Walking, talking machines will soon act as guides, companions and deliverers | Science & technology.
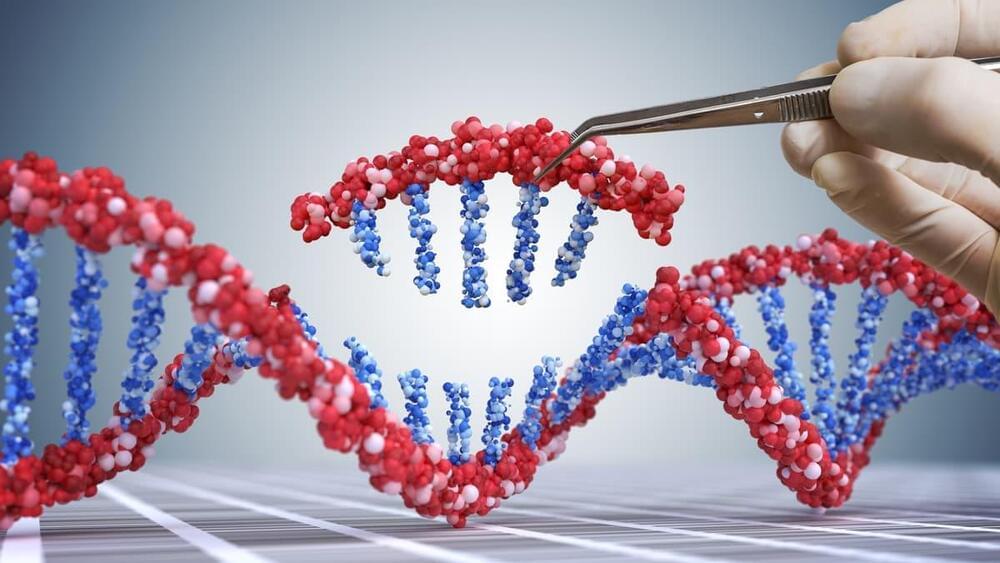
A new technique has been added to the CRISPR gene-editing toolbox. Known as PASTE, the system uses virus enzymes to “drag-and-drop” large sections of DNA into a genome, which could help treat a range of genetic diseases.
The CRISPR system originated in bacteria, which used it as a defense mechanism against viruses that prey on them. Essentially, if a bacterium survived a viral infection, it would use CRISPR enzymes to snip out a small segment of the virus DNA, and use that to remind itself how to fight off future infections of that virus.
Over the past few decades, scientists adapted this system into a powerful tool for genetic engineering. The CRISPR system consists of an enzyme, usually one called Cas9, which cuts DNA, and a short RNA sequence that guides the system to make this cut in the right section of the genome. This can be used to snip out problematic genes, such as those that cause disease, and can substitute them with other, more beneficial genes. The problem is that this process involves breaking both strands of DNA, which can be difficult for the cell to patch back up as intended, leading to unintended alterations and higher risks of cancer in edited cells.
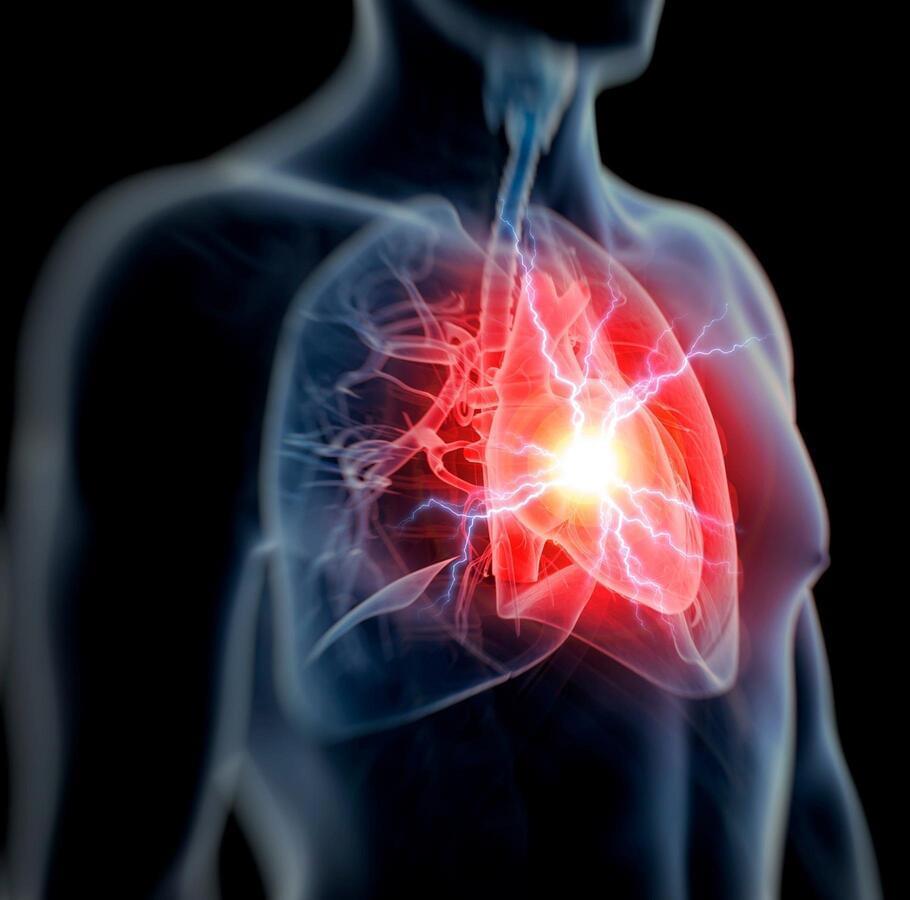
Scientists in Berlin have been studying a strange hereditary condition that causes half the people in certain families to have shockingly short fingers and abnormally high blood pressure for decades. If untreated, affected individuals often die of a stroke at the age of 50. Researchers at the Max Delbrück Center (MDC) in Berlin discovered the origin of the condition in 2015 and were able to verify it five years later using animal models: a mutation in the phosphodiesterase 3A gene (PDE3A) causes its encoded enzyme to become overactive, altering bone growth and causing blood vessel hyperplasia, resulting in high blood pressure.
“High blood pressure almost always leads to the heart becoming weaker,” says Dr. Enno Klußmann, head of the Anchored Signaling Lab at the Max Delbrück Center and a scientist at the German Centre for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK). As it has to pump against a higher pressure, Klußmann explains, the organ tries to strengthen its left ventricle. “But ultimately, this results in the thickening of the heart muscle – known as cardiac hypertrophy – which can lead to heart failure greatly decreasing its pumping capacity.”
DNA can be utilized to reliably store massive amounts of digital data. However, it has hitherto proven challenging to retrieve or manipulate the specific data embedded in these molecules. Now, scientists from the CNRS and the University of Tokyo have developed the use of a novel enzyme-based technique, providing the initial clues as to how these technical obstacles may be overcome. Their research was recently published in the journal Nature.
Nature has unquestionably developed the best method for massive data storage: DNA. Based on this knowledge, DNA has been used to store digital data by translating binary (0 or 1) values into one of the four different DNA “letters” (A, T, C, or G).
But how can one search through the database of data encoded in DNA to discover a certain datum? And how is it possible to execute computations using DNA-encoded data without first transforming it into electronic form? These are the questions that research teams from the LIMMS (CNRS / University of Tokyo) and Gulliver (CNRS / ESPCI) laboratories have attempted to answer. They are experimenting with a new approach using enzymes and artificial neurons and neural networks for direct operations on DNA data.
Blazars are some of the brightest objects in the cosmos. They are composed of a supermassive black hole.
A black hole is a place in space where the gravitational field is so strong that not even light can escape it. Astronomers classify black holes into three categories by size: miniature, stellar, and supermassive black holes. Miniature black holes could have a mass smaller than our Sun and supermassive black holes could have a mass equivalent to billions of our Sun.
Learning-based computer-generated holography (CGH) has shown remarkable promise to enable real-time holographic displays. Supervised CGH requires creating a large-scale dataset with target images and corresponding holograms. We propose a diffraction model-informed neural network framework (self-holo) for 3D phase-only hologram generation. Due to the angular spectrum propagation being incorporated into the neural network, the self-holo can be trained in an unsupervised manner without the need of a labeled dataset. Utilizing the various representations of a 3D object and randomly reconstructing the hologram to one layer of a 3D object keeps the complexity of the self-holo independent of the number of depth layers. The self-holo takes amplitude and depth map images as input and synthesizes a 3D hologram or a 2D hologram. We demonstrate 3D reconstructions with a good 3D effect and the generalizability of self-holo in numerical and optical experiments.
Microscopy data suggest that degradation starts from grain boundaries and propagates inwards.
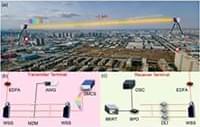
Large-capacity wireless data transmission systems are demanded along with the development of multimedia services, video-based interactions, and cloud computing in the era of big data. Compared with radio-frequency communication systems, free-space optical (FSO) signal transmission technology has the merits of high data rate, great flexibility, less power consumption, high security, and large license-free bandwidths [1– 3], which has been widely applied in terrestrial transmission [4], last mile solutions [5], ground-to-satellite optical communication [6], disaster recovery [7], and so on. To date, up to 10 Gbit/s FSO communication system has been realized for transmission distance over 1,000 km of star-ground or inter-star communications [8], and 208 Gbit/s terrestrial communication is also reported at 55 m transmission distance [9]. Wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) technology is commonly employed to improve data transmission capacity in fiber communication systems, which would be more effective in FSO communication systems benefitting from very weak non-linear cross talk between different frequency channels in free space. Based on a simulation platform, a WDM FSO communication system could boost the signal transmission capacity to 1.28 Tbit/s by modulating 32 optical channels with dual-polarization 16 quadrature amplitude modulation signals [10]. To date, beyond 10 Tbit/s FSO communication systems have been experimentally demonstrated recently using WDM technology [11,12]. However, a WDM communication system becomes power-hungry and bulky with the increase of transmission channels while traditional distributed feedback lasers are used as optical carriers. In addition, more rigorous requirement is imposed on the frequency tolerance of carrier lasers to avoid channel overlap with the decrease of channel frequency interval.
The invention of microresonator-based optical frequency combs provides novel integrated optical laser sources with the natural characteristic of equi-spaced frequency intervals which can overcome the challenge of massive parallel carrier generation [13 – 19]. In particular, the spontaneously organized solitons in continuous-wave (CW)-driven microresonators provide a route to low-noise ultra-short pulses with a repetition rate from 10 GHz to beyond terahertz. Soliton microcombs (SMCs) are typical stable laser sources where the double balances of non-linearity and dispersion as well as dissipation and gain are reached in microcavities. Meanwhile, the linewidth of the comb lines is similar with the pump laser, which enables low power consumption and costs multiwavelength narrow-linewidth carriers for a wide range of applications. Through designing the scale of microresonators, the repetition rate of SMCs could be compatible with dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) communication standard. To date, several experiments have demonstrated the potential capacity for ultra-high-speed fiber communication systems using SMCs as multiwavelength laser sources [20 – 30]. For instance, a coherent fiber communication system has improved the transmission capacity up to 55 Tbit/s using single bright SMCs as optical carriers and a local oscillator [20]. And dark solitons and soliton crystals are also employed as multiwavelength laser sources for WDM communication systems [27 – 30]. However, few studies have carried out massive parallel FSO communication systems using the integrated SMCs as laser sources.
In this paper, we experimentally demonstrate a massive parallel FSO communication system using an SMC as a multiple optical carrier generator. 102 comb lines are modulated by 10 Gbit/s differential phase shift keying (DPSK) signals to boost the FSO transmission rate up to beyond 1 Tbit/s. The transmitter and receiver terminals are installed in two buildings at a distance of ∼1 km, respectively. Using a CW laser as reference, the influence of optical signal-to-noise ratios (OSNRs) on the bit error rate (BER) performance is experimentally analyzed. Our results show an effective solution for large-capacity spatial signal transmission using an integrated SMC source which has potential applications in future satellite-to-ground communication systems.
Depth of field (DOF) and resolution are mutually restricted in integral imaging (II) display. To overcome the trade-offs, we propose an II display system that simultaneously enhances the DOF and resolution. The system consists of a transmissive mirror device (TMD), a semi-transparent mirror (STM), and two II display units. Each II display unit consists of a 4K display screen and a micro-lens array (MLA). Benefiting from the parallel placement of the TMD and the STM, two central depth planes are reconstructed, which effectively enhances the DOF. Meanwhile, the resolution in the overlapping DOF region is increased to two times due to the interpolation of the light field information from two II display units. The impact of the distance between the two II display units and the TMD on the 3D image quality is analyzed. In geometric optics, a distance between the II two display units and the TMD is optimized to eliminate ghost images. In wave optics, a distance is optimized to eliminate 3D pixel gaps by exploiting the diffraction effect of the TMD. Both the geometric and wave optics are considered simultaneously to obtain a high-quality 3D image without ghost images and 3D pixel gaps. A DOF and resolution-enhanced II display system is developed, and the experimental results verify its feasibility.
21 oct 2022.
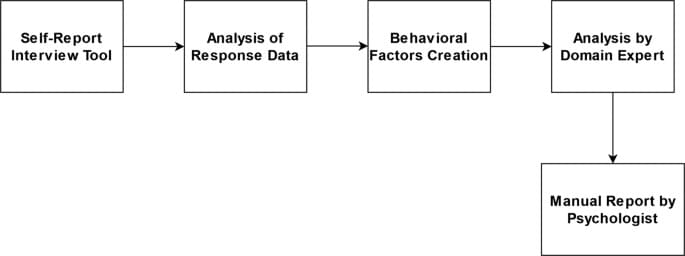
Adolescent (or juvenile) delinquency is defined as the habitual engagement in unlawful behavior of a minor under the age of majority. According to studies, the likelihood of acquiring a deviant personality increases significantly during adolescence. As a result, identifying deviant youth early and providing proper medical counseling makes perfect sense. Due to the scarcity of qualified clinicians, human appraisal of individual adolescent behavior is subjective and time-consuming. As a result, a machine learning-based intelligent automated system for assessing and grading delinquency levels in teenagers at an early stage must be devised.