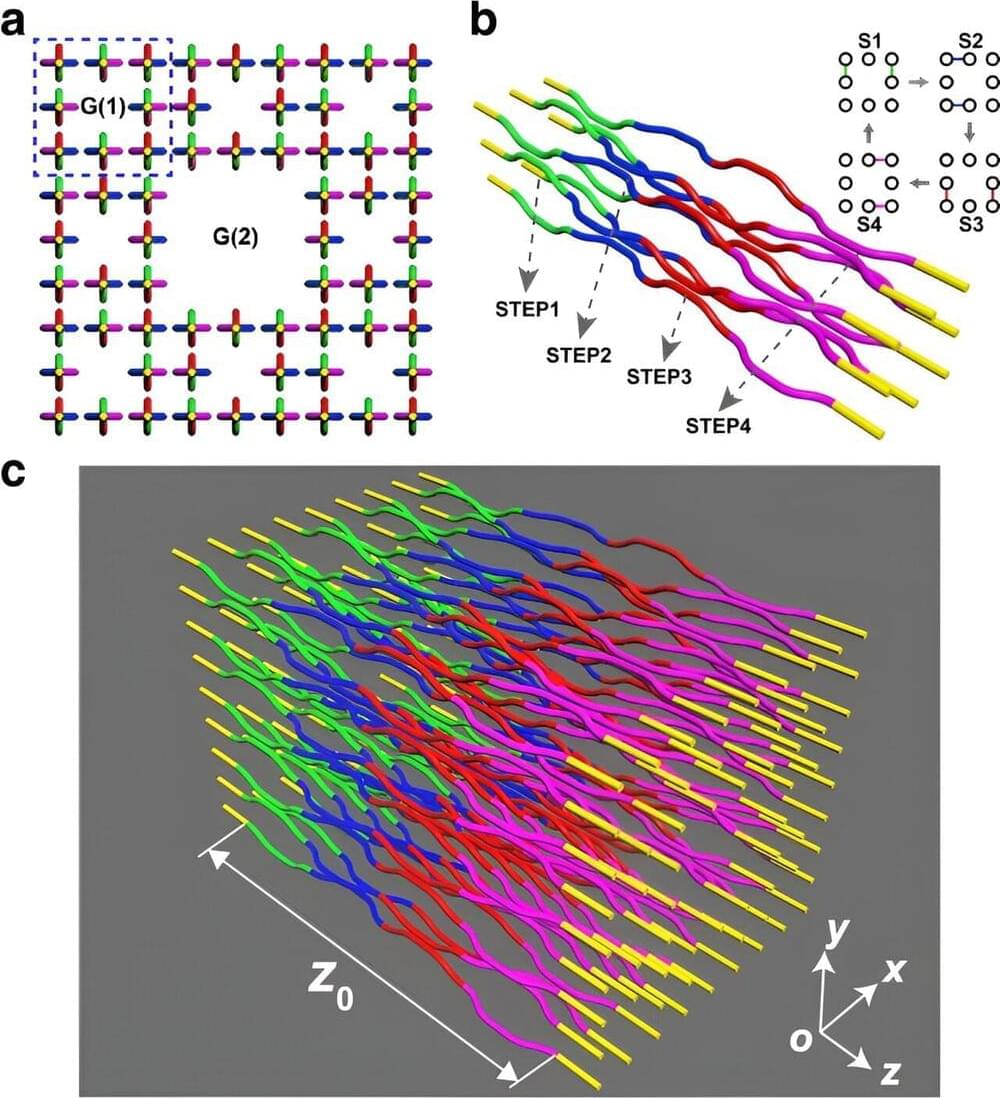
An anomalous Floquet topological insulator (AFTI) is a periodically driven topological insulator (TI with nonzero winding numbers to support topological edge modes, though its standard topological invariants like Chern numbers are zero.
The photonic lattice constructed by an optical waveguide array fabricated by the femtosecond laser direct writing (FLDW) is an important platform for quantum simulation to realize photonic AFTIs, because the FLDW offers flexible design of true three-dimensional (3D) waveguide structures and precise control of each coupling between waveguides. Moreover, the evolution distance of the lattice can be mapped as the evolution time.
In femtosecond-laser-direct-written photonic AFTIs, selective coupling of adjacent waveguides in a cycle is explicitly defined by the discrete periodically driving protocol. At the complete transfer discrete driving protocol, chiral edge modes co-exist with dispension-less bulk modes, and the lattice energy transfer efficiency of the chiral edge mode is the highest among all TIs (close to 100%), so it is very suitable for the transport of fragile quantum states.

On the highway of heat transfer, thermal energy is moved by way of quantum particles called phonons. But at the nanoscale of today’s most cutting-edge semiconductors, those phonons don’t remove enough heat. That’s why Purdue University researchers are focused on opening a new nanoscale lane on the heat transfer highway by using hybrid quasiparticles called “polaritons.”
Thomas Beechem loves heat transfer. He talks about it loud and proud, like a preacher at a big tent revival.
“We have several ways of describing energy,” said Beechem, associate professor of mechanical engineering. “When we talk about light, we describe it in terms of particles called ‘photons.’ Heat also carries energy in predictable ways, and we describe those waves of energy as ‘phonons.’ But sometimes, depending on the material, photons and phonons will come together and make something new called a ‘polariton.’ It carries energy in its own way, distinct from both photons or phonons.”
Google launched Gemini, their GPT4 killer, and it beats GPT4 in almost every way. Some of the demos are absolutely insane. Let’s go over all the news! Enjoy smile Become a Patron 🔥 — https://patreon.com/MatthewBerman Join the Discord 💬 — https://discord.gg/xxysSXBxFW Follow me on Twitter 🧠 — https://twitter.com/matthewberman Subscribe to my Substack 🗞️ — https://matthewberman.substack.com/ Media/Sponsorship Inquiries 📈 — https://bit.ly/44TC45V Need AI Consulting? ✅ — https://forwardfuture.ai/ Massed Compute (GPU Rental) 🚀 — https://bit.ly/matthew-berman-youtube Links: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jV1vkHv4zq8 https://developers.googleblog.com/2023/12/how-its-made-gemin…pting.html https://deepmind.google/technologies/gemini/#introduction https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UIZAiXYceBI https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sPiOP_CB54A https://www.youtube.com/watch?

A new theory suggests that the unification between quantum physics and general relativity has eluded scientists for 100 years because huge “fluctuations” in space and time mean that gravity won’t play by quantum rules.
Since the early 20th century, two revolutionary theories have defined our fundamental understanding of the physics that governs the universe. Quantum physics describes the physics of the small, at scales tinier than the atom, telling us how fundamental particles like electrons and photons interact and are governed. General relativity, on the other hand, describes the universe at tremendous scales, telling us how planets move around stars, how stars can die and collapse to birth black holes, and how galaxies cluster together to build the largest structures in the cosmos.
A quantum property dubbed “magic” could be the key to explaining how space and time emerged, a new mathematical analysis by three RIKEN physicists suggests. The research is published in the journal Physical Review D.
It’s hard to conceive of anything more basic than the fabric of spacetime that underpins the universe, but theoretical physicists have been questioning this assumption. “Physicists have long been fascinated about the possibility that space and time are not fundamental, but rather are derived from something deeper,” says Kanato Goto of the RIKEN Interdisciplinary Theoretical and Mathematical Sciences (iTHEMS).
This notion received a boost in the 1990s, when theoretical physicist Juan Maldacena related the gravitational theory that governs spacetime to a theory involving quantum particles. In particular, he imagined a hypothetical space—which can be pictured as being enclosed in something like an infinite soup can, or “bulk”—holding objects like black holes that are acted on by gravity. Maldacena also imagined particles moving on the surface of the can, controlled by quantum mechanics. He realized that mathematically a quantum theory used to describe the particles on the boundary is equivalent to a gravitational theory describing the black holes and spacetime inside the bulk.